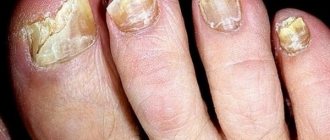
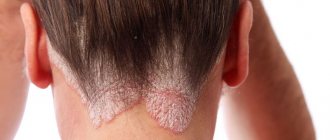
Eczema is an allergic disease that can occur both acutely and chronically with frequent exacerbations of the process. It is characterized by polymorphism (variety) of rashes, itching, burning and a stable course, prone to constant relapses. The favorite place for localization of pathology is open areas of the body: face, neck, legs, but most often it occurs on the fingers.
Regardless of the form of the disease (idiopathic, microbial, mycotic, seborrheic, etc.), treatment should only be comprehensive and quite long-term. The main treatment regimen in the fight against eczema:
- antihistamines, for example, Tavegil, Suprastin;
- immunomodulatory agents;
- detoxification drugs;
- external therapy with ointments and creams - hormonal and non-hormonal anti-inflammatory agents;
- sedatives;
- avoiding contact with the substance that triggered the allergy;
- hypoallergenic diet.
The leading and most effective method of treatment is the local use of drugs. They are divided into two types - hormonal and non-hormonal. But at the same time, any ointment for eczema on the hands must meet several criteria:
- eliminate the symptoms of eczema - itching, burning, rash;
- prevent the penetration of infection;
- moisturize the skin;
- not have a negative effect on the body, or side effects should be very mild.
What is eczema
The type of disease is an allergic reaction. The skin on the body becomes inflamed, and numerous rashes appear in the form of blisters. They cause itching, burning, dryness, cracks and erosions form on the surface of the skin. It is a chronic disease, exacerbations are seasonal. Usually this is autumn or spring. It manifests itself individually, but mainly depends on the severity and form of the disease itself. Affects the extremities of the arms (fingers, hands) and legs (legs, feet). The causes of the disease are quite banal. The list of them is large:
- the nervous system malfunctioned, stress, nervous breakdowns,
- diseases of internal organs,
- heredity,
- allergy,
- decreased functioning of the immune system.
It is the latter reason that is the most common for the occurrence of the disease. After serious illnesses and stress associated with them, the body and system fails. Recovery is a long process, and if a person had an allergy before, then the probability of eczema occurring will be 80% out of a hundred. Most often, the change of seasons (autumn, spring) provokes a relapse of all chronic diseases. Eczema is no exception. Sometimes a severe allergic reaction becomes a trigger. Such allergies include: to cleaning and detergents, personal hygiene products, perfumes (this includes creams and lotions). If a person works in an enterprise with chemical acids and alkalis, this also includes varnishes and paints. Based on the causes and pathogens, the classification of eczema occurred:
- allergic or also called atopic,
- professional,
- seborrheic,
- microbial
The last class includes other factors for the onset of the disease. It is clear that its treatment depends on the class of eczema, and dosage forms are selected. In addition to the listed classes, the disease can be wet or dry. This will depend on the variety and general symptoms. These include itching, skin rashes, cracks, and erosions. They look at the nature of the rash, whether it is peeling or dryness. Regarding treatment, this process is quite lengthy. Consists of a number of complex activities and procedures. The basis is dosage forms for therapy, cream, strict diet and regimen. Most often, they still turn to dosage forms for external use. If you start listing all possible creams, ointments and gels, the list will be several sheets long. Among them, it is quite difficult to choose a remedy so that the treatment is effective, reliable and preferably fast. Here you need to approach responsibly. A different product may be suitable for each area of the skin.
When choosing, you should be guided not only by material aspects, but also by an individual approach (possible contraindications, form and class of the disease, allergic reaction to the ingredients of the composition, skin type). We bring to your attention the most popular among effective drugs for the treatment of eczema.
Eczema manifests itself as unpleasant cracks in the skin
Drug treatment of eczema: a review of effective drugs
Drugs for the treatment of eczema are prescribed by a doctor personally for each patient. The type of disease, the degree of the inflammatory process and a number of important factors are taken into account. Self-medication is not allowed. The therapeutic course is based on the use of antihistamines, painkillers and corticosteroids. Treatment must be comprehensive and orderly.
Advantages and disadvantages of using medications
Each type of medication has specific uses. Hormonal drugs create addiction to the skin - the effectiveness of the medications decreases. A number of contraindications should be taken into account. Before treatment, visit a doctor who will determine the optimal recovery plan. The main advantages of medications against eczema (atopic, plaque, mycotic):
- removal of the inflammatory process;
- prompt elimination of itching and pain syndromes;
- relieving irritation of the epidermis and dry skin (use Lipikar);
- minimal risk of side effects;
- the ability to treat children without serious complications;
- elimination of affected skin areas on the neck and face.
Medicine for eczema is taken for a long time. To achieve a positive result, it is necessary to monitor the quality of food and hygiene rules. Follow your doctor's instructions to ensure the healing process is as fast as possible. In some cases, traditional methods are used.
Among the disadvantages of medications, the body’s addiction and the harm of antibiotics stand out. After recovery, it is recommended to take tests for bilirubin content in the liver. After the inflammatory process, you will have to wait a long period until the tissue heals completely.
Features of therapy for different types of eczema
The plan for eliminating eczema depends on the extent of the disease. Experts determine the stage of the disorder and options for contact with allergenic factors. Internal pathology should be taken into account.
If the pathology is limited, local treatment of the disease is suitable. When weeping develops, Oxycort and Oxycyclosol aerosols are used. Corticosteroids (Dexamethasone) are used.
Creams and ointments are not suitable.
Medications are selected based on the form of the disease. Frequent options:
- subacute form - corticosteroid-based ointments (Diprosalik, Celestoderm, Ultralan);
- the paratraumatic type is eliminated with Fukortsin, apply a thin layer;
- lichenification is eliminated by ointments with salicylic acid (Lorinden, Lokasalen);
- for children, gentle therapy will be required; Prednitop and Lokoid are prescribed;
- varicose complications are treated by surgery, laser therapy (intravenous influence);
- disseminated eczema is eliminated with antihistamines, and a combination of sleeping pills and sedatives is used.
Physiotherapy involves the use of anti-allergy treatments. Elder flowers, tansy, violets, and St. John's wort are collected. Valerian and hawthorn infusion have a healing effect. Visiting spas is recommended in chronic cases. Specialists in health resorts use healing wax and gel. Drinking alcoholic beverages and nicotine is prohibited! Anti-allergenic effect 100%.
Types of medications prescribed for eczema
The mechanism of eczema formation is based on the manifestation of allergic reactions. Increased sensitivity of the body is associated with a number of irritants. The main sources are food, aggressive substances, diseases of internal organs. Eczema is a consequence of disorders of the gastrointestinal tract (gastritis, enzyme disruptions, liver dysfunction).
Treatment of eczema should be systemic. It is necessary to eliminate pathogenic microorganisms. Therapeutic regimens using hormonal ointments, tablets, antihistamines, and antibiotics are being approved.
Sorbents and antihistamines
In chronic forms, antihistamines will help. Chemical compounds block receptors (Loratadine) and minimize the amount of free histamines. As a result, itching and inflammation disappear. Common drugs:
- "Tavegil", "Diphenhydramine". First generation blockers. The effect of the compounds lasts 6 hours. To ensure a consistent therapeutic effect, monitor the timing of your medications.
- "Fexadin", "Telfast". The 3rd generation medicine contains the active ingredient Fexofenadine. They have no contraindications and do not produce a cardiotoxic effect.
- "Lordestin", "Dezal", are not suitable during pregnancy.
- "Chloropyramine" is used for exacerbation of the disease with the release of exudate. The substance is administered by injection into a vein. An alternative is calcium gluconate/calcium chloride.
In practice, dermatologists prescribe Suprastin and Claritin. Medicines inhibit histamine receptors. The main therapeutic component is chloropyramine hydrochloride.
The pharmacological product is available in the form of tablets and injection solutions. Among the sorbents used are “Polysorb”, “Acipol”, activated carbon, “Enterosgel”.
Hyoxysone and Triderm are a complex preparation for eliminating redness on the skin.
Antibiotics
Tablets for eczema are prescribed with caution to children under 10 years of age. Applies to substances containing tetracycline. The chemical compound can negatively affect bone formation and skeletal development. Before prescribing antibiotics, the body is diagnosed and tested. Popular and safe ointments:
- Mupirocin;
- Fukortsin;
- Locacorten;
- Sinalar-N;
- Erythromycin.
The above-mentioned pharmacological products are rich in hormonal components. The substances have antibacterial properties, allowing them to be used in short courses (up to 2 weeks). Medicines are used to eliminate bacterial infections. Ceftriaxone is widely used for eczema.
Anti-itch and soothing
Elimination of itching in eczema is carried out using special medications. Appointed:
- moisturizers, give preference to ointments that do not irritate the skin;
- itching is eliminated by oral substances, compounds minimize inflammation, rash, itching, focus on Stellanin;
- corticosteroids in ampoules (dose approved by the doctor);
- pricking with special needles (legs, arms, limbs).
An effective remedy is the steroid ointment Sinaflan. The active component "Acetonide" has an antiallergic effect. The substance minimizes the risk of neutrophil accumulation in tissues. As a result, the exudative process declines. "Elidel" is a drug for children over 3 years old. You can buy Skin-Cap at an affordable price. Consult your doctor before treatment.
Among the sedative medications, Novopassit, Persen, and Valemidin are effective. Don't want to overpay? Use valerian, motherwort and glycine. Salicylic ointment will give a healing effect.
Hormonal
Therapeutic regimens use hydrocortisone. Hormonal substances are represented by ointments, tablets, lotions. Other options are Prednisolone, Lokoid, Lorinden. The compounds should not be used for more than 15 days. Otherwise, the elements may enter the bloodstream, causing additional complications.
Corticosteroid-based creams are effective for weeping eczema. The compounds dry out the skin. Ointments are suitable for rough crusts, having a healing effect. When eczema is localized on the scalp in the hair, high-quality emulsion and lotions are used. Light forms of consistency do not allow hair to become oily.
Antiseptic and anti-inflammatory
Getting dirt and germs onto the affected area of the skin is fraught with additional complications and disorders. Effective antiseptic drugs:
- "Betadine" - it is prohibited to use for thyroid disorders (including analogues);
- “Miramistin” or “Thiosulfate” - applied to the affected skin in the form of compresses, milk lotions are used;
- “Resorcinol”, a chemical substance suitable for treating deep wounds during lactation, is approved for pregnant women;
- “Boric ointment” is an antiseptic that is effective against skin lesions by parasites;
- “Dekasan” - the medicine is effective against microbes, the dosage is determined by the doctor;
- "Dimexide" is an analgesic medication suitable for dyshidrotic mycosis;
- "Clotrimazole" and "Polyphepan" - antifungal compounds;
- "Radevit" - quickly restores damaged skin;
- "Chlorhexidine" is an antiseptic for the skin during the period of urticaria, eliminates the causes of irritation.
Other
Elimination of eczema must be comprehensive. Doctors recommend using thiamine, a B1 vitamin. The compound restores carbohydrate balance in the body and metabolism. Thiamine Alternative:
- ascorbic acid;
- biotin + riboflavin relieves inflammation;
- the vitamin complex “Aevit” promotes cell regeneration, suppression of allergic manifestations, inflammatory processes gradually decline;
- microbial acetate;
- brilliant green, iodine (Iodinol composition), substances rich in iron and sodium (Hyposulfite);
- “Retinol” is a fat-soluble vitamin that reduces inflammation, the use of the medication is determined by the doctor.
Remedies for Effective Healing
All proposed means for drug treatment can be divided into two types.
- Ointments containing a synthetic steroid hormone. They are called hormonal. They help neutralize the process and relieve inflammation. Accordingly, sensations of dryness, burning, itching or irritation also disappear. But there is a minus - quick addiction. As a result, effective therapeutic treatment begins to disappear. Such drugs should be treated with caution, because there are a number of contraindications and quite serious ones. To improve the therapeutic effect, it is advisable to use drugs with hormonal supplements in short courses. This way you avoid addiction and side effects. There is a certain classification.
- The list of non-hormonal drugs is also not small. Unlike hormonal ointments, they can be used for a long time without fear. These ointments are used to moisturize and relieve irritation. The composition of the drugs is different. They may contain antiseptics and anti-inflammatory substances. But, like all medicines, they have contraindications. In order not to get into trouble, you need to carefully study the package leaflet of the drug, and it is better to consult a doctor.
Prednisolone ointment, a mild drug
Medical advice: how to prevent relapse of the disease
The following simple tips will help minimize the chance of eczema recurring:
- adhere to proper nutrition: avoid fatty, spicy, heavy-for-the-stomach foods and fast food;
- eliminate alcoholic beverages from your diet, stop smoking;
- Before each meal, wash your hands thoroughly, as well as vegetables and fruits that you eat;
- avoid psycho-emotional overstrain, stress, overwork - almost all skin diseases have a psychosomatic background.
Classification of hormonal drugs
As mentioned earlier, all drugs for external use are divided into classes or categories. For every skin area, tissue type and individual approach.
- Weak ointments come first. They are allowed to be used to eliminate and treat eczema in children, pregnant or nursing mothers. This ointment is suitable for eczema on the hands, neck or face. In other words, for use on small areas of the skin. If you use ointment for eczema on your face, you should ensure that it does not have any side effects. The drugs Lekoid and Prednisolone ointment cope well with this. They quickly stop and neutralize all the symptoms and characteristic phenomena of the disease.
- The second group includes products that have a moderate effect. If the first class of ointments does not cope with its purpose, then it is recommended to use this group. This is Zinocort or Afloderm. This cream for eczema on a child’s hands will be more than effective.
- Sinoflan, Advantan and Sinalar are means for a stronger effect on inflammatory foci of the disease. They quickly and efficiently relieve unpleasant sensations (burning, itching). Widely used against eczema and its exacerbation.
- The last class is fourth. The most powerful drugs. Prescribed in special cases (if other classes have failed and treatment has declined). It is recommended to be very careful with them, as they have an increased number of side effects. Drugs of this class have a special therapeutic effect. Penetrate deeply into the epidermis. It is prescribed by a specialist after undergoing a series of tests and calculations of the patient’s condition, possible risks and contraindications for a particular person. Possibility of application is limited. To complete treatment, the dose is gradually reduced.
You should not choose your own treatment regimen, believing that this or that effective ointment advertised will be your salvation. The course of treatment and medications should be prescribed only by the attending physician, who takes into account all factors and risk areas for the patient.
Advantan quickly relieves burning and itching
Video about cream for eczema on hands
Unfortunately, the exact cause of the disease has not yet been established.
According to dermatologists, the disease is neuro-allergenic in nature, the predisposition to the lesion is genetic, and no cases of infection through contact with the patient have been recorded. With proper treatment, which involves the use of anti-eczema creams on the hands, it is quite possible to get rid of the symptoms of the disease. Neglect leads to the addition of a bacterial infection to the main ailment. In such cases, it will no longer be possible to cure the lesion with the help of creams and ointments. In the fight against the infectious form of the disease, you cannot do without antibacterial agents.
There are a number of factors contributing to the occurrence of pathology:
- reduced immunity, vitamin deficiency;
- gastrointestinal dysfunction;
- disorders of the cardiovascular system;
- hormonal imbalances;
Additional Information! Women at risk are during pregnancy and menstruation, as well as adolescents during puberty.
- injuries, mechanical damage to the skin;
- abuse of cosmetics and detergents containing chemicals;
- receptivity and sensitivity of the epidermis, tendency to allergic reactions;
- disruption of daily routine, chronic fatigue, poor nutrition;
- sudden temperature changes.
Important! Patients suffering from diabetes mellitus, vegetative-vascular dystonia, and diseases of the endocrine system are exposed to eczema much more often than other people.
The heredity factor plays a special role in the development of pathological formations on the skin of the hands and other parts of the body. Moreover, it is not the disease itself that is genetically transmitted, but the predisposition to it. However, this should not sound like a death sentence, since it is quite possible to avoid eczema if you follow the recommendations of dermatologists and adhere to the principles of a healthy lifestyle.
To cure eczema on the hands and fingers, it is necessary to use hormonal and non-hormonal external remedies. You can find out which drug is best to use during a visit to the doctor; it is not recommended to use an ointment or cream against eczema without prior consultation.
Before moving on to listing creams for eczema on the hands, let’s take a closer look at their properties and characteristic qualities.
How non-hormonal drugs work:
- have an antifungal, antimicrobial, antiallergic effect on the skin affected by the disease;
- promote wound healing, healing of cracks, restoration of the epidermis;
A feature of non-hormonal creams for eczema is the fact that in most cases they are effective only in the initial stages of the disease. Advanced forms require more serious treatment, involving the use of general medications. Also, one should not forget about the limitations; creams are not recommended to be used:
- pregnant women;
- patients prone to allergic reactions;
- women during breastfeeding.
Non-hormonal creams for eczema on hands:
- Argosulfate. The product has antibacterial properties and inhibits the development of harmful bacteria. The cream regenerates and restores the epidermis, gives it elasticity;
- Iricar. Actively inhibits inflammatory processes, reduces burning, itching, and muffles pain;
- Elidel. Helps eliminate inflammation. It is recommended to apply twice a day, the ointment is dispensed only with a prescription;
- Skin cap. Recommended for use in dry forms of eczema, suitable for all groups of patients. Has antifungal and antibacterial properties;
- Dermasan. Helps reduce symptoms in the early stages of the disease; progressive forms of eczema require the use of hormonal creams;
- Aurobin is a non-hormonal cream for eczema, the main purpose of which is to heal wounds and ulcers, restore the skin;
- Dermaref, Biopin. They have anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties.
Additional Information! Non-hormonal creams such as Bepanten, Magnipsor, Naftaderm, Aisida, Gistan, and Videstan also have a beneficial effect on the epidermis in the initial stages of the disease.
At the initial stages of pathology development, the use of folk remedies, in particular ointments and creams, is allowed. Creams made from honey and oats are especially popular. Cooking method:
- take 5 tbsp. spoons of oats;
- chop the oats and add warm water;
- leave the mixture for a while;
- add 5 tbsp. spoons of honey.
The infusion is ready, apply it to problem areas 2-3 times a day for 3-4 days.
This group of drugs has long been successfully used to treat inflammatory skin pathologies.
All corticosteroid ointments can be divided into the following subcategories:
- Ointments with a weak effect - suitable for the treatment of dermatitis on the hands, fingers or toes in children under 3 years of age, can also be used in the case of eczematous dermatitis of the neck and face, for the treatment of pregnant women and women during breastfeeding. Examples: Prednisolone ointment 0.5%, hydrocortisone cream “Lokoid”.
- Moderate drugs - used in case of ineffectiveness of the previous category, for more severe inflammation, in case of varicose eczema of the legs. Examples: Afloderm, Dexamethasone 0.05%.
- Strong remedies - prescribed in severe cases of eczema, when a secondary infection occurs. Examples: Advantan, Sinalar.
- The most powerful drugs - used in case of complete failure of all previous ointments, especially for eczema of the skin of the feet and fingers. Examples: Galcinonide, Dermovate.
As we have already found out, eczema is always associated with allergies, so treatment must be comprehensive. First of all, you should undergo an examination and identify the allergen.
Secondly, you need to follow a certain diet, which involves excluding a number of foods. For example, citrus fruits, chocolate, alcohol, smoked foods, spicy and salty foods.
In order to relieve the inflammatory process that accompanies the manifestation of skin allergies, medications that contain corticosteroids are prescribed. Equally important is the removal of harmful substances from the body. For this purpose, a medicine from the antihistamine group is prescribed.
Classification of non-hormonal drugs
There is no classification as such, but there are distinctions between dosage forms. The fact is that there are many skin diseases, and many manufacturers produce them for use and treatment of several diseases at the same time. It immediately becomes clear that broad-spectrum drugs cannot fully help in all cases.
- For diseases of bacterial origin: eczema, boils, herpes, and also to relieve swelling, Eplan is used. If you have eczema on your hands, the ointment is exceptionally suitable. It will relieve irritation, inflammation, and swelling on the fingers.
- A frequently used ointment for eczema on the fingers and neck is Bepanten. But it is ideal for prevention, as well as the initial form of the disease in children at an early age. There are analogues - Panthenol and Pantoderm. A broad-spectrum ointment can be considered one of the simplest and most harmless medicines for this disease.
- Skin-Cap can be produced in the form of an aerosol, gel or cream. It is used as an ointment for eczema on the legs, as it has additional functions - an antifungal agent. Relieves inflammation, kills microbes that provoke disease. It is used as an effective remedy for such types of eczema: atropic and seborrheic. It is recommended for use in the treatment of childhood skin diseases and is the safest of all non-hormonal dosage forms. An ointment for eczema on the hands is also used.
- If ointment is required, then Radevit will do. It helps with eczema of allergic and atropical origin. It not only softens, but also helps damaged areas of the skin become keratinized. Relieves itching and burning and has an anti-inflammatory effect.
- Herbal eczema ointment is safer in all respects. Natural ingredients have always been highly valued. Such a medicine is Gistan. It should not be confused with the hormonal drug Gistan-N, which is widely used for allergic eczema.
- Strong, but dangerous with long-term use, is an ointment for weeping eczema called Elider. It contains pimecrolimus, which can influence the patient’s immune system. Can cause swelling and swelling of the skin. It is used only as prescribed by a doctor, and only when other remedies have not helped.
- To relieve pain on the skin due to eczema on the hands, experts recommend Fenistil.
- A commonly used ointment for eczema is Losterin. In addition to urea, almond oil, and plant extracts, it contains D-panthenol and salicylic acid. This drug not only has an anti-inflammatory effect, but also neutralizes, relieves itching and flaking.
- For the treatment of chronic types of eczema, Thymogen ointment is recommended. Used as prescribed by a doctor. Use with caution if the child is sick.
- When treating dry eczema, Naftaderm ointment will provide effective treatment. This drug is obtained from petroleum products. It is an antiseptic and pain reliever. Softens and resolves, and also relieves inflammation.
- Videstim can be used to regenerate the skin. Ingredients: retinol, vitamin A, palmitate. Has a healing effect.
For eczema that is not complicated by the inflammatory process, you can use preparations that contain zinc, tar, and naphtha oil. These are zinc, salicylic, boron-naphtha ointments. As well as a drug with silver nitrate and Meshchersky ointment. They will help reduce itching and the beginning process of tissue inflammation and dryness. They will help in regenerating the skin and softening it.
Even with prolonged use they will not cause harm to the body, since there are no special contraindications for their use. It is necessary to smear regularly several times a day. All ointments are applied to clean, dry skin.
Elidel cannot be used for a long time
Zinc ointment
Particular attention should be paid to a drug that has been used for a long time and provides truly effective treatment. Zinc ointment for eczema has an astringent, antimicrobial and antiseptic effect. It is used to treat all types of eczema, especially suitable for patients with wet eczema; in this case, the ointment helps dry out the weeping areas and prevents the infection from spreading further. The ointment is applied to the skin with the affected areas in a thin layer. Preferably 3-4 times a day. Since it has no contraindications, it can be used during pregnancy and children from infancy. If used for wet eczema, the result will be in a week: the skin will dry out, itching, burning, redness and irritation will disappear. The only point in which the use of zinc ointment is not recommended is increased sensitivity to the drug and purulent rashes.
Zinc ointment, a safe and affordable remedy for eczema
Fat-based ointments
Three oil-based drugs are prescribed and used for a type of eczema called dyshidrotic. Ordinary water provokes the appearance of this type. To effectively soften crusts on the skin and better penetration of medicinal substances, Elokom, Beloderm and Triderm are prescribed. The initial stage of treatment begins with the use of hormone-containing dosage forms, since they have a stronger effect than non-hormonal ones. The second part of treatment uses medications with fewer or no hormones.
Such ointments promote healing and reduce all symptoms of the disease. Apply no more than twice a day to the affected areas of the skin for one, maximum two weeks.
Beloderm, fat-based ointment