It is believed that a boil on the head is the most dangerous skin disease. It occurs due to an inflammatory process in the hair follicle and the tissue that surrounds it. Inflammation is caused by Staphylococcus aureus bacteria, which penetrate the skin through minor mechanical damage. If a tumor is detected on the head, you should immediately consult a doctor.
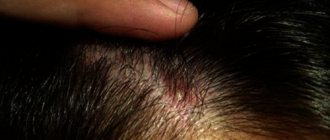
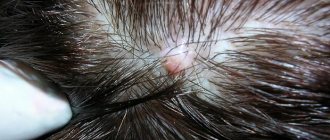
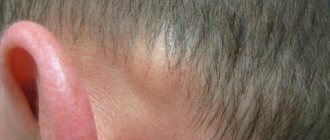
Boils can grow on the scalp and go unnoticed by a person for some time.
What reasons?
A boil on the head in the hair is a common occurrence, because it is there that many hair follicles are located, in which the inflammatory process occurs. Staphylococcus, which gets under the skin and causes inflammation, may not manifest itself immediately. For some time, harmful bacteria are in the stage of suspended animation if conditions do not allow them to begin full-fledged life activity. As soon as conditions change (for example, immunity decreases), inflammation will immediately begin to progress.
The infection penetrates the skin through microtraumas. Scratching a mosquito bite or carelessly using a comb (when the scalp is irritated) leads to furunculosis.
What contributes?
You can easily detect a boil in the scalp if you do not adhere to the rules of personal hygiene. Here are several reasons that contribute to the appearance of boils on the head:
- using other people's household items (comb, razor, towel);
- cheap or inappropriate hair products;
- scratching the scalp.
Dirty hands are the main cause of infection in the scalp. If a person has a weak immune system, boils can affect a large area of the scalp. Factors contributing to decreased immunity and the occurrence of furunculosis:
- avitaminosis;
- stressful situations;
- long-term illnesses;
- chronic fatigue.
Causes of boils
The cause of boils is infection of the hair follicle with Staphylococcus aureus bacteria (most often) or other pathogenic microorganisms. An infection can get into the hair root when scratching the head with dirty hands. Any cracks, scratches, or burned surface are suitable conditions for the penetration of pathogenic flora into the dermis.
A boil appears on the head suddenly, without previous general symptoms. According to statistics, there is a surge in furunculosis in the head and neck area in the autumn and spring periods. This seasonality is explained by provoking external conditions - drafts, wind, increased humidity - and a decrease in one’s own defenses due to hypovitaminosis and deterioration of immunity.
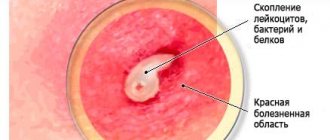
After infection of the hair follicle on the head, an inflammatory reaction begins in nearby tissues. In place of the hair, a purulent rod forms. This process is caused by a defense response when macrophages are released to fight infection. Dead leukocytes and bacteria form purulent masses. With significant suppuration of the boil, tissue at the site of inflammation may partially die. This process is called necrosis.
What are the symptoms?
A growing boil on the head can cause pain, itching, and temperature fluctuations.
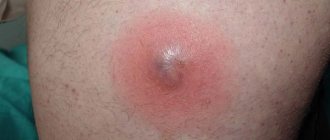
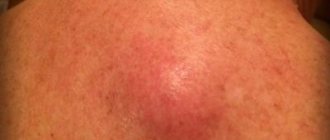
The first symptom of the development of a boil is the appearance of ostiofolliculitis. This phenomenon is a small pustule that forms at the mouth of the follicle. After some time, folliculitis develops. A boil begins to develop when inflammation extends beyond the follicle itself. The scalp becomes red with purple and bluish tints. There is swelling and pain in the inflamed area when touched. The inflamed skin rises and a pulsation is felt underneath.
The development of the inflammatory process entails an increase in the inflamed area to the size of a walnut. After 2-3 days, a necrotic core appears, at the top of which there is a pustule. When it is opened, greenish pus is released, which accumulates around the rod under the skin. The boil should open on its own or with the help of a doctor. It is strictly forbidden to open the boil yourself, as this can lead to serious consequences.
Signs
The first symptoms of a boil on the head in the hair are the appearance of local hyperemia and thickening.
In the case when a carbuncle develops, that is, inflammation of several nearby hair follicles occurs, the patient feels severe pain when palpating the affected area on the head. A single small boil, as a rule, almost does not provoke pain symptoms; discomfort is felt more.
With your fingers you can feel a small bump or infiltrate in the layers of the skin. If you examine the pathological area on the head in the mirror, redness will be visible.
Boils on the head quickly fester, and white or yellow contents begin to be visible in the center of the hyperemic area under the skin. The tissues of the head are better supplied with blood, and the scalp is no exception. Therefore, the process of formation of a purulent-necrotic core proceeds faster than in other parts of the body.
If extensive ulcers occur on the head, the following may appear:
- chills;
- significant increase in body temperature;
- general weakness up to loss of consciousness.
These are signs of the spread of infection, which leads to serious consequences.
Features of a child
When boils appear on a child’s head, adults need to be extremely careful. Treating furunculosis in a child on your own is dangerous for his life and health, so you should immediately consult a doctor. Since in children the immune system is not yet fully formed, when boils develop on the head, the general condition of the body suffers. Feeling worse, temperature rises, headache. Signs of general intoxication may appear.
With timely consultation with a doctor and proper treatment of furunculosis, the child recovers faster than the adult.
Additional diagnostics
Usually the diagnosis of a boil is not in doubt. It is determined by the doctor based on examination and medical history. If the patient develops multiple ulcers on the head that are difficult to treat or recur after treatment, then additional studies may be needed:
- General blood analysis.
- Immunogram.
- Analysis of purulent discharge (microscopy, culture, sensitivity to antibiotics).
Based on the results of diagnostic tests, it is possible to establish the cause of purulent inflammation and the factors contributing to its development. This makes it possible to conduct targeted therapy.
Diagnostic procedures
In order to quickly and effectively cure a boil that has formed on the head in the hair, you should determine the cause of its appearance and eliminate it. To diagnose a boil, the doctor performs a visual examination and, if necessary, prescribes additional tests and diagnostic procedures. To determine the cause of furunculosis, the following tests are performed:
- general urine analysis;
- general blood analysis;
- bacterial culture of purulent contents;
- examination of internal organs.
If the examinations carried out do not give satisfactory results, you may need to consult a doctor of another profile. To establish the pathogenic cause, it is recommended to conduct a full examination of the body and diagnosis of the immune system. The doctor will prescribe treatment methods only after studying the diagnostic results.
Treatment methods
What to do when a boil appears on your head? Surgical, local drug treatment, and restorative therapy will be required. Treatment methods should be determined by a specialist after assessing the external condition of the boil, collecting anamnesis, and clarifying concomitant chronic diagnoses.
The choice of treatment method is influenced by:
- localization (the closer to the temple, the more dangerous);
- area of inflammation;
- the presence of necrotic lesions;
- general health of the patient;
- the presence of endocrine pathologies, especially aggravating the course of furunculosis, diabetes mellitus;
- the presence of other infectious diseases delays recovery (sore throat, acute respiratory infections, intestinal infections);
- pathologies of the immune system (HIV, secondary immunodeficiency).
Having specified all concomitant diseases and characteristics of the body, the doctor will prescribe general and local treatment. In case of severe, advanced suppuration or in the presence of complications, the doctor may resort to surgical intervention.
Conservative
An abscess on the head under the hair, if it has a small affected area, can be treated using conservative methods.
To quickly rid the patient of a boil on the scalp and prevent the spread of infection, the doctor prescribes vitamins and microelements. Complex multivitamins activate immune reactions and accelerate the process of tissue epithelization.
Local therapy consists of several stages:
- It is necessary to treat the surface of the boil and the skin around it. To do this, the hair is parted, the localization of the pathological process is wiped with a swab moistened with alcohol, furatsilin or another antiseptic.
- Lubricating the scalp where the boil is located with an antibacterial drug. This may be an ointment containing streptomycin, erythromycin, chloramphenicol, etc. Ichthyol ointment or Vishnevsky liniment is often used.
- After the boil has opened on its own, its surface is smeared with antiseptics, which have a drying effect. These include a 1% alcohol solution of brilliant green, a weak solution of salicylic acid.
- The use of healing ointments to accelerate regeneration. You can use Methyluracil, Solcoseryl.
How to treat?
To protect your health and avoid complications, boils on the head under the hair are best treated in a hospital or under the supervision of a doctor. To speed up the rejection of the purulent core at the site of the boil, it is advisable to cut the hair and apply a dry bandage. The tubercle is lubricated with iodine or salicylic acid.
Squeezing, piercing and cutting the boil is strictly prohibited. Such manipulations, if necessary, are carried out only by a doctor. Furunculosis in the scalp can be treated using broad-spectrum antibiotics. If the chiri are large in size, general therapeutic methods are used to accelerate their maturation: ultraviolet and infrared irradiation, electrophoresis.
If the boil does not open on its own for a long time, surgical intervention is necessary. The doctor, using local anesthesia, cuts the formed abscess and removes the necrotic core. Next, the hole is thoroughly cleaned of pus and treated with an antiseptic. A clean bandage with erythromycin ointment is applied to the resulting wound.
Treatment with folk remedies
It should be remembered that traditional methods of treatment are considered an adjunct to medical therapy. Therefore, it is possible to treat boils using traditional methods only with the permission of a doctor and under his supervision. Below are several recipes that can be used to successfully get rid of boils on the head.
Beeswax ointment
Take 250 milliliters of unrefined vegetable oil, pour into an enamel bowl, and put on fire. When the oil boils, add 50 grams of spruce sulfur and beeswax to it. Cook for 30 minutes. Add 10 lower parts of the onions to the resulting mass. Remove the resulting foam with a slotted spoon. After 30 minutes, remove the dishes from the heat, cool the mixture, then strain. Apply ointment to boils 2 times a day.
Garlic compress
During the period of ripening of the boil (the first few days), a garlic compress should be applied to the inflamed area, having previously degreased the inflamed surface of the skin with alcohol or cologne. Finely chop the head of garlic, apply one clove to the inflamed area and secure with a clean bandage or plaster. If the boil is already ripe, use crushed garlic.
Untreated boils on the head can become chronic or cause extensive suppuration.
Pimples on the scalp
Pimples are inflammatory elements of a rash. They may appear as papules or pustules.
In common parlance, acne refers to any small red rash that rises above the skin. Comedones are identified separately. These are non-inflammatory elements that are most often seen in acne.
Painful pimples cause the greatest discomfort to a person. Along with the rash, other symptoms are possible (itching, burning, redness of the skin, peeling, scarring, purulent discharge).
The causes of acne vary.
The main etiological factors are:
- seborrhea;
- acne;
- hormonal disorders;
- pediculosis;
- furuncle;
- folliculitis.
Sometimes bubbles appear.
This is possible with dermatitis herpetiformis and pemphigus.
Not everyone knows why small pimples appear on the head.
Predisposing factors are:
- lack of personal hygiene;
- occupational hazards;
- increased sweating;
- dysfunction of the sebaceous glands;
- changes in hormonal levels;
- disturbance of nervous regulation;
- adrenal gland diseases;
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- bearing a child;
- puberty;
- irregular sexual activity;
- presence of thick hair;
- taking steroids;
- using chlorinated water for washing hair;
- smoking;
- using a synthetic fabric pillow;
- stress;
- wearing tight hats;
- infrequent hair washing.
Pimples on the scalp can be caused by allergies or exposure to high temperatures.
Rash due to lice
The causes of the rash may lie in lice. This is a parasitic disease caused by lice and nits. They live on the hair and feed on the blood of the host. Their color ranges from white to brown. Head lice live up to 40 days. Infection occurs through contact. Risk factors are:
- using one comb;
- overcrowding of teams;
- use of one sofa, bed or chair;
- wearing other people's hats;
- non-compliance with hygiene measures in hairdressing salons.
The main symptoms of this pathology are severe itching and the presence of a rash.
The appearance of exanthema is promoted by scratching, infection and lice bites.
With head lice, the hairy area is involved in the process. The rash appears at the sites of insect bites. It has the following features:
- represented by red spots, papules and pustules;
- multiple;
- accompanied by itching.
When infected, ulcers form in the form of pustules or vesicles. In the scalp, the number of rash elements can reach several tens or even hundreds.
A similar clinical picture is often observed in people without a fixed place of residence. Not only pimples, but also pigment spots may appear on the head. Without proper treatment, the skin becomes crusty and rough.
Acne with seborrheic dermatitis
When acne appears on the head in the hair of men, the cause often lies in seborrhea. This is a pathological condition in which sebum production is disrupted. Seborrhea can be oily or dry.
With the first option, purulent pimples on the head appear much more often.
Without proper treatment, seborrheic dermatitis develops.
The appearance of a rash on the head under the hair is due to several reasons.
The main ones are:
- lipid metabolism disorder;
- changes in blood hormone levels;
- burdened heredity;
- excessively frequent hair washing;
- improper care;
- visiting beaches and solariums;
- washing your hair with laundry soap;
- excess fatty and spicy foods in the menu.
HIV-infected people often face this problem. Pregnant women and teenagers also often experience acne in their hair. With seborrhea, the face (chin, nose, forehead) and scalp are affected.
Signs of oily seborrhea in men and women include redness of the skin, oily hair, gaping pores, itching, large dandruff, secretions, hair loss and thickening of the skin.
If a person is not treated in a timely manner, an infection develops. Seborrheic dermatitis develops.
The rash consists of papules (nodules). Pimples on the head are located singly. They are localized in the central part of the seborrheic plaque. Blisters with purulent contents (pustules) often appear. They contribute to itching.
Pimples dry out and form yellow-brown crusts. For such people, their hair quickly becomes oily even with daily showering.
If seborrhea is not cured in a timely manner, the skin of the face becomes involved in the process. In such people it is strewn with acne. This clogs the hair follicles and sebaceous ducts.
Presence of acne
If pimples appear on your head, the cause may be acne. The skin where hair grows and the face is affected. Millions of teenagers have acne.
In recent years, the disease is increasingly detected at the age of 30-35 years. This is a chronic dermatosis that requires long-term and complex treatment.
With this pathology, a rash appears in the head, hair and facial skin. The development of the disease is based on blockage of the mouths of the hair follicles.
Comedones form in the form of blackheads or inflammatory elements (pustules).
They can appear for various reasons.
Predisposing factors are:
- irregular sex life;
- chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- pregnancy;
- adolescence;
- abuse of hormonal drugs;
- taking anabolic steroids;
- skin irritation with soap, peelings and scrubs;
- contact with chemicals (herbicides, insecticides, oils).
You need to know not only what causes acne, but also what it looks like. Elements of the rash form in the area of the hair follicle. They are represented by pustules, nodules and nodes up to 10 mm in size. The most common occurrence of acne is on the head. They often disappear by adulthood. The process involves the skin of the forehead, scalp, cheeks, chin and temples.
Self-squeezing pimples leads to the formation of erosions and scars. Ulcers can be single or multiple. In severe cases, their number exceeds 30.
Pimples on the head of men and women rise above the skin, combined with redness and slight swelling of the tissues, red in color. Often the rash causes discomfort to patients due to burning and itching.
Late acne is less common. They occur at 40-50 years of age. In women, they may appear before menstruation.
Against the background of thick seborrhea, spherical red pimples may form on the head. Mostly men are affected. Sometimes acne occurs like facial pyodermatitis, when nodules and papulopustular rashes form in the area of redness.
Over time they merge. Large purulent conglomerates form. Only the face is affected. Sometimes pustules appear on the head of newborns. If proper hygiene measures are taken, they disappear quickly.
Boil in the head area
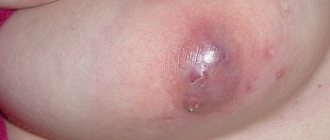
A common pathology such as a boil on the head is common. It hurts and can cause intoxication of the body. In another way, this abscess is called a boil. It is based on damage to the hair follicle, sebaceous gland and surrounding soft tissues. Boils are painful pimples.
They have the following distinctive features:
- up to 2-3 cm in size;
- painful;
- often accompanied by fever;
- have a purulent core;
- open on their own;
- single or multiple;
- disappear after 7-10 days.
These pimples under the hair rarely appear. The face is most often affected. It all starts with the formation of an area of infiltration (compaction). Swelling occurs.
There may be a slight tingling sensation. Pain occurs on palpation. Purulent pimples appear on the lips, cheeks and chin. In the second stage, suppuration occurs.
A rod is formed. At the top it ends in a pustule. It rises above the skin. Emerging ulcers lead to fever, chills, headache and general malaise.
Intoxication is caused by the proliferation of staphylococci and their entry into the blood. If the ears are damaged, hearing loss may occur. After some time, the pimple on the head opens and the pus comes out. The patients' condition is improving.
Sometimes there are several such pimples on the head. This is called furunculosis. The duration of the disease does not exceed 10 days. The most severe boil is localized in the area of the nasolabial triangle. If acne on the head is not treated, complications develop in the form of erysipelas, carbuncle, phlebitis, lymphadenitis, abscess and phlegmon.
Prevention of boils on the head in the hair
To prevent furunculosis on the head, you should adhere to the basic rules of personal hygiene. The hair on your head should be kept clean at all times.
To wash your hair, do not use cheap products containing aggressive ingredients that irritate the skin. A healthy, nutritious diet plays an important role in prevention. The necessary complex of vitamins and minerals must be supplied to the body daily to maintain a healthy immune system. If the first signs of the development of boils on the head appear, it is important to visit a doctor and begin treatment.
Treatment of a boil: Video
What to do when a boil appears on your head? Surgical, local drug treatment, and restorative therapy will be required. Treatment methods should be determined by a specialist after assessing the external condition of the boil, collecting anamnesis, and clarifying concomitant chronic diagnoses.
The choice of treatment method is influenced by:
- localization (the closer to the temple, the more dangerous);
- area of inflammation;
- the presence of necrotic lesions;
- general health of the patient;
- the presence of endocrine pathologies, especially aggravating the course of furunculosis, diabetes mellitus;
- the presence of other infectious diseases delays recovery (sore throat, acute respiratory infections, intestinal infections);
- pathologies of the immune system (HIV, secondary immunodeficiency).
We suggest you familiarize yourself with How to remove papillomas at home on the eyelid, neck, armpits, face, body, intimate places, folk remedies and medicines
Having specified all concomitant diseases and characteristics of the body, the doctor will prescribe general and local treatment. In case of severe, advanced suppuration or in the presence of complications, the doctor may resort to surgical intervention.
Conservative
An abscess on the head under the hair, if it has a small affected area, can be treated using conservative methods.
To quickly rid the patient of a boil on the scalp and prevent the spread of infection, the doctor prescribes vitamins and microelements. Complex multivitamins activate immune reactions and accelerate the process of tissue epithelization.
Local therapy consists of several stages:
- It is necessary to treat the surface of the boil and the skin around it. To do this, the hair is parted, the localization of the pathological process is wiped with a swab moistened with alcohol, furatsilin or another antiseptic.
- Lubricating the scalp where the boil is located with an antibacterial drug. This may be an ointment containing streptomycin, erythromycin, chloramphenicol, etc. Ichthyol ointment or Vishnevsky liniment is often used.
- After the boil has opened on its own, its surface is smeared with antiseptics, which have a drying effect. These include a 1% alcohol solution of brilliant green, a weak solution of salicylic acid.
- The use of healing ointments to accelerate regeneration. You can use Methyluracil, Solcoseryl.
To quickly rid the patient of a boil on the scalp and prevent the spread of infection, the doctor prescribes vitamins and microelements. Complex multivitamins activate immune reactions and accelerate the process of tissue epithelization. Tablets and powders based on brewer's yeast are often used to combat boils.
Operational
If the boil on the head continues to fester for more than five days, the doctor suspects complications, then surgical intervention will be required. Incision of the skin slightly below the center of the chirp will allow the purulent exudate to be quickly eliminated.
After promptly opening the abscess, the wound is washed with antiseptic solutions, then antibacterial ointments are applied, which will lead to the destruction of pathogenic microorganisms. The faster the inflammatory pathogens die, the sooner the healing process will begin.
In severe advanced cases of diffuse furunculosis, when pus spreads towards the brain, more serious surgery is required. The surgeon cleans the damaged surface as much as possible and leaves drainage for the outflow of pus. At the same time, he prescribes tableted antibiotics in large quantities.
Treatment at home can be carried out for small, local processes when the root of one hair on the head is inflamed.
Boils on the head are treated with natural antiseptics: onions, garlic. Mumiyo quickly heals and kills bacteria. It is applied to the center of the boil and secured on top with a gauze cloth. If this procedure is done at night, then by morning the inflammation will be significantly reduced.
In children, boils appear on the head under the hair quite often due to poor hygiene and hypothermia. Small ulcers on the head are not dangerous; they go away with minimal treatment. However, the child needs to be explained that he should not touch the inflamed area. If boils appear in several places on the scalp, you should immediately consult a specialist for treatment.
A feature of the course of furunculosis in children is frequent relapses. The children's immune system is not able to maintain the production of protective immunoglobulins for a long time. When pathogenic microbes enter the skin layers again, the skin’s own defense does not work and inflammation develops again. Another feature is that children's skin is thin and easily vulnerable.
It can be difficult to independently detect a boil on your head, since it is difficult to externally examine the lump on your head. Many people do not pay attention to the pain in their head. But you should immediately contact a dermatologist. He will diagnose the disease and carry out the necessary procedures and prescribe medicine.
Perhaps, for diagnosis, the doctor may need a general blood and urine test, data on the performance of the endocrine system and organs.
Today there are many ways to get rid of a boil, both at home and with medications. But complex treatment is considered the most effective; it includes the use of drugs of various forms and traditional methods. The doctor prescribes the medicine, and it is also necessary to agree with him on the traditional method used for therapy.
Surgical intervention will effectively and quickly remove the core and pus from the boil. After the procedure, Levomekol and Erythromycin ointments are prescribed.
During treatment, the following conditions must be observed:
- Following a diet that excludes fatty foods, spicy foods, and alcohol.
- Treatment of the affected area with an antiseptic. Alcohol, hydrogen peroxide, and furatsilin solution are excellent for this role. But iodine should not be used - it can cause skin burns and lead to complications. The skin must be treated beyond inflammation.
- The procedure that has a very effective effect on treatment is UV radiation therapy and laser radiation. These procedures accelerate skin regeneration.
- For chronic furunculosis, antibiotics and complex treatment are prescribed.
Depending on the stage of the disease, various treatment methods are used:
- For surgical intervention, first cut off the hair area around the boil, treat the skin with an antiseptic, and cool the affected area.
- The core and pus are removed from the source of the disease. Apply a bandage with salicylic acid.
- Antibiotics are prescribed to the patient.
- Ointments are prescribed to protect against infection.
There are many different ways to treat a boil on the head, forehead, or hair at home.
Traditional methods become most effective when used in conjunction with medications, since home remedies enhance their effect. Treatment must be comprehensive, and do not use folk recipes on their own. Before using "grandmother's" recipe, consult your doctor.
People use various forms of funds. Thus, dandelion will perfectly improve immune defense and metabolism, promoting healing. A tincture is made from the flower. This product can be used to treat healthy areas, thereby preventing the development of furunculosis.
Aloe is used in its pure form to treat boils. Its leaf is cut, washed, then cut lengthwise and the inside is applied to the boil and left for 3-4 hours. Aloe juice accelerates the process of boil ripening, it treats the skin, disinfects it, destroys germs and relieves pain.
At home, homemade ointments are prepared from laundry soap and baked onions. A paste is made from onions, grated soap is added, then applied to the affected area with a bandage. An ointment made from salt, honey, eggs and flour is also effective. Ointments accelerate the process of boil ripening.
To treat boils and furunculosis, doctors prescribe various forms of drugs.
For example, with furunculosis you cannot do without antibiotics, since the reappearance of boils is affected by immunity, metabolism and the functioning of internal organs. Antibiotics also prevent re-infection. Doctors prescribe antibiotics on their own, but often use Amoxlav and Cephalexin.
To accelerate maturation, use Tetracycline and Erythromycin ointments. They are applied to bandages. Even after the rod and pus have come out, the skin should be treated with these ointments.
Alcohol and hydrogen peroxide are used as an antiseptic to disinfect the skin.
Ointments are used to restore the skin - Heparin, Contractubex.
Boil therapy consists of a set of measures that help stop inflammatory processes. In some cases, surgery may be prescribed.
Conservative
The most effective drugs are antibacterial agents. The doctor prescribes a course of antibiotics lasting 4-5 days. Such medications reliably and painlessly eliminate inflammatory skin processes.
Auxiliary agents are antiseptics (hydrogen peroxide, brilliant green, miramistin, iodine). A solution of salicylic acid is used for drying. To speed up the breakthrough of the abscess, they practice applying ichthyol, Vishnevsky ointment.
After opening the boil, an antiseptic solution and healing ointments (methyluracil, Actovegin) are used.
We suggest you find out how long after antibiotics you can drink bifidobacteria
Operational
If the inflammation cannot “mature” on its own and release the rod, surgical intervention is required. The operation is simple and the patient does not require hospital treatment.
A boil on the head is a dangerous skin disease. The inflammatory process develops against the background of infection of the hair follicle and neighboring tissues. The pathological condition occurs due to the activity of Staphylococcus aureus. The infectious agent penetrates through small pores resulting from mechanical damage. At the first sign of a disorder on your head, seek help from a doctor.
The localization of boils in most cases concerns areas where hair is concentrated. The most common area is the back of the head. The rash occurs on the forearm, thighs and face. The development of a boil can lead to complications in the form of purulent structures on the facial veins. The inflammatory process can develop into cavernous gnat and purulent forms of meningitis.
Operational
Folk remedies and recipes
- To cleanse the scalp, wipe it with strawberry juice.
- Add 2 tablespoons of calendula tincture to a glass of water. Soak a cotton pad with the product and wipe the affected areas.
- Make a hair mask from 2 tablespoons of olive oil and lemon juice. Apply to the head and keep, wrapped in polyethylene, for 1 hour. Rinse off with warm water using shampoo.
- Pour 100 g of anise seed with water overnight. Grind the seeds and apply the resulting paste to your hair. Cover with film and leave for an hour. Rinse off with warm water. It is recommended to make this mask every other day for 2 weeks.
- Apply lotions from dandelion decoction to the affected areas.
- After each hair wash, rinse your hair with infusions of yarrow, chamomile, string, and sage herbs.
- You can prepare shampoo at home. Make a paste of 2 tablespoons of colorless henna and water. Beat 1 egg into it and mix thoroughly. Apply to hair, massaging skin. Rinse well with warm water.
Attention! Before using traditional methods of treatment, consultation with a dermatologist is required. You can also find out everything about acne on other parts of the body and methods of treating it on our website
For example, about acne on the back is written here, about a pimple on the lip in this article, about subcutaneous acne on this page, about acne on the forehead at this address, and here you can read about how to remove the redness of acne
You can also find out everything about acne on other parts of the body and methods of treating it on our website. For example, about acne on the back is written here, about a pimple on the lip in this article, about subcutaneous acne on this page, about acne on the forehead at this address, and here you can read about how to remove the redness of acne.