Why does a rash appear on the stomach of an adult?
Very often, a rash on the stomach can be evidence of some kind of allergic reaction. Most often, the allergen is pet hair, plant pollen or food. Sometimes the rash can be caused by taking medications.
In this case, the appearance of the rash is accompanied by other symptoms; usually the person feels slightly drowsy, and there is irritation of the mucous membrane of the nose and eyes. Typically, such a rash is accompanied by unpleasant sensations and constant itching.
If, in addition to the rash, there are no other symptoms of an allergic reaction, then most likely the cause is an infectious disease. Very often the cause is chickenpox, rubella, measles or scarlet fever.
In which there is a rash not only on the stomach, but also in the groin, it is accompanied by severe itching, and over time the skin begins to peel off. Measles is accompanied by the appearance of a rash, first on the head, and only then, on the third day, on the stomach.
During measles, the rash is usually large, and it often coalesces to form large lesions. Usually, after recovery from most infectious diseases, no traces remain on the skin.
Also, the causes of rashes on the abdomen in adults are psoriasis, dermatitis or eczema. The rash associated with infection with the herpes virus has a special appearance; it is located around the lumbar region, forming a kind of belt.
Very serious consequences can be observed when the scabies mite invades; the rash is observed not only in the abdominal area, but also on the back, between the fingers. A special feature is increased itching at night. This disease requires immediate treatment.
Symptoms of the disease
They appear at all stages of the disease, but symptoms often differ depending on the age of the person.
- In infancy, itching appears on the face, arms or legs (itchy dermatosis).
- Allergic reactions most often occur in childhood.
- During adolescence, acne usually appears on the face, and seborrheic dermatitis is also observed.
- In old age, warts appear and the skin atrophies.
Fungal, viral, pustular and parasitic dermatoses
may appear regardless of age.
Depending on the clinical manifestation, skin pathologies can be divided into 2 large groups:
- diseases in which skin manifestations are mild, but general symptoms are observed (fever, weakness, etc.).
- diseases in which there is the appearance of itching, burning, numbness, rash, and age spots on the skin.[1]
What pathology causes a rash without itching?
The appearance of a rash on the abdomen of an adult without itching can be a consequence of serious diseases, which are usually associated with pathological changes in the body.
Therefore, before starting treatment, you should determine the cause:
- Allergic reaction. The body's reaction to an allergen can be expressed in the form of a rash on the skin, unaccompanied by itching. Usually there is a profuse rash.
- Dermatitis. This disease is accompanied by a rash not only on the stomach and other areas of the skin, but very often occurs without itching.
- Infection. A rash associated with an infectious infection can appear in various forms, differing in size, type and thickness.
- Prickly heat. The disease, which is typical for children, but is sometimes observed in adults, is also accompanied without the appearance of itching.
- Pathologies of internal organs. A rash on the abdomen, in this case, is most often associated with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as the liver and kidneys.
- Hormonal disbalance. Hormonal imbalance can be caused by both natural factors, such as pregnancy, and the use of hormonal medications. Such a failure is accompanied by skin damage, and very often without itching.
- Reaction to the sun. Direct sunlight can negatively affect the skin if it is hypersensitive.
It should be noted that the appearance of a rash in the abdominal area, without the appearance of a rash, is very often associated with serious diseases and requires immediate treatment.
Symptoms of dermatosis and treatment
Atopic dermatosis can manifest as eczema. This condition is characterized by itchy spots on the bends of the joints. This group also includes prurigo and pruritic folliculitis. Atopic dermatitis in pregnant women can only be distinguished by a specialized doctor. This species is not dangerous either for the expectant mother or the fetus.
Prurigo in pregnant women does not occur as often as eczema, but in any trimester. Pruritic folliculitis is very rare, but is accompanied by severe itching, as well as a large number of pimples and nodules that can be seen on the back, chest, and least of all on the stomach. This group resolves on its own without the use of special treatment.
Pemphigoid is very rarely observed in pregnant women. It appears in the form of plaques, which then become blisters. This species can affect the mucous membranes of the body of the expectant mother. Most often, symptoms disappear towards the end of pregnancy, but they can also worsen during childbirth, when the body is under severe stress. They disappear immediately after childbirth without the use of treatment.
What to do if the pathology itches
A rash on the abdomen, which is accompanied by itching, brings not only cosmetic discomfort, but also indicates serious problems with the functioning of internal organs or some kind of infectious disease.
The skin, regardless of a man or a woman, can be considered a mirror of the work of the whole organism. Therefore, even the slightest rash or change in skin pigmentation becomes an indicator of a problem and requires an immediate visit to the doctor.
The causes of such an unpleasant pathology
There can be many reasons for the appearance of a rash with accompanying itching in an adult. It should be noted that itchy rashes very often move from the abdominal area to the perineum, which brings even more discomfort.
Main reasons:
- allergic dermatitis caused by wearing clothes made of synthetic fabric, as well as the use of dirty linen;
- herpes zoster is an infectious disease caused by the herpes virus;
- fungal infection of the skin, which usually occurs in overweight people who do not follow the necessary rules of personal hygiene;
- scabies, a disease caused by the infestation of scabies mites, most often manifests itself when personal hygiene rules are not followed;
- contact dermatitis;
- eczema.
Effective methods for treating this problem
Treatment of skin problems associated with an allergic reaction requires following a special hypoallergenic diet and taking antihistamines.
Unfortunately, it is impossible to cure herpes zoster completely; remission can only be achieved through the use of antiviral ointment.
Treatment of fungal skin infections begins with observing the rules of personal hygiene, treating the affected areas with a special powder and antifungal ointments.
Treatment methods
When choosing a method of treating a skin disease, take into account the stage of the pathology, form, individual course and associated ailments.
Among the main directions in the treatment of dermatoses are:
- removing the cause;
- softening the skin;
- medications that reduce inflammation (contain steroids and hormones);
- oral medications (if large areas of the skin are affected).
Drugs for the treatment of dermatoses, used externally, have a symptomatic effect, that is, they relieve inflammation, itching, and stimulate regenerative, antifungal and antibacterial processes.
Each type of disease is characterized by special manifestations, depending even on the patient’s age, allowing the diagnosis to be determined
To relieve itching, antihistamines are prescribed: Suprastin, Loratadine, Diazolin, Tavegil. Sedatives: “Novopassit”, “Barboval”, valerian officinalis.
If the patient suffers from allergies, the doctor prescribes sorbents: white coal, Enterosgel. If the patient is in serious condition, treatment with steroids (Prednisolone) is prescribed.
Dosage forms such as lotions, soaps, powders, mixtures, solutions are prescribed in a certain dosage, taking into account the desired depth of penetration. External preparations are divided into hormonal and non-hormonal.
Since fungal diseases become the main factors of dermatosis of the lower extremities, medications used for their treatment contain antibacterial components that inhibit the activity of pathogenic microorganisms (zinc, silver nitrate).
In order to remove allergy mediators from the body in case of allergic dermatosis, patients are prescribed sorbents (Polyvidone, Activated Carbon, Hydrolyzed Lignin), alkaline drinking and cleansing enemas are recommended.
On a note. Severe forms of bullous dermatosis are treated with plasmapheresis in conjunction with Prednisolone therapy. If a secondary infection occurs, then, depending on bacteriological studies, antibiotics are prescribed.
Drying and healing of damaged skin surfaces is a criterion for stopping certain therapeutic effects
Traditional medicine
Skin rashes occur for many reasons. If their integrity is compromised, scars may remain after healing.
Important. Before starting home treatment methods, you should consult a doctor, since therapeutic methods depend on the cause of the dermatosis.
Home therapy methods:
- Eat gooseberries.
- Pour boiling water over birch buds in a 1:2 ratio. Wipe affected areas.
- Apply an aloe leaf to the fire.
- Take baths with the addition of a decoction of string.
- Half an hour before meals, drink celery juice (1 tbsp.).
- Make a mixture of herbs (motherwort, mint, leaves and flowers of black elderberry). 1 tbsp. l. pour a glass of boiling water and drink throughout the day before meals. A significant portion should be drunk at night.
- Take nettle infusion.
- Instead of tea, drink a decoction of blackcurrant leaves.
Often, the doctor prescribes physiotherapy, diet therapy, and sanatorium-resort treatment.
Diet
It is not recommended to include foods that cause disease in your diet . This can be hot and spicy foods, smoked and pickled foods. It is harmful to your health to eat foods high in carbohydrates.
Lean meats are recommended: skinless chicken, lean beef, turkey. It is necessary to steam or simmer with a minimum amount of salt and oil.
If the patient suffers from a chronic type of dermatosis, it is necessary to exclude eggs, some types of fish, mushrooms, honey, chocolate, tomatoes and red berries, nuts, and citrus fruits from the menu. And also reduce the consumption of potatoes, lamb, corn, buckwheat.
Doctors recommend including in your diet foods that promote skin cell regeneration: seaweed, zucchini, boiled beef, turkey, lean pork. Porridge should be on water. For dairy products, goat milk, kefir, and yogurt are recommended.
Treatment of pregnant women
Treatment methods depend on the initial factor. If the disease is infectious in nature, the basis of treatment is the fight against the pathogen. In other cases, all measures are aimed at identifying and removing external or internal causes. In the event that it is not possible to influence the source of the disease itself, therapeutic methods are aimed at eliminating the symptoms or the mechanism of development of the disease.
Despite the many treatment methods, it is important to identify and eliminate the cause of the rash.
The following medications are prescribed to expectant mothers:
- sedatives (sedatives) that do not have an alcohol base (motherwort, valerian);
- antihistamines.
External remedies recommended for pregnant women:
- shaken antipruritic mixtures;
- corticosteroid drugs;
- creams containing calamine.
Before applying any medication, the affected area should be cleaned of dead tissue and dirt using hydrogen peroxide, potassium permanganate or alcohol.
Therapy used to combat the disease should be general and local
Important. Pregnant women should carefully monitor their diet, which will not only get rid of the rash problem, but also prevent it.
Small type of rash
A small rash on the abdomen in an adult is a very common occurrence that requires immediate treatment.
The cause of this type of rash is most often an allergic reaction to some allergen. Usually, it is associated with taking medications, but can also often occur after eating allergenic foods, and is less often associated with infections.
After small pimples appear on your stomach, you should contact a dermatologist, who will determine the nature of the rash and may refer you to an allergist for additional examination.
It should be noted that any treatment should begin only after visiting a specialist. As it turned out early, there are many reasons for the appearance of a rash, some of which can negatively affect human health and the general condition of the body.
Some causes cannot be eradicated, such as herpes zoster, but they can be controlled and symptoms can be minimized. Depending on the cause, treatment is carried out using special ointments, sprays, gels, as well as various medications.
But, if you know the cause, if it reappears, you can treat it yourself using traditional methods and medications. Note that the use of folk remedies is acceptable only in the treatment of allergic rashes.
A decoction of bay leaves, which is used locally, helps very well. It is also recommended to use dill juice in the form of compresses. Very effective decoctions based on medicinal herbs such as sage, thyme and chamomile.
If exposure directly to the skin does not help, you can take medications orally. The most effective method is considered to be taking nettle infusion.
Causes and symptoms of the disease
Diseases of internal organs and metabolic problems are often displayed on the skin. As a result of such disorders, allergic or bullous dermatoses (multiple blisters) appear, which over time are replaced by crusts and erosions.
Of all the causes of bullous dermatosis, the most common is contact with an aggressive environmental factor.
When resistance decreases, fungal dermatoses, pustular or viral, occur. For example, when a scabies mite bites, the skin becomes infected, and as a result, scabies occurs.
Itchy dermatosis (urticaria, neurodermatitis) is provoked by neurological disorders, stress, as well as chronic foci of infection (caries, sinusitis).
On a note. A rash caused by a mental disorder or severe emotional stress is called nervous dermatosis.
We recommend studying this topic:
How to quickly and effectively treat scabies at home
7689
0
4
reading information
Depending on the causes of the pathology, the patient may suffer either for quite a long time or for a very short time. For example, with dermatosis of pregnant women, the disease is temporary. But despite this, a woman needs to be constantly monitored by a doctor.
Most of the health problems of the expectant mother are associated with changes in hormonal levels that affect the processes of the female body
Polymorphic dermatosis of pregnant women mainly affects primiparous women. The baby's health is not in danger.
Important. Some types of pathologies are contagious, so you should follow your doctor’s recommendations and observe personal hygiene rules.
The pharmaceutical market makes it possible to effectively manage the symptoms and treatment of such ailments. Corticosteroid ointments are used for external use. For oral administration, the doctor prescribes sedatives and antihistamines.
Remember. The clinical features of the disease may change with the patient's age. For example, psoriasis is easier to treat in children, although at this age it has more pronounced exudation. Scabies in infants can appear on the face, which is not entirely typical for adults.
The disease appeared in the lower abdomen
Typically, the appearance of pimples in the lower abdomen is associated with sexually transmitted diseases; they are accompanied by similar manifestations in the groin area.
Therefore, in order not to risk your own health, you must definitely consult a specialist, despite fear and advice from experienced friends.
Let's consider the main reasons for the appearance of a rash in the lower abdominal region:
- Dermatological diseases. They appear in various variations and are mainly associated with the appearance of symptoms of psoriasis.
- External stimuli. Very often, the cause of pimples in the lower abdomen is the harmless impact of various irritants. This can usually be associated with wearing uncomfortable clothes or wardrobe items made of low-quality materials. Also a negative factor is high ambient temperature, which causes increased sweating and irritation. You should also pay attention to the laundry detergent used to wash clothes and personal care products that may cause irritation.
- The most common cause, of course, is infectious and viral diseases that are sexually transmitted.
As in the previously described cases, starting treatment on your own is strictly prohibited. Only after identifying the cause can prevention and administration of appropriate medications begin.
If the cause of the rash is an external physical irritant, but no treatment is required, you simply need to change the detergent or exclude clothing from the relevant materials. Treatment of sexually transmitted diseases should only be carried out under the supervision of an appropriate specialist.
Diagnosis of polymorphic dermatosis in pregnant women
Due to the variety of clinical and morphological manifestations of PEP, other dermatoses may be mistaken for drug-induced dermatosis, gestational pemphigoid, erythema multiforme exudative, and scabies. The following are features of PEP and gestational pemphigoid that facilitate the differential diagnosis of these diseases.
It is important to pay attention to the localization of the elements of the rash in relation to the striae of pregnancy, since in 90% of women with PEP these elements are localized on the striae, and with gestational pemphigoid such localization is rare.
Although vesicles form in 40% of patients with PEP, they rarely exceed 2–3 mm in diameter. In gestational pemphigoid, when vesicles appear, they quickly enlarge, turning into large, tense blisters.
With gestational pemphigoid, skin lesions around the navel are often observed (84%), and with PEP, the rash elements are localized in the umbilical area only in 10% of cases.
However, direct immunofluorescence testing is recommended in all cases of PEP to avoid misdiagnosis of gestational pemphigoid.
Causes of itchy abdominal skin without rash
Itchy skin without the appearance of external factors can be a consequence of a serious pathology. In such cases, the skin begins to itch due to the appearance of irritating substances in the blood. Very often their appearance is associated with the development of cancer, problems with the functioning of the kidneys and liver, as well as various blood diseases.
It should be noted that the appearance of itching without accompanying symptoms very often turns out to be an indicator of problems with the liver and kidneys, since very often pathologies of these organs occur without visible symptoms. Therefore, if such itching occurs, you should consult a doctor.
Very often, the skin begins to itch during the development of hepatitis, and in some cases, cirrhosis. Sometimes similar symptoms are accompanied by stagnation of bile in the biliary tract.
It should be noted that very often the appearance of discomfort in the abdominal area without a rash can be a sign of the development of diabetes mellitus, while similar sensations are observed on the skin of the legs.
It is very important that if you experience unpleasant sensations, consult a doctor, as this may be associated with various blood diseases, which can threaten not only a person’s health, but also his life.
We must not forget that very often the skin begins to itch under the influence of various stressful situations, as well as prolonged exposure to negative psychological factors.
Given the variety of causes, treatment should begin only after identifying the cause.
Localization also on the chest
Sometimes a rash on the abdomen is accompanied by a rash on the chest, as the skin in the chest area is very sensitive. The most common causes of irritation are infectious diseases and allergic reactions.
The most common infectious disease is secondary syphilis, which is characterized by the appearance of necklace-shaped pimples on the chest. Such a rash is almost invisible and does not cause any discomfort, so it is very difficult to determine the time of its appearance.
Also, the cause of the appearance of pimples on the chest is an allergy, the symptoms of which are very difficult to distinguish from the symptoms of various infections. The most common allergen is clothing made from low-quality synthetic material.
In this case, the rash is accompanied by general redness of the skin. If the influence of the allergen on the skin is not excluded, the pimples will begin to burst and crust over. This should be avoided, as an infection can penetrate through damaged skin, which will lead to more serious consequences.
Causes of the disease
One of the main reasons for the manifestation of dermatosis during pregnancy is hormonal fluctuations. A large amount of harmful substances also increases the chances of this disease manifesting itself. Experts also include disruption of the thyroid gland and the body’s immune system as a whole as causes.
Dermatosis may worsen if a pregnant woman has:
- overweight;
- diabetes;
- strong emotional stress;
- prolonged toxicosis in the first months of pregnancy;
- consumption of allergens.
The cause of manifestations of dermatosis can be identified by scraping the affected areas of the skin in the laboratory.
The main reason for the development of the disease is the body’s poorly developed defense system. Reduced immunity can be hereditary and can develop due to many factors. Skin pathological processes are provoked by the following reasons:
- large amounts of carbohydrates consumed;
- products containing allergens;
- room dust;
- consequences of insect bites;
- Living with pets can cause dermatosis in children and adults upon contact with fur;
- the presence of mold in the bathroom, kitchen and other rooms;
- using household chemicals without gloves, using them incorrectly;
- hormonal imbalances;
- viral, bacterial, fungal infections;
- puberty;
- in women, skin changes can be observed during menopause;
- drinking alcohol, drugs, smoking;
- frequent use of medications;
- blood diseases;
- HIV – infections;
- stressful situations to which a person reacts strongly;
- presence of helminthic infestations;
- oncological diseases;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- disorders in the nervous system;
- the period of pregnancy can form polymorphic dermatosis of pregnant women;
- inadequate rest.
Dermatosis, which occurs during pregnancy, tends to go away without special therapy, leaving the woman’s body on its own.
Mechanism of disease development
Pathological processes develop under the influence of allergens that penetrate into organs through damaged skin or mucous membranes. The first stage of “acquaintance” between foreign bodies and dermal cells takes place without obvious external manifestations. This action is called sensitization.
By repeatedly contacting a sensitized organism, the allergen forms an allergic process in a short period of time. Blood stagnation occurs, causing swelling. The patient complains of severe itching sensations on the affected areas of the skin.
Itchy dermatoses have epidermal characteristics, which contributes to the formation of itchy blisters. Swelling occurs due to the presence of epithelium. The red color of the skin is due to vasodilation. The main mediator of allergic manifestations is histamine, which causes pain and itching sensations.
When the acute reaction subsides, the second mechanism begins to operate, which is usually characterized as delayed-type hypersensitivity. It is this sensitivity that has the ability to maintain the course of the disease for many weeks, months and even years.
The etiology of specific skin lesions detected during pregnancy has not been sufficiently studied. Most specialists in the field of obstetrics and gynecology associate them with physiological hormonal and immune changes during gestation. A certain provoking role is played by changes occurring in the skin - stretching of connective tissue fibers, activation of eccrine sweat glands.
The immediate causes of dermatoses are considered to be: • Increased Th2 activity. Changes in immunity in pregnant women are aimed at preventing fetal rejection. During pregnancy, the production of humoral antibodies decreases and the activity of T-helper type 1 (Th1) cells is inhibited. A relative increase in the activity of T-helper type 2 stimulates the formation of allergen-specific Ig antibodies and the proliferation of eosinophils, which becomes a prerequisite for the formation or exacerbation of atopic dermatitis.
• Damage to connective tissue. An increase in abdominal volume caused by the growth of the pregnant uterus is accompanied by stretching of the skin and damage to connective tissue fibers. Fragments of collagen and elastin can be perceived by cells of the immune system as allergens, which leads to the development of a local autoimmune reaction with the appearance of a skin rash.
Such disorders are more often observed during multiple pregnancies and significant weight gain. • Hereditary predisposition. The basis of most specific dermatoses diagnosed in pregnant women are autoimmune processes. Often, atopic skin diseases are familial in nature and arise as a result of a genetically determined allergic reaction to human leukocyte antigen A31 (HLA-A31), haptogen HLA-B8, placental antigen, which is similar to the basement membrane collagen of the skin (BPAG2, BP180).
Spread of pathology on the back
A rash on the stomach and back of an adult may be accompanied by itching, or may occur without visible discomfort. But if the skin does not itch in this case, there is no need to be passive; treatment should be started in any case.
As in most cases, damage to the skin of the back is usually associated with allergies. However, it may be accompanied by other symptoms, such as nasal congestion, photophobia and lacrimation, a slight cough and inflammation of the lymph nodes.
It should also be noted that syphilis is a common cause. The manifestation of which occurs through the appearance of small bluish papules, which over time acquire a white head. Such a rash is associated with a large number of toxins that enter the body of a person suffering from syphilis.
It also happens that the appearance of a rash on the back is associated with the appearance of lichen. In this case, itching does not appear at the first stage of infection, but only increases over time. Such symptoms bring a person significant discomfort. This disease very often appears in people with excessive sweating and poor personal hygiene. It is caused by yeast fungi.
The rashes are also localized on the legs
There can be many reasons that cause rash and itching on the stomach and legs.
Let's look at the main ones:
- Injuries. Rash and itching can be caused by damage to the skin, which usually occurs in people who handle plant materials. Such skin damage requires thorough cleaning and treatment with antiseptic substances.
- Allergic reaction. The most common allergen is the material from which clothing is made. Solving the problem requires replacing synthetics with natural materials.
- Insect bites. Insect bites cause significant discomfort and are very distinguishable from other causes of irritation; treatment requires treatment with special ointments or gels.
- Infectious diseases. Infectious diseases can be caused by various types of bacteria or viruses, and their treatment requires a detailed examination.
- Dermatitis. Often the cause is dermatitis of various types, both chemical and contact.
- Mechanical influence of external factors. This is usually due to exposure of the skin to elements of clothing due to prolonged friction. Solving this problem requires the use of special ointments or replacing clothes with softer ones.
Why does a rash appear on the stomach of an adult?
5 (100%) 7 votes
Our skin, like a litmus test, reflects all the disorders in the body. A rash on the stomach of a child or adult can mean a fairly serious illness. Therefore, you should not experiment with health, especially if it concerns your child.
A rash on the abdomen can manifest itself in different ways. It should be distinguished:
- In appearance, these can be small spots or large ones that merge with each other.
- By color - the rash can discolor the skin or intensify its color (red, white, pink spots).
- According to the structure, bubbles with clear liquid and spots covered with light scales and crusts may appear on the abdomen.
It is worth noting that in most cases the rash itches, causing a lot of inconvenience. When determining the cause of the rash, analyze what new products you consumed, where you went, with whom you talked, and what cosmetic items you used.
A rash on the stomach can mean various diseases. You cannot do without the help of a doctor in such a situation.
Causes of a rash on the stomach
Various types of rashes in the abdominal area can appear for various reasons - it can be a banal allergic reaction, for example, to wool, or it can indicate a serious illness.
What are the most common causes of rashes on the chest and abdomen? The table shows the most common factors that cause rashes in the abdominal area.
Rash on the abdomen in an adult
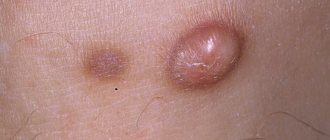
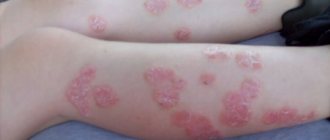
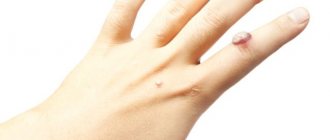
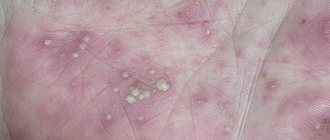
| Name | How it manifests itself | Photo |
| Allergy | With allergies, a rash can appear on any part of the body. As a rule, with allergies, a person becomes drowsy, lethargic, the rash itches, and watery eyes appear. An allergic reaction can occur to food, contact with animals, dust, and medications. | |
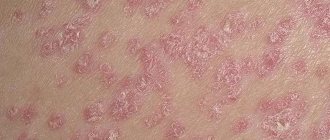
| Psoriasis | Psoriatic rashes can be caused by severe emotional tension, prolonged stress, and poor nutrition. In addition to the abdomen, the rash forms on other parts of the body. Accompanied by itching and peeling of the skin. | |
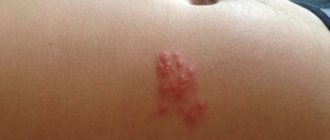
| Herpes | Herpes that appears in the abdomen and back is called "". The rash appears in the form of blisters filled with clear liquid. The rashes are located along the rib line. | |
| Scabies | The rash may appear in the abdomen, chest, between the fingers, and legs. The rashes are located at a short distance from each other, accompanied by itching, which intensifies at night. | |
| The disease is accompanied by rashes in the abdominal area of various sizes and shapes. These can be small nodules or extensive rashes. |
Rash on a child's stomach
| Name | How it manifests itself | Photo |
| Allergy | Most often, an allergic reaction begins to formula milk, complementary foods, or food products that the mother consumed. can form on any part of the body. Often accompanied by itching. | |
| Sweating | Characterized by a small red rash. Appears in response to prolonged contact with wet laundry. Formed on the neck, tummy, back, arms. | |
| Measles | Dark red spots appear on the abdomen. Most often, measles is accompanied by fever and peeling of the skin. | |
| Scarlet fever | The disease is characterized by the appearance of a small red rash, most often in the lower abdomen of infants. | |
| Chickenpox | First, a small rash forms on the baby’s skin, which later fills with a clear or slightly cloudy liquid. The affected areas of the body itch. |
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosis of the disease does not cause difficulties or difficulties, since almost all the symptoms of Dühring's dermatosis appear on the patient's skin. Difficulties in determining dermatosis can arise only in the case of the formation of exudative erythema multiforme, characterized by symptoms such as:
- Rapid increase in body temperature;
- Feeling of nagging, excruciating pain in the joints.
How and with what to treat a rash on the stomach
Treatment of a rash on the abdomen should proceed according to this principle - elimination of the main cause of the rash.
Treatment of rashes in adults
If the rash occurs due to an allergic reaction to something, the first step is to limit contact with the allergen. For allergies, antihistamines are prescribed:
- Suprastin;
- Tavegil;
- Fenistil;
- Claritin.
If the rash was caused by scabies, long-term and complex treatment is carried out. The premises and the patient's belongings are disinfected. The following drugs are prescribed:
- Aerosol "Spregal";
- Benzyl benzoate;
- Esdepalletrin.
If the rash occurs due to infectious diseases, then treatment involves:
- taking antibiotics;
- taking immunostimulating drugs;
- taking antipyretic drugs.
Treatment with folk remedies
Lemon balm tea will help relieve itching.
In addition to basic treatment, you can seek help from traditional medicine. Before use, you should consult a doctor, as individual intolerance to any components may occur.
- An infusion of herbs will help with itching. Herbs are used in dry form. Take 2 tbsp. spoons of licorice root, nettle, valerian, burdock flowers. Mix the composition well. Pour 2 teaspoons of the resulting mixture into 0.5 liters. boiling water We take 20 ml. 3 times a day.
- Tea with lemon balm is very useful. It calms the nervous system and eliminates itching.
- It is useful to eat foods rich in vitamin A - sea buckthorn, pumpkin seeds.
- A compress based on Kalanchoe juice copes well with itching. Take gauze, moisten it with Kalanchoe juice and apply it to the itchy area.
Treatment of rashes on the tummy in children
The main factor in treating rashes in children, as in adults, is to establish the true cause of the rash. Of course, you can’t do this on your own; you need to see a doctor. What to do if you find a rash on your baby's tummy:
- Call your pediatrician at home . If this is not possible, contact the clinic.
- Before being examined by a doctor, it is not recommended to apply any medications to the rash; this may prevent an accurate diagnosis.
- To reduce irritation, remove the child's clothing and cover with a soft diaper or blanket.
- Tell the specialist everything in detail about what is tormenting the child, when the rashes began, and what the child experienced.
If your baby has a common heat rash, you should not call a doctor. You need to worry if:
- The rash begins to quickly spread throughout the body.
- Body temperature rises.
- Pustules and spots begin to appear on the skin.
- The child becomes lethargic and drowsy.
Any skin irritation indicates a disturbance in the natural balance in the body or the manifestation of a disease, instability in the functioning of the internal organs of a person. A small pink rash on the abdomen can be caused by poor-quality household chemicals, cosmetics, or a painful fungal infection. A dermatologist must understand the cause and determine the source of irritation using special diagnostic methods.
Pruritic dermatosis
This disease belongs to one of the groups of dermatoses - neurodermatitis. Sensations of severe itching are the main symptom of this dermatological lesion in humans.
Itchy dermatosis can occur on the skin as a consequence of any internal disease, nervous exhaustion, or as a reaction of the body to allergens.
Symptoms:
The most important sign of the disease is severe itching, which is accompanied by other symptoms:
- decreased performance;
- irritability;
- insomnia;
- rash and redness on the skin.
The main complication of itchy dermatosis is infection of wounds formed as a result of scratching these inflammations.
Treatment
itchy dermatosis in the photo
For proper treatment of itchy allergic dermatosis, it is necessary to find out the cause of its occurrence. If this is the influence of a food product, then you need to exclude it from the diet. And if the symptoms of a dermatological disease are caused by an internal disease, then all measures must be aimed at curing it.
In some cases, glucocorticosteroid drugs are prescribed, which cope well with inflammatory processes and itching sensations. It is advisable to prescribe antiallergic drugs such as Fenistil, Diazolin, Suprastin, etc. As well as sorbents: activated carbon, Enterosgel; prebiotics and probiotics to remove toxic substances from the body.
To reduce nervousness, you can take valerian, Afobazol, Novo-passit, etc. It is recommended to take vitamin complexes containing substances and microelements important for the body.
Skin symptoms can be effectively eliminated with ointments:
- ichthyol;
- naftalan;
- sulfuric;
- tar;
- zinc paste;
- Panthenol;
- Advantan;
- Levovinisole;
- Skin cap.
These drugs have an anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial effect, eliminate itching and flaking on the affected areas of the skin.
Of the large number of different traditional medicine recipes, the following are particularly popular and effective:
- Treatment of rashes with an alcohol tincture of lemon balm, which you can prepare yourself. To do this, you need to pour a small amount of herb with vodka or alcohol and leave for a week in a dark place.
- Take dill infusion internally.
- You can make compresses from a decoction of burdock root, or wash your skin with it.
- An infusion of mint, oak bark, sage and St. John's wort for external use.
- For oral administration, pour boiling water over licorice root, nettle, string, and chamomile. Then cool, filter and drink several times a day before meals.
Traditional methods are used only as a supplement to basic drug therapy.
Causes of dermatitis
Rash in the groin and abdomen - molluscum
In the vast majority of cases, a small rash on the abdomen in an adult or child is a serious disease directly related to fungi. It is caused by several types of pathogenic pathogens that are found in the environment:
- epidermophytons;
- trichophytons;
- dermatophytes;
- candida fungi.
All of the listed species constitute the natural microflora of humans and are easily transported with personal belongings or bathing accessories. You can become infected with fungal spores by wearing someone else's clothes or through shared bedding. Most subspecies of epidermophytons or dermatophytes are found on human skin and are suppressed by the human immune system. But in a weakened body, mycotic pathogens are quickly activated, which manifests itself in the form of dermatitis.
The main factors that lead to the appearance of a rash from fungal dermatitis:
- frequent colds or flu;
- presence related to the endocrine system;
- stressful situations;
- immunodeficiency conditions (HIV or hepatitis);
- sudden climate change;
- increased sweating or wet skin;
- poor hygiene, poor body care.
Among the dermatologist's patients with complaints of the lower abdomen, many are overweight. Excessive sweating, hormonal imbalance or diabetes mellitus are serious predisposing factors. Treatment with complex antibiotics and disruption of the normal microflora in the intestines greatly weaken the immune system.
In children, many forms of dermatomycosis appear against the background of stressful situations in the family or school, after a series of viral diseases (influenza, chickenpox or ARVI). Babies whose diet is unbalanced and contains a minimum amount of vitamins and beneficial components are susceptible to infection.
Causes of dermatosis in children
In children, Dühring's dermatosis occurs in cases of hypersensitivity to cereal protein (gluten). It is synthesized in the intestines during the digestion and processing of food. The second reason for the formation of Dühring's dermatosis is the mother's difficult pregnancy, which occurs with a number of endocrine disorders; consequences of vaccination; increased physical, neuro-emotional and mental fatigue.
It has been established that patients with Dühring's dermatitis have an increased allergic reaction to iodine components, which indicates the patient's tendency to develop endogenous irritants.
Types of rashes on the stomach
Fungal skin diseases have a largely identical clinical picture. It depends on the type of pathogen and the stage of the disease. A red rash on the skin of the abdomen may be a symptom of:
- large folds: the disease is localized in the lower abdomen. Large areas of the epidermis are covered with red spots, the rash is irritating and itchy. The patient experiences severe discomfort and cannot fully rest or work.
- Shingles: often occurs in people of all ages, presenting as itchy lesions with a small rash. It has a chronic form and manifests itself during viral diseases and decreased immunity. The disease is extremely unpleasant and difficult to treat.
- Tinea versicolor (): often occurs in the abdominal area. The fungus attacks the dermal cells responsible for the production of pigment. The rash on the skin of the abdomen is accompanied by small dark spots that are covered with large scales. The disease is contagious to others and requires immediate treatment under the supervision of a specialist.
- : Large rounded spots are easily diagnosed by a specialist. They quickly appear on the abdomen and can merge into a large inflamed area. Inside it there are tiny rashes that cause discomfort and burning. A formation on the skin of the abdomen with pityriasis rosea is a sign of fungal inflammation of the internal organs.
- on the skin: always a consequence of untreated thrush in any form (vaginal, on the nails or in the oral cavity). The fungus easily gets onto the skin of the abdomen from the hands, or is carried in with clothes or bedding. In addition to a small itchy rash, it is covered with a characteristic white oily film.
A correct diagnosis can only be made after a detailed study, comprehensive tests and a visual examination by a dermatologist.
Atrophic stripes
Atrophic stripes:
They appear in most pregnant women on the skin of the abdomen, buttocks, and mammary glands.
Pathogenesis:
Apparently, in addition to the mechanical factor (stretching), degeneration of the dermis caused by endocrinopathy, autonomic disorders, etc. is of certain importance.
Clinical picture. Atrophic stripes of skin up to 4-6 mm wide, located symmetrically. Areas of band-like atrophy are sharply defined, with a wrinkled surface of a whitish-lilac hue, slightly sunken.
Treatment:
Use of Mederma or Contratubes creams after childbirth.
Synonym:
Striae of pregnant women.
In addition, during pregnancy, more pronounced general skin pigmentation is observed, especially in brunettes, developing in the area of the nipples of the mammary glands, genitals, and midline of the abdomen. In many women, the number and size of melanocytic nevi increase. The hair thins somewhat, even diffuse alopecia is possible, but after childbirth, over time, the properties of the hair are restored. Sometimes there is some hypertrichosis in combination with acne, usually in the second half of pregnancy. This may be the result of an androgen-secreting tumor, luteoma, luteal cysts, or polycystic ovarian disease and requires careful evaluation. Vascular changes are associated with the action of estrogens; they manifest themselves in 70% of pregnant women with erythema of the palms, which in some cases can be expressed only in the thenar and hypothenar areas. Small hemangiomas may occur, most often on the scalp and neck. Varicose veins of the extremities, hemorrhoids, and, less commonly, deep vein thrombophlebitis are often observed. Swelling of the face, eyelids, feet, and hands is also possible, which occurs in the morning and disappears in the evening. 80% of pregnant women develop gingivitis (swelling and redness of the gums), sometimes accompanied by pain and ulceration. In 2% of cases, changes in the gums are accompanied by the appearance of small vascular formations such as pyogenic granuloma, which bleed when touched (granuloma of pregnancy). These symptoms are somewhat relieved by taking vitamin C.
During pregnancy, there may be an increase in the frequency of infectious lesions, especially candidiasis, genital warts, herpes simplex, bowenoid papulosis. During pregnancy, autoimmune diseases (especially lupus erythematosus), lymphomas, and atopic dermatitis worsen. The effect of pregnancy on psoriasis can be different, and some patients may develop an acute pustular form.
Main symptoms
A common symptom of all forms of fungal dermatitis is a small rash on the abdomen of an adult, which gradually turns into spots of varying sizes. In addition, mycoses are characterized by:
- Severe redness in areas that have been in contact with the fungus. Puffiness, swelling and lichen with jagged edges are often observed.
- Itching or burning, the intensity of which depends on the type of disease: certain forms of dermatomycosis are practically asymptomatic at the initial stage, so the patient does not immediately notice a rash or large inflamed areas on the abdomen.
- Peeling of the upper layer of the epidermis. With tinea versicolor, it has large solid particles. When pink, it is barely noticeable, reminiscent of dandruff.
In its advanced form, tiny rashes gradually grow, turning into small blisters filled with clear purulent liquid. When you comb or rub synthetic fabric on your clothing, it releases, which leads to the appearance of weeping eczema. This problem is especially relevant on hot summer days, when natural sweating increases and the skin overheats.
Children's doctor
Only in some cases, the use of external remedies is sufficient to cure the patient (scabies, lice, lichen versicolor, some forms of pyoderma). In most cases, external therapy is part of the ongoing complex treatment and is symptomatic, as it affects the visible signs of the disease and the patient’s subjective sensations.
The prescribed external therapy depends on the form of dermatosis in the patient, the severity and severity of manifestations on the skin. You should remember the old saying: “The more active the changes in the patient’s skin, the more gentle the external therapy should be.”
The concentration of externally used products also depends on the properties of the patient’s skin and his age. The skin of children is delicate and is often highly sensitive to all externally used drugs, which dictates the need to use them in less irritating forms and in lower concentrations, or to limit or eliminate them from use altogether.
The prescription of certain medications for external use depends on the effect that the doctor wants to obtain, as well as on the depth of the intended effect on the affected areas of the skin (aqueous solutions have a superficial effect, alcohol solutions have a deep effect; pastes have a more superficial effect, and ointments have a deeper effect ).
When carrying out external treatment of dermatoses, the sequence of drug administration must be followed - from less concentrated to more concentrated, from superficially acting to those affecting the deep layers of the skin.
To obtain the effect of external treatment, it is necessary not only to choose the right drug, but also the form in which it should be applied. Means for the external treatment of dermatoses are more often used in the form of powders, lotions, solutions for external use, shaken suspensions of “talkers”, pastes, ointments, creams, varnishes, and patches.
When prescribing a particular dosage form for external use, it is necessary to determine the individual sensitivity of the patient’s skin to the prescribed drugs, for which it is recommended to apply the test drug to a small area of the affected skin for 30-40 minutes, followed by its removal. In the absence of an exacerbation reaction in the form of hyperemia, swelling, increased or itching, further use of this dosage form is permitted.
Dosage forms for external treatment of dermatoses.
Directions for using powders.
Powders or medicinal powders are a mixture of tiny powdery substances of mineral, plant and, less commonly, organic origin. They have a cooling, i.e. anti-inflammatory effect, increase evaporation, and subjectively soothe the feeling of burning and itching. In infants, they are used to protect the contacting surfaces of the skin (natural folds), from friction, maceration, exposure to sweat, urine, as well as on inflamed surfaces and without the phenomena of weeping and maceration. Less commonly used on erosive surfaces to create a protective film and reduce the loss of tissue fluid. In older children and adults, powders containing enzyme preparations such as trypsin, chymopsin, chymotrypsin are used on ulcerative surfaces covered with purulent hemorrhagic crusts.
Instructions for using lotions.
Lotions are weakly concentrated solutions of medicinal substances in distilled water. The same solutions are used for cooling wet dressings to stimulate epithelialization and have an anti-inflammatory effect. Lotions are used for pronounced inflammatory processes, accompanied by persistent weeping, swelling, and the formation of erosions (eczema, stage III diaper rash, some mycoses). In children, especially in the first half of life, it is better not to use them, but to use them only in extremely rare cases. Take 4-5 layers of gauze corresponding to the size of the affected skin surface, moisten it with a cold lotion, lightly wring it out and apply it to the lesion. The lotion must be changed after 20 - 30 minutes, as it dries out as it evaporates. In this case, heat is removed from the inflamed skin and, consequently, it cools, the vessels narrow, the skin becomes anemic, and the exudate is absorbed. The first napkin is removed and thrown away, and then the surface of the napkin used to apply the lotion is soaked with lotion from the pipette after 20 - 30 minutes. The use of lotions is inconvenient for infants who need more frequent changes of diapers and linen, and also because of possible hypothermia.
Depending on the medicinal substances included in the lotion, an astringent, disinfectant, and drying effect is obtained, which gives an anti-inflammatory effect.
Wet-dry dressings. Wet-drying dressings are applied after lotions from the same solutions.
Also take a napkin made of 5 layers of gauze according to the size of the affected area of skin, moisten it with a cooled solution, but do not wring it out. It is applied to the lesion. A thin layer of absorbent cotton is applied on top to hold the solution in the napkin.
The bandage is fixed with 2 - 3 rounds of bandage. Remove the bandage after 4-5 hours. If necessary, apply the bandage again.
Instructions for prescribing solutions for external use.
Solutions of agents with antimicrobial, fungicidal and antipruritic effects are more often used. Alcohol solutions of aniline dyes, boric acid, salicylic acid, resorcinol, iodine and other substances are usually used, but aqueous solutions can also be used. The alcohol strength is 50 - 70°. It should be remembered that alcohol can be irritating to the skin, so it is not recommended to use it for dry skin or for a long time.
Instructions for the use of shaken suspensions (“chatterers”).
Agitated suspensions or “chatterers” are finely dispersed powdery substances suspended in water with glycerin, or in vegetable or mineral oil. After the liquid evaporates, the powders are deposited in a thin layer on the skin and remain on it for a long time. Glycerin, having hygroscopic properties, helps to fix powders on the skin and distribute them evenly. The quantitative ratios of powder and liquid vary depending on the effect to be achieved. If it is necessary to obtain a surface effect, then powders and liquids are taken in equal parts (zinc, talc, glycerin, distilled water in equal quantities). To obtain a cooling effect, more liquid is taken (40 - 50%). To create a protective film of liquid, use less (20 - 30%). To speed up drying, you can add alcohol (5 - 10%). To enhance the therapeutic effect , one or more different medications are added to the “chatterbox”: menthol, ichthyol, tar, sulfur, etc. Shaked suspensions (“chatterboxes”) are used for itching, not accompanied by weeping, inflammatory dermatoses, especially in cases where the skin does not tolerate regular foundations. Long-term use of aqueous shaken suspensions (“chatterers”) leads to dry skin. Therefore, if you have dry skin, you should not use water “talkers”, but use oil suspensions.
Directions for using pastes.
Paste is a dosage form of dough-like consistency, consisting of equal parts of powdery substances and a fat base. Fatty and fat-like substances in the base must be chemically neutral so as not to cause skin irritation and have a soft, elastic consistency that does not change under the influence of body temperature. The paste differs from powder and shaken suspension in its deeper effect on the skin. The anti-inflammatory, drying and softening effect of the paste is based on its cooling effect, due to its ability to absorb and evaporate exudate and anemize the skin. The paste well protects the skin from external influences, irritation from secretions and is used in cases where acute inflammatory phenomena have subsided, but residual effects of the former exudative process still persist (slight hyperemia, serous crusts, individual small erosions at the site of former vesicles). The name of the paste is due to the addition of medications (naphthalene, ichthyol, tar, etc.).
Instructions for prescribing ointments.
Ointment is the most commonly used medicinal form of external therapy. The basis of the ointment can be vegetable and animal fats, mineral oils or mixtures thereof, in which various medicinal substances are evenly distributed. Depending on the therapeutic effect of these substances, ointments with exfoliating, softening, itching, epithelializing (keratoplastic), absorbable and other effects are distinguished. Thanks to the fat base, heat transfer decreases, the skin warms up, and hyperemia occurs. The water that does not evaporate under the ointment macerates the upper layers of the epidermis and thereby facilitates the penetration of medicinal substances included in the ointment into the thickness of the skin. Ointments are contraindicated for acute inflammatory dermatoses and oozing. The name of the ointment, as well as the paste, is determined by the name of the medicines included in this ointment (sulfur, naphthalene, dermatol, boron-rivanol, etc.).
In pediatric practice, we recommend using ointments containing antibiotics, sulfonamides, novocaine with caution, due to possible allergic reactions when using these drugs externally.
The ointment is applied in a thin layer to the affected area of the skin, or, if not possible, on a napkin, which is then applied to the affected area and bandaged. Application to the skin can be carried out either in a continuous or streaked manner, which is most important when using ointments containing glucocorticoids.
Related medical articles
- Systemic mastocytosis A man, born in 1979, has undergone an appendectomy and surgery for […]
- Why do acne appear? Acne on the face occurs at different ages and can indicate different [...]
- Molluscum contagiosum is a complication of chemotherapy Patient K, born in 1959, accountant. Among the diseases he notes: autoimmune thyroiditis [...]
Diagnostic features
A rash on the skin of the abdomen is not always a symptom of a fungal disease, so you cannot do without the help of a dermatologist. To make an accurate diagnosis, the patient must undergo a whole range of studies:
- examination using a special lamp, the glow of which indicates the presence of mycosis;
- taking a scraping from an irritated and itchy area of the epidermis;
- carrying out iodine tests;
- general or clinical analysis of blood and urine.
The fungus is often activated against a background of weakened immunity. If the cause is a disease of the internal organs, treatment will be ineffective without examining the liver, kidneys or intestines.
Differential diagnosis
Despite the pronounced clinical symptoms, making a correct diagnosis for dermatosis of pregnancy is often difficult due to the nonspecificity of the rashes, which can be observed in many skin diseases. The gestational origin of the pathology is supported by its occurrence during pregnancy, the absence of signs of microbial damage, the staged development of the elements of the rash, and their spread over the skin.
In diagnostic terms, the most informative are: • Determination of antibody levels. Atopic dermatitis is characterized by an increase in the content of IgE, a specific marker of allergic reactions. With herpes in pregnant women, the content of IgG4 antibodies increases in the blood of patients; in all patients, direct immunofluorescence determines the deposition of complement 3 along the basement membrane, which is sometimes combined with the deposition of IgG.
Using ELISA, anti-collagen antibodies characteristic of pemphigoid are detected. • Skin biopsy examination. The results of histological studies are more indicative of pemphigoid and polymorphic dermatoses. In both cases, swelling of the dermis and perivascular inflammation with tissue infiltration by lymphocytes, eosinophils, and histiocytes are observed.
For herpes of pregnant women, subepidermal blisters are pathognomonic, for polymorphic dermatosis - epidermal spongiosis. Pathohistological changes in atopic dermatitis and itching of pregnancy are less specific. • Blood chemistry. The standard method for diagnosing obstetric cholestasis is the study of pigment metabolism.
Due to the impaired outflow of bile, a high level of bile acids is determined in the blood. In 10-20% of pregnant women with severe dermatosis, the bilirubin content increases. In 70% of cases, the activity of liver enzymes increases, especially ALT and AST. In other gestational dermatoses, biochemical blood parameters are usually not affected.
Differential diagnosis is carried out between different types of gestational dermatoses, excluding scabies, drug toxicoderma, diffuse neurodermatitis, Dühring's dermatitis herpetiformis, seborrhea, acne, microbial folliculitis, eczema, hepatitis and other liver diseases. A dermatologist is involved in examining the patient; if indicated, an infectious disease specialist, a neurologist, a gastroenterologist, a hepatologist, and a toxicologist.
Treatment of different forms of dermatomycosis
Therapy for any form of fungus begins with the use of special ointments and solutions. They affect the colonies of the pathogen, destroy them and reduce the unpleasant manifestations of the disease: itching and burning. The most convenient to use are.
There are probably at least two dozen diseases that can cause various rashes on the stomach. A rash on the stomach of a child appears for completely different reasons than a rash in an adult. And rashes on women’s and men’s bellies can be of a completely different nature.
Well, let's look for the reasons for the appearance of a rash on the stomach.
Rash on the stomach of a pregnant woman
During pregnancy, so many reactions occur in a woman’s body that rashes on the body no longer surprise anyone. If red papules appear on the abdomen, which unite into small edematous plaques with a white rim, then this is a clear sign of dermatosis. To treat the disease, special creams and ointments are used, as recommended by a doctor.
The body of pregnant women is very sensitive to various irritants. A rash on the abdomen can occur as a result of an allergic reaction to a particular allergen. on the abdomen they look like small bubbles filled with liquid. Such bubbles cause noticeable itching and easily burst when scratched. To prevent the development of the disease, it is necessary to get tested and avoid contact with the allergen.
Also, the cause of a rash on the abdomen in pregnant women can be prickly heat, infectious diseases, and disruption of the functioning of internal organs.
Rash on the abdomen in men
Abdominal rashes are often infectious in nature. For example, a rash in the lower abdomen in the form of small grayish-red tubercles clearly indicates the presence of a sexually transmitted infection in the body (syphilis, etc.).
Other reasons why men develop a rash on their stomach include eczema and psoriasis. Chronic skin conditions are characterized by large red patches that eventually scab over and cause extreme discomfort.
With herpes, the rash looks like a kind of belt of blisters filled with bloody contents. Such a belt is located on the stomach, hips and back of the patient.
A rash on the abdomen in the form of small red dots located close to each other can be caused by scabies mites. This diagnosis can be confirmed by severe itching that occurs during sleep.
Watery blisters on the abdomen appear as a reaction to an allergy, and multi-colored multiple spots can serve as a sign of "".
Rash on the stomach in children
The causes of a rash on a child’s stomach can be various infectious diseases. These can also be universal diseases (for example, measles, chickenpox, rubella), which affect both adults and children. For example, a rash in the lower abdomen in children can be caused by scarlet fever. With scarlet fever, the stomach and other parts of the body become covered with a small red rash, which is very itchy, and after a few days turns into peeling.
With measles, a rash appears on the child’s body 3-4 days after the illness. In this case, first small papules abundantly cover the cheeks, and then the rash spreads to the lower part of the body, including the abdomen.
Why else might a rash appear on the stomach?
In adult men and women, a rash on the abdomen most often indicates a sexually transmitted disease. By type, the rashes that cover the abdomen with STDs can be: hard inflamed bumps, blisters, cavities with liquid, blisters, spots of various shapes and sizes, scales and scabs. But, regardless of the type and size of the rash on the abdomen, you should remember: you cannot put off seeking qualified medical help. A rash on the stomach, of course, can be caused by completely harmless reasons, but sometimes the factors are so serious that a lot will depend on delay.
Dmitry Belov
You can often find out about problems in the body by the condition of the skin. Red or light spots, blisters, itching and flaking on the abdomen can be symptoms not only of skin diseases, but also of general pathologies.
By the type and nature of the rashes, a specialist can understand what problems caused them.
Types of disease
More than a hundred years ago, scientists identified and united diseases that are included in the group of neurodermatitis. The main characteristics of pathological processes are:
- severe itching sensations;
- the appearance of thickening on the skin (lichenification).
Modern medicine has not determined the etiology of each type individually, so neurodermatitis has been combined into itchy dermatoses. The most common ailments are:
- prurigo, patients are children and adults;
- atopic dermatitis;
- polymorphic dermatosis of pregnant women;
- bullous dermatoses;
- herpes during pregnancy;
- Broca's pigmented perioral dermatosis.
Each of the most common types of pathology has its own characteristics, symptoms, and treatment methods.
Prurigo Hebra
Prurigo is classified as an itchy dermatoses. Another name for the pathology is pruritus. There are two main types of disease:
- Hebra prurigo;
- Hyde prurigo.
The patient of Hebra prurigo often becomes a child suffering from hypovitaminosis and having dystrophic disorders. The disease makes itself felt in the first year of a baby’s life, manifesting itself externally as urticaria. Afterwards, large nodules form, which provoke a very itchy sensation. The nodules are located on the bends of the legs and arms. During the first period of appearance, they are not distinguished by color. After combing with tiny pieces of tissue, the skin thickens, peels, and has a gray-brown color.
Cases have been recorded where prurigo has complex processes when a secondary infection is attached. The disease is characterized by a significant increase in inguinal and femoral lymph nodes. Severely itchy sensations lead to uneven breakdowns and disorders. A chronic disease.
A dermatologist will tell you how to treat pruritus and, if necessary, refer you for consultation to other specialized specialists. To reduce itching, antipruritic creams and ointments are prescribed, the composition of which includes sulfur and tar. The ultraviolet irradiation procedure also reduces the level of itching of the skin. The specialist prescribes general restorative and sedative medications in parallel with antipruritics:
- Bromine.
- Diphenhydramine.
- Suprastin.
- Vitamin complex C, B1, PP.
- Glycerophosphates.
To effectively eliminate pruritus, you should listen to the advice of specialists and take all necessary medications. Complex treatment shows positive results over many years of practice.
Atopic dermatitis
Heredity, stressful situations, food allergens, poor-quality household chemicals, and medications develop allergic dermatoses in children and adults. The disease has three types:
- infantile appearance;
- children's uniform;
- adult look.
The symptoms of the three types are similar and have the following manifestations:
- severe itching;
- significant redness on the skin;
- redness thickens;
- papules appear;
- self-injury of skin tissue in the form of self-ruptures;
- dry or weeping crusts appear;
- skin is flaky and very dry.
In infants, rashes often appear on the face. They appear en masse on the outer and inner folds of the legs and arms. Older children with atopic dermatitis suffer from severe redness of the affected areas of the skin, which manifest themselves in combination with the formation of papules, peeling, and infiltration. An additional crease often appears on the lower eyelid.
Adult patients complain of the appearance of lichenification, when dense folds appear on the skin. Red areas take on a blue tint. The rash is located on the face, neck, upper limbs, and upper body. After the disease is cured, pigmentation may remain in the affected areas.
Treatment of allergic dermatoses involves strict diet therapy, excluding foods that can provoke allergies. Experts prescribe antihistamines and tranquilizers. For external use, anti-inflammatory, hormonal, anti-itch creams, ointments, infusions, and compresses are recommended.
Polymorphic dermatosis
Polymorphic dermatosis of pregnant women most often begins to develop in the third trimester. Polymorphic dermatosis has symptoms similar to other types of pathology:
- itching, which manifests itself and greatly interferes with the expectant mother’s normal rest or activities;
- the abdomen becomes covered with papules, the compactions reach a diameter of up to 2 mm;
- If treatment is untimely, papules spread to the skin tissue of the chest and arms.
The rash can last for 10-14 days; after 10 days of active rashes, they stop affecting the skin of the pregnant woman. With a polymorphic type of pathology, the fetus does not suffer, rashes and other symptoms do not have a negative impact on the unborn baby. This dermatosis is treated with sedatives and antihistamines. Corticosteroid ointments are used for external use.
Herpes in pregnant women
The herpes virus and the type of dermatosis are not related to each other. Only the names are similar. It belongs to blistering dermatoses, causing severe itching. Pathology is observed during pregnancy or in women after childbirth. Signs of the disease appear at any time during pregnancy or a day after labor.
Papules are located at the first appearance near the navel, but actively spread to the thighs, abdomen, chest, palms, and feet. Over time, the papules turn into small blisters filled with liquid, causing itching. Symptoms often disappear without therapy, on their own. But they tend to return during the period of repeated pregnancy, menstruation, and use of contraceptives.
To limit your body from the appearance of dermatoses, experts advise taking preventive measures. Strengthen your immune system by taking vitamins and eating right. Observe the rules of personal hygiene and do not be afraid to consult a professional at the first changes in the skin.
Systematization of the forms of the disorder takes into account etiological factors, features of pathophysiological changes, and the clinical picture of the disease. Experts in the field of dermatology distinguish the following types of dermatoses in pregnant women, which differ in prevalence, skin symptoms, and the likelihood of a complicated course: • Atopic dermatitis in pregnant women.
Accounts for more than half of cases of skin lesions during gestation. Caused by an enhanced Th2 response. In 80% of cases, it is first diagnosed during pregnancy and subsequently does not manifest itself in any way. May present as eczema, prurigo (scratchiness) or pruritic folliculitis of pregnancy. Typically, these forms of dermatitis are accompanied by discomfort, but do not pose a threat to the course of pregnancy.
• Polymorphic dermatosis of pregnancy. The second most common skin pathology of the gestational period (incidence is 0.41-0.83%). It is more often detected in the 3rd trimester in patients with multiple pregnancies and in women with large weight gain. Associated with an autoimmune response to damage to collagen fibers.
Characterized by itching, polymorphic rash. Does not affect the likelihood of complications during gestation. • Intrahepatic cholestasis (itching) of pregnancy. A hereditary disease that occurs in 0.1-0.8% of patients with genetic defects of the HLA-B8 and HLA-A31 alleles. Usually develops in the last trimester of pregnancy.
Most likely, dermatological symptoms are the result of the irritating effects of bile acids circulating in the skin. Of all gestational dermatoses, it is the most dangerous in terms of complications. • Pemphigoid (herpes) of pregnant women. A rare autoimmune pathology, the prevalence of which is 0.002-0.025%.
Causes of dermatitis
External reasons
Skin manifestations on the abdomen in the form of irritation, rashes of various types appear with prolonged squeezing, friction, as well as exposure to chemicals on the body. This could be tight clothing, or a man wearing a belt buckle that constantly puts pressure on his stomach. Long-term exposure to high temperatures and sweat contribute to the appearance of microtraumas of the skin and the attachment of infectious pathogens.
Other causes of abdominal rashes:
- different types of radiation - x-ray, ultraviolet;
- high and low temperatures;
- dust and pollen;
- components and household chemicals from clothes.
Damaged epidermis is easily infected with fungus, bacteria, viruses, and scabies mites. Irritation that occurs in the folds of the skin often becomes the site of infection and leads to mycosis, scabies, and herpetic infections.
Internal factors
A rash on the abdomen may be a consequence of internal problems of the body associated with metabolic processes and other diseases.
She is called:
- unbalanced diet;
- hypo- and vitamin deficiency;
- metabolic disorders;
- taking medications;
- neuropsychiatric diseases;
- autointoxication, accompanied by dryness of the skin.
Most often, a rash with itching and irritation of the skin in children is caused by improper feeding and emerging.
In case of dermatomycosis, scrapings from the skin are examined under a microscope to determine the type of fungus. The luminescent method is also used.
Skin diseases are caused by a whole group of pathogens:
- microsporum;
- trichophyton;
- candida.
For effective treatment, it is often necessary to know the exact type of pathogen in order to select the right antibiotic.