Causes
The occurrence of subcutaneous lipoma is influenced by the following factors:
- Neglect of hygiene rules increases the risk of a tumor if pimples and wounds on the surface of the skin were opened with dirty hands, which provokes infection under the skin. The infection causes subcutaneous inflammation and the formation of a lipomatous capsule with the help of sebaceous secretions.
- Heredity is considered a reason that increases the risk of pathology.
- The appearance of a tumor directly depends on a person’s lifestyle. The presence of junk food, alcohol and tobacco abuse in the diet disrupts fat metabolism and increases cholesterol levels, resulting in the appearance of fatty tumors.
- People suffering from obesity, diseases of the digestive system, the presence of waste and toxins in the body and slow metabolism are at risk for the formation of subcutaneous pathology.
Causes and dangers of breast lipoma
Hello, dear readers! Today we will talk about what a breast lipoma is, whether it is oncology and how dangerous the tumor is for the patient, if it is dangerous!
What is lipoma?
So, lipoma - what is it? This tumor (neoplasia) belongs to the category of oncological diseases. Can a formation such as a lipoma be cancer, patients with a similar diagnosis ask. In no case and does not even become one!
Lipoma is a benign connective tissue formation, originating from loose subcutaneous tissue.
Sometimes neoplasia penetrates between the muscles and bundles of blood vessels up to the periosteum, but more often it quietly “sits” in the adipose tissue and does not malignize (do not transform into a malignant formation).
It is extremely rare (in exceptional cases) that such neoplasia transforms into connective tissue cancer—liposarcoma.
The word “lipoma” comes from the Latin word for “fat”, so in everyday life it is often called a wen or a fatty tumor. The disease can be independent or a manifestation of lipomatosis (multifocal damage to the body by similar tumors). The ICD 10 code classifies the disease as section D-17. About 10% of detected breast tumors are lipomas.
Who is diagnosed with pathology?
These neoplasms are most often diagnosed in women in the premenopausal period, at the time of the onset of involution of the mammary glands (age 40 years and older). At this age, fibrous tissue most often predominates in the tumor.
If neoplasia is diagnosed in women of childbearing age, the cytological picture is more diverse (fat cells, mucus or connective tissue predominate).
The disease is diagnosed not only in women, but also in men (yes, the stronger sex also has a mammary gland, and there may be diseases of this organ).
What about the children, you ask. Unfortunately, this disease does not bypass this category of the population either. Lipomas can be diagnosed in children and adolescents. Most often these are girls under 14 years old. In this case, consultation with a mammologist is mandatory!
Signs of illness
There are no subjective symptoms of tumor appearance. Most often these are small formations up to 2 centimeters. Rarely, formations grow up to 10 centimeters in diameter.
During palpation examination, neoplasia is detected in the form of a neoplasm:
- elastic;
- elastic;
- round;
- with clear boundaries;
- not fused with surrounding tissues, but inactive.
The tumor is painless and is usually detected by chance during a routine examination, ultrasound, or mammography.
What does such a neoplasm look like?
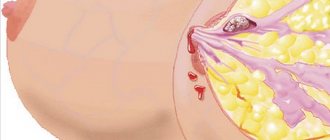
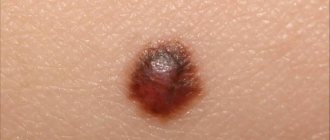
Any woman should know what a lipoma looks like. If this is a superficial (subcutaneous) formation, you can easily see and feel a slightly protruding “bump”, elastic and elastic. If the neoplasia is located deep in the tissue, you will not see it at all. This can be done by a doctor during examination using hardware diagnostics.
On an ultrasound, the doctor sees a hyperechoic (light gray) formation in the glandular tissues with clear boundaries. CT scan shows homogeneous (homogeneous) structures with clear contours. The tissue density corresponds to fat.
An X-ray image shows the lipoma on the contrary as a lighter formation than the surrounding tissue. See a comparison of the signs of the appearance of one of the types of lipomas on an ultrasound and on a mammography image (picture below).
If the tumor was large (a giant wen weighing about half a kilogram and measuring about 5-12 centimeters) and it was removed, it will look something like this:
Classification of lipomas
The tumor is classified according to the number of formations in the breast (single and multiple), according to the shape and structure of neoplasia, forms of the disease are distinguished:
- nodular (focal formation);
- diffuse.
A nodular fatty tumor is a rounded formation, clearly limited by a capsule, which, when removed along with the capsule, looks like a ball filled with fat.
A fatty tumor in a diffuse form grows through the capsule and loses its clear rounded outline.
According to the location of the formation, it is customary to distinguish:
- intramammary formations, defined against the background of glandular tissue (growing between the lobules of the mammary gland);
- subcutaneous, not affecting the parenchyma of the organ;
- deep tumors localized behind the mammary glands.
Typically, such neoplasias develop in one gland. If your right breast tissue is affected, it does not mean you will ever have problems with your left breast.
According to the cytological picture, there are several types of lipomas:
- fibrolipoma;
- myolipoma;
- myxolipoma;
- angiolipoma;
- lipofibroma;
- adenolipoma;
- hemartoma (fibroadenolipoma);
- classic lipoma or wen, represented exclusively by adipocytes (adipose tissue cells).
In the first case, fibrous cells predominate in the tumor tissues (this type of tumor is found in older patients). In the second, the neoplasm contains a combination of adipose tissue and muscle fibers. In the third, the tumor is a combination of fat and mucus.
An angiolipoma is a tumor in which vascular network cells are found in the biopsy specimen. It is believed that such a formation is literally entangled in a network of capillaries. Lipofibromas are neoplasias composed primarily of adipose tissue with a small amount of fibrous tissue.
Adenolipoma is a formation consisting of glandular epithelial cells and adipose tissue. There are also combinations of the neoplasias described above (hemartoma).
Causes of the disease
Discussions in the medical community about the causes of the disease continue. The formation of tumors from adipose tissue is considered a multicausal process. There are 4 main theories put forward:
- Metabolic.
- Genetic.
- Hormonal.
- Exogenous or regulatory.
Metabolic, attributes the leading role in the development of the disease to the accumulation of low-density lipoproteins in tissues. These substances diffuse poorly through the walls of blood vessels, accumulate in the intercellular space and become covered with a connective tissue capsule.
Genetic focuses on the defect of a specific gene leading to hereditary lipomatosis.
Hormonal - highlights hormonal changes in the body (this explains the growth of tumors in teenage girls and women around 45 years old). Failure in the development or involution of the gland leads to the formation of neoplasia.
The regulatory theory states that adipocytes are distributed in tissues according to a specific program regulated by the internal mechanisms of the body. If the mechanism fails, adipocytes accumulate in one place and become overgrown with a fibrous capsule.
Factors contributing to the growth of wen and combined formations include:
- wearing tight underwear;
- bust bruises;
- breast plastic surgery
Some authors even believe that neglect of hygiene requirements leads to disruption of sebum (sebum) and indirectly stimulates the formation of adipose tissue tumors. Most likely, the causes of the disease are a complex of several factors that negatively affect the mammary gland.
Diagnostics
Since neoplasia is not accompanied by characteristic symptoms, non-invasive hardware and cytological diagnostics are of primary importance:
- The ultrasound examination protocol describes iso- or hyperechoic formations in the bust area. Increased echogenicity is an echo sign indicating the predominance of fibrous cells.
- An x-ray or mammography presents this tumor as an x-ray transparent (light, light gray) formation. The capsule of the lipoma is radio-opaque (clearly visible, the outline is darker than the tumor). X-ray does not make it possible to identify diffuse growths, since there is no clearly visualized capsule.
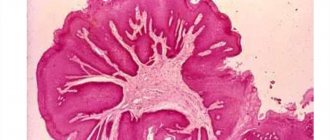
- The biopsy is most often taken by aspiration. Cytology (the study of cells) provides the most reliable information about the structure of the tumor. This method is used to verify (confirm) the diagnosis.
If necessary, the doctor may prescribe a CT or MRI of the bust and a blood test to determine CA-15-3 glycoproteins. These are tumor markers. A breast oncologist is often involved in making a diagnosis.
There is no need to be afraid of this. The doctor will examine you to distinguish a lipoma from other breast tumors, primarily mastopathy, fibroadenoma, liposarcoma or bust involution.
The described neoplasms are usually not confused with papillomas.
Treatment
Treatment methods depend on the size and type of tumor. If you have a small tumor of 1-5 mm, your doctor recommends monitoring over time. Unfortunately, conservative therapy, including treatment with folk remedies, is not effective for wen. These tumors are either removed or observed.
They are removed in several cases:
- if you are planning a pregnancy;
- the wen has formed under the skin and disfigures the appearance, causing psychological discomfort;
- the tumor has reached a large size and compresses the gland, causing pain and causing necrosis;
- the tumor grows rapidly (high risk of malignancy);
- signs of liposarcoma appeared.
What to do if you are pregnant and have a tumor? Listen to your doctor's advice. Most likely, you will only be recommended observation. Removal is required if the neoplasia is painful and growing rapidly. Outside of pregnancy, the tumor can be removed at the patient's request.
Nodular neoplasms are enucleated along with the capsule. The operation is called “enucleation” and is performed for the nodular form of the tumor.
With the growth of “pure” lipomas, aspiration of fat from the neoplasm is possible. The advantages of the procedure are the absence of a scar after surgery, the disadvantage is the inability to remove the fibrous capsule and the risk of relapse.
If a diffuse tumor has formed in the gland, doctors recommend resection (removal) of the affected sector with a section of healthy tissue.
For small neoplasia, minimally invasive procedures (cryosurgery, laser correction, radio wave therapy) can be offered.
Recommendations after surgery are general: harmonious nutrition, moderate physical activity, exclusion of injuries and other factors that provoke neogenesis (growth of new formations), including rational use of OCs (contraceptives in tablets).
Source: https://krasivayagrud.ru/zabolevaniya-grudi/lipoma-molochnoy-zhelezi.html
Types of lipoma by location of origin
Soft tissue lipoma most often forms under the layer of skin. Growing to a substantial size, the pathology penetrates through the epithelial layers of the skin to muscle tissue and bones. There are different types of wen depending on the location.
- A lump on the face and forehead is no different from a common skin defect - a pimple. Squeezing out the sebaceous fluid does not bring favorable results, and the wen appears again, accompanied by an inflammatory process and painful sensations, since the capsule remains inside. Increasing in size, the tumor becomes soft and mobile, which helps to distinguish a lipoma from a boil or other skin defect. Facial lipomatosis looks unsightly.
- A lump on the back does not show painful or external symptoms and grows slowly. The skin of the back is susceptible to the occurrence of such pathologies due to the active work of the sebaceous glands. Growing in diameter, the subcutaneous tubercle puts pressure on the nerve endings, causing pain, and first appears at a late stage of development. A giant lipoma must be surgically removed and causes discomfort to the patient.
- The tumor-like formation on the head, neck and shoulder is spherical in shape and occurs mainly in women over 50 years of age. The presence of pathology is accompanied by apathy, drowsiness and loss of appetite. Pain when pressing, fluid discharge and discoloration of the lipoma cause surgical intervention. The causes of lipomatosis of the head include the onset of menopause, physical trauma to the skull area, hypothermia, burns and diseases of the reproductive system.
- Wen on the leg, arm, forearm and thigh is prone to rapid progression and frequent inflammation that occurs due to friction and compression from shoes and clothing. Physical activity, physical and chemical exposure are the root causes of the appearance of tumors on human limbs. Multiple lipomatous growths rarely form on the legs.
READ ALSO: Clean line perfect skin price from 83 rubles, Clean line perfect skin buy in Moscow, instructions for use, analogues, reviews
- Lipomatosis of the trunk involves the formation of subcutaneous growths in the abdomen, back and armpits. One lipomatous cell is enough to trigger the onset of the disease.
- Pathology of the oral cavity is a rare disease that reaches a maximum of three centimeters in diameter and has a yellow tint. The growths occur on the roof of the mouth, the inside of the cheek, and the outside of the mouth. At the initial stage, the growth does not hurt and does not cause discomfort to the patient.
- Fibrous lipoma is distinguished by the presence of connective tissue in its composition. It can form on the skin of any part of the body.
Wen in the breast and nipple area: causes and treatment
Breast lipoma is a benign tumor consisting of adipose tissue. This disease is quite common, and lipoma can also occur in other parts of the human body. According to statistical studies, about 10% of all nodular formations in the female breast are lipomas.
Features of lipoma
A lipoma in the mammary gland is located in a capsule and is mobile when palpated.
A lipoma in the mammary gland usually has a nodular shape (round, oval). It is soft to the touch, but as the volume increases it can become denser. The neoplasm is located in a capsule that is not fused to the skin and other tissues, and therefore is relatively mobile. There is also a diffuse type of disease - in this case, the adipose tissue does not have a clear shape, it grows without a capsule. Sometimes a wen also appears on the nipple, or on both nipples symmetrically.
By the time it is detected, the lipoma is usually about 1–2 cm in size. Over time, it gradually grows and becomes more noticeable. Sometimes the tumor reaches 10 cm. Then one breast looks larger than the other and provokes the appearance of complexes in a woman regarding aesthetic attractiveness. Lipoma does not stop accumulating fat even when the body is exhausted. Therefore, it is impossible to get rid of the bump by losing a lot of weight.
Causes of lipoma
Most often, a lipoma under the breast is formed not in the mammary gland itself, but in the fatty tissues. The causes of this disease can be very diverse:
- disturbance of metabolic processes in the body (fat and protein);
- blockage of the sebaceous glands;
- long-term use of contraceptives;
- slagging of the body as a whole;
- disruption of lymph flow due to a sedentary lifestyle;
- hormonal changes in the body;
- frequent stress;
- numerous pregnancies that provoke stretching in the chest area;
- hereditary predisposition;
- wearing uncomfortable underwear;
- chest injuries;
- environmental influence.
An unbalanced diet and the presence of bad habits (smoking, alcohol and drug abuse) aggravate the situation and are an additional risk factor.
Breast lipomatosis can appear at any age, but women aged 40–50 years are most susceptible to it. If the disease is diagnosed in a young girl, this in most cases indicates the presence of a hereditary factor.
Symptoms of lipoma development
The nodule itself is usually not painful, but squeezing it may be accompanied by minor pain.
Symptoms of a breast lipoma may be as follows: a dense, sedentary neoplasm protrudes above the skin. It doesn’t hurt and doesn’t “squelch” when pressed. You may feel discomfort when performing certain movements and while wearing underwear.
Many people are interested in whether a breast lipoma can be cancer. Under certain circumstances, this option is possible. In particular, the transformation is promoted by friction of underwear and contact with direct sunlight (tanning). In this case, they talk about the development of liposarcoma. Most often, such degeneration of a neoplasm (malignancy) occurs in the premenopausal period, against the background of hormonal changes.
If there is degeneration of a wen in the mammary gland, the symptoms may be as follows:
- there is pain;
- discharge appears from the chest;
- there is rapid growth of the wen.
If you have the slightest doubt about your health, you should immediately visit a doctor.
We recommend reading the article about inflammatory elements, acne in the décolleté and neck area. From this article you will learn the reasons why rashes may occur, the principles of diagnosis, treatment and prevention of rashes in the chest area.
Types of lipoma
The lump in the breast most often has a dough-like soft consistency. There are several types of lipoma:
- myolipoma (smooth muscle fibers predominate);
- myelolipoma (a rare type, adipose tissue is mixed with hematopoietic tissue);
- myxolipoma (mucilage of adipose tissue is observed);
- lipofibroma of the mammary gland (predominantly adipose tissue and a small amount of connective tissue);
- fibrolipoma (connective tissue predominates);
- angiolipoma (a large number of blood vessels are noted).
Breast fibrolipoma is one of the types of wen. In this case, the internal contents of the capsule are transformed into fibrin fibers of connective tissue. The course of the disease is complicated by a high risk of calcification in tumor cells (deposition of calcium salts occurs). With this type of lipoma, a woman may experience not only discomfort, but also pain. This occurs because the wen compresses the nerve endings.
Treatment of breast fibrolipoma does not differ from methods of elimination in the presence of other types of this disease.
How is the diagnosis confirmed?
Ultrasound and mammography methods confirm the diagnosis of breast lipoma.
If the wen is located deep in the tissues, it may be invisible. Even a mammologist does not always detect a lump upon palpation. Therefore, it is important to periodically do breast ultrasound and mammography.
The final diagnosis is established based on:
Once a breast lipoma is detected, a decision is made on treatment methods. In this case, the size of the tumor and the woman’s well-being are taken into account.
Effective ways to treat breast lipoma
Any treatment must be agreed with a doctor. You should not take any measures to eliminate the wen on your own.
Modern methods of lipoma removal
If the lump in the mammary gland does not increase in size, a decision may be made to simply observe the growth. However, treatment for breast lipoma often involves removing the lump. The most painless and non-traumatic method is radio wave destruction of cells using a laser. However, this procedure is not performed in public clinics.
Another option for low-traumatic removal of a wen is the introduction of drugs into the affected tissues that dissolve the neoplasm. The course of treatment lasts about a month (with breaks).
Surgical method and its varieties
The optimal method for treating breast wen is surgical.
Indications for surgical intervention may include:
- the presence of painful sensations;
- increase in size of the wen on the chest;
- presence of a cosmetic defect;
- impaired breast functionality.
As for surgical intervention, it can be carried out using different methods. In order to preserve the aesthetic appeal of the breast, a gentle method of exposure is used: puncture-aspiral. The contents of the wen are pumped out through a needle, while the capsule itself remains inside. This is a significant drawback of the method that must be taken into account (there is a risk of relapse).
Many doctors tend to believe that the optimal way to remove a lipoma is to excise it with a scalpel. In this case, the tumor is removed completely (in the capsule), which prevents the development of relapse.
Of course, the operation will leave the patient with a small scar.
If the lipoma is small in size and located in an accessible location, the operation is performed under local anesthesia. The patient is observed after the procedure for several hours and can return home. In case of complex localization and large size of the wen, hospitalization is necessary; the operation is performed under general anesthesia.
In the postoperative period, the patient is prescribed complex treatment: antibiotics, antiseptics, vitamins and immunomodulatory drugs.
ethnoscience
Many women are afraid to use radical methods of eliminating wen and are looking for alternative options. What herb will help resolve breast lipoma? This question probably worries every patient who has encountered this problem. However, treatment of breast lipoma with folk remedies and medications is not recommended due to the lack of a positive result.
What traditional healers don’t come up with:
- compresses from golden mustache, coltsfoot, aloe, onion;
- rubbing in melted lard;
- cauterization with oil;
- eating cinnamon;
- applying egg film to the wen, etc.
All these procedures do not give the desired result. A woman is simply wasting her time and risking her health.
Prevention of disease relapse
After removal of a lipoma, it is important to take measures to prevent the recurrence of a wen on a woman’s sternum. Since no one can definitely say what triggered the initial appearance of lipoma, therefore there are no clear recommendations regarding prevention. Many doctors agree that it is necessary to adhere to a healthy lifestyle and set yourself up for a positive development of the situation. Every woman can do the following.
- Adjust your diet. Introduce a large amount of vegetables, fruits, lean meat and fish. Eliminate or reduce the consumption of fatty, starchy foods and sweets. Limit the amount of salt.
- Drink a lot of water (at least 1.5 liters per day).
- Lose weight (if obese). This will help the body become stronger.
- Monitor blood pressure readings (do not allow it to increase).
- Be regularly examined by a mammologist or gynecologist.
- Get rid of bad habits (smoking, frequent drinking in large quantities).
- Wear comfortable underwear that does not restrict movement.
Taking vitamins, proper sleep, an optimal work and rest schedule - all this will help the body to be strong in order to prevent a relapse.
Doctors say that breast lipoma rarely develops into a malignant neoplasm. However, such a possibility cannot be excluded. Therefore, if you detect the slightest changes in the mammary gland, you must consult a specialist and undergo a thorough examination. Regular assessment of the dynamics of the disease through ultrasound, mammography, and tests will help prevent unwanted complications.
grudinfo.ru
Localization of internal lipomatosis
- Most often, a woman who has reached 40 years of age can detect a round nodule inside the mammary gland that does not cause pain or discomfort. A mammologist is able to correctly diagnose breast pathology using palpation, X-ray examinations and biopsy. Breast lipoma is soft to the touch and is capable of moving in the subcutaneous layers. Fibrolipoma is a single formation, consisting of connective and cartilaginous tissue, found in the chest area and has similarities in symptoms to lipoma. Occurs in women who have entered the postmenopausal period. The symptoms of the disease are similar to those of lipomatosis. Solid growths are removed through surgery if they increase in size, and a small tumor requires supervision by the attending physician. As a result of ignoring, the disease can develop into a malignant form.
- Brain lipoma is a rare disease located in the frontal cortex. The pathology does not develop into a cancerous form. A person cannot identify a tumor on his own - this is possible with the help of computed tomography, x-rays and neurosonography. Mental tension, stress, heredity and head injuries become the causes of wen. The described brain pathology is dangerous because it contributes to the development of mental disorders, impairs the quality of sleep and causes headaches, weakness, apathy and depression. Treatment of a brain tumor includes surgery, minimally invasive therapy, puncture and ultrasound.
- The abdominal fat is dangerous because it puts pressure on the internal organs, interfering with the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. In the presence of internal wen, the kidneys, liver, pancreas and intestines are affected. Multiple tumors growing inside the abdominal cavity are extremely rare. A lump on the anterior abdominal wall cannot be diagnosed at an early stage by palpation, and the patient seeks help if it grows significantly. A diagnosis is possible after undergoing a series of diagnostic measures. Palpation can be used to detect if the size of the growth increases. Effective methods are ultrasound and computed tomography.
- The mediastinum is located in the region of the heart, lungs and aorta. To detect a tumor, it is advisable to undergo a profile examination annually. The fatty tissue appears at a late stage and is accompanied by shortness of breath, fever, arrhythmia, pain in the chest cavity and tachycardia.
- Lipoma of the cardiophrenic angle occurs in the preperitoneal region, mainly in women over 50 years of age.
Lipoma in the breast area: causes of appearance and difference from malignant tumors
Home-Wen (lipoma)
A lump on the chest is a subcutaneous benign nodular formation. Appears by the same mechanisms as in other parts of the body. The seal does not cause any discomfort other than aesthetic.
Causes and symptoms of the appearance of wen on the chest
A mass in the chest area does not pose a health hazard in the absence of provoking factors. A cluster of lipid cells forms a tubercle that rises on the surface of the skin, which is easy to notice or feel during examination.
It is much more difficult if the wen has formed in vascular or muscle tissue; it is almost impossible to detect it in the early stages. To determine this, you will need to undergo a comprehensive examination to identify the true causes. Prerequisites that cause the appearance of a lump on the chest:
- Hormonal imbalances. Women at risk include women during pregnancy, menopause, taking hormonal contraceptives and with disrupted menstrual cycles.
- Exchange disorders.
- A sedentary lifestyle that causes physical inactivity.
- Injury to the mammary gland.
- Inadequate underwear that rubs and compresses the chest area.
- Disturbances in the circulatory system and lymph flow.
- Blockage of the sweat gland.
You can understand that it is a lipoma on the chest by the symptoms that characterize fat formation:
- a bump rises on the surface of the skin;
- does not cause pain when palpated;
- soft seal that is easily pressed into the skin.
Fatty deposits never appear on the nipple circumference because there is no lipid tissue in the pigmented area.
If the formation is large, you may feel pain and compress the vessels and tissues nearby. In addition to painful sensations, there is a need for surgical intervention to get rid of the tumor that spoils the symmetrical shape of the breast.
How to distinguish a lipoma on the sternum from other dangerous formations
You can determine whether a benign lump is on your own based on its appearance, but to be sure, it is recommended to visit a mammologist. Characteristic signs of a breast wen that is not dangerous:
- Diameter no more than 1 centimeter.
- It rises like a mound above the surface of the skin or can be felt when pressed.
- The skin at the top of the tubercle is flesh-colored.
- It has a round or oval shape.
- The seal is soft and mobile, surrounded by a capsule.
- Does not cause inconvenience, does not hurt, does not itch, does not squeeze out.
Growth can be caused by a tight bra or the effect of ultraviolet radiation on the breasts during sunbathing or visiting a solarium. Radiation and injury have a negative effect.
Need advice from an experienced doctor? Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
As a result of the development of the disease, the wen begins to quickly increase in size, the skin acquires a white or yellow tint, and becomes tense.
Pain on touch and movement. These are the first warning signs that should not be ignored. Hurry to the clinic for help from specialists.
A lump-like formation on the nipple or areola needs to be examined by a dermatologist. This is a sign of another growth.
Localization Features
A wen can pop out on the right or left side of the chest, armpit and mammary gland. In most cases, the lump forms in women after forty years, but men, adolescents and children are affected by the disease. This is due to the presence of adipose tissue in the chest area in all patients without exception.
If the formations do not bother you, but to calm your conscience, it is recommended to contact a mammologist. He will make an accurate diagnosis, give a prognosis and possibly prescribe effective treatment.
Methods for safely getting rid of wen around the nipples
Before starting treatment, it is important to undergo an examination to identify the causes of the formation on the chest, its nature and shape. During the diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe a number of tests and additional studies:
- A biopsy of the contents of the wen will help identify the nature of the formation and eliminate the risk of cancer.
- Ultrasound and mammography make it possible to detect the location of the formation of the compaction, determine exactly its shape and size, and the presence of complications.
- MRI - prescribed after a biopsy confirming the malignancy of the tumor. During the examination, the doctor sees the full picture of what is happening around and in the middle of the wen, the presence of metastases.
The doctor examines the test data and makes a diagnosis.
In most cases, surgery is prescribed. Based on the overall picture, the specialist selects the most suitable method of getting rid of the problem on the chest. Several methods are used in medical practice:
- Surgery is indicated if the formation is large, has signs of malignancy and puts pressure on blood vessels and tissues. The operation takes place under anesthesia, during which the surgeon removes the seal along with the capsule. The effectiveness of the operation is justified; it is possible to completely remove the tumor and eliminate recurrence.
- Laser and radio wave therapy is used in cases where the formations are benign and small in size. The defect is eliminated with a beam that does not leave scars and reduces the likelihood of relapse.
- The operation is performed under local anesthesia using a needle that sucks out the wen or injects a special medicine that promotes resorption. The puncture is used after confirmation of benignity and only with small growths on the chest, but there remains a high percentage of the likelihood of reappearance. This is due to the fact that during the process of inserting the needle, only the contents are sucked out, and the capsule remains in place and, over time, is filled with fat cells again.
Getting rid of it with folk remedies and medications is ineffective; there is a high risk of re-formation of breast wen, and in some cases even growth throughout the body. The traditional method is dangerous due to the development of an allergic reaction and consequences that will have to be treated in a hospital.
Can a harmless lipoma turn into a malignant tumor?
The form of the disease is determined by its content. Timely visit to the clinic and diagnosis of the nature of the wen reduces the risk of developing cancer. Ignoring the problem can lead to life-threatening consequences.
It is impossible to insure against the formation of breast wen, but it is possible to reduce the possibility of occurrence by leading a healthy lifestyle. Keep your skin clean, promptly respond to any rashes and formations, and do not delay treatment.
The article has been reviewed by the site editors Link to the main publication
Didn't find suitable advice?
doctor or see all questions...
Article rating:
vashaderma.ru
Lipoma symptoms
Signs of lipomatosis:
- the presence of a round movable tubercle under the skin;
- painlessness;
- absence of symptoms at an early stage of development;
- the presence of pain if the pathology affects nerve endings;
- internal tumor puts pressure on any nearby organ;
- loss of fat mass and simultaneous increase in pathology;
- stretching of the skin at the site of localization;
- slower cellular regeneration and obvious pallor of the skin;
- weakness, apathy, sleep disturbance and headaches due to a brain tumor;
- increased blood pressure;
- heartburn, belching and vomiting with internal abdominal lipoma;
- decreased muscle contractility due to heart pathology;
- pressure on the airways and the larynx with cervical lipomatosis.
READ ALSO: Types of rash: photo and description, rash in a child on the arms, legs, body, legs
Symptoms
Wen on a woman's sternum develops very slowly and therefore may not show any symptomatic signs. This formation is usually discovered during routine examinations or during independent palpation of the breast.
At a time when tumor growth increases and a lump develops in the mammary gland, symptoms can be detected simply by looking at the breast. A change in the color of the skin above the surface of the tumor is visually detected; when palpated, the tumor is dense and motionless, and may cause some inconvenience.
The favorite localization of lipoma is the upper and lower part of the mammary gland, sometimes a wen develops on the nipple. The first symptomatic manifestations are observed when the tumor reaches a large size.
As the growth of the tumor progresses, the following signs appear:
- pain, which is characterized by a bursting sensation;
- pain when pressing on the pathological focus;
- change in the appearance of the affected breast.
In the case of malignant degeneration of the tumor, metastasis occurs to the regional lymph nodes, which is manifested by their enlargement and pain, and the woman’s general condition suffers.
Difference between lipoma and atheroma
Externally, lipoma and atheroma are no different from each other, and the patient can easily confuse them. Lipoma differs from atheroma in its internal contents, and the difference is detected upon examination by a doctor. The structure of the pathologies is different: lipoma does not have a capsule and is capable of movement, and atheroma is a capsule, most often occurring in the hairline area.
Atheroma is a congenital tumor, but a wen is not. There are differences in the size of the pathologies: the wen reaches 20 centimeters, and the atheroma reaches a maximum of three centimeters. On the surface of the atheroma you can see a small hole through which the contents of the tumor exit. Most often, an infection gets through it, causing inflammation and suppuration of the skin growth. The inflammatory process of atheroma requires urgent surgery. Unlike atheroma, lipoma has a smooth surface, is not connected by a duct to the external environment and eliminates the possibility of swelling and infection. Lipoma secretions do not come out. You should contact a professional dermatologist who can easily distinguish between the types of pathologies.
Complications and danger of the disease
Lipoma in the breast of women is dangerous because its enlargement leads to compression of the thoracic ducts and their subsequent deformation.
If a lipoma in a woman’s breast is large, then it becomes dangerous. The fact is that such a neoplasm leads to deformation of the excretory ducts of the gland and violates the structural integrity of the surrounding tissues.
The most dangerous complication is the risk of developing a malignant tumor, which can lead to death.
Many people are interested in the question of whether a breast lipoma can be cancer. Yes, such a development of events is not excluded. If the wen reaches a large size, then it can degenerate into a malignant tumor - liposarcoma.
Lipoma in children
Despite the fact that lipomatosis occurs more often in older people, repeated cases of this pathology in infants have been recorded in medicine. The tumor in a child can be congenital, and also occurs as a result of a violation of fat metabolism. In adults and in infants, the symptoms of the disease are the same.
The internal location of the tumor is rare: growths occur in the lumbar region, on the extremities, in the chest and abdomen. The area where pathology occurs is the preperitoneal cavity. A fatty tumor in an infant can reach ten centimeters. Cases of malignant tumors in newborns – liposarcomas – have also been recorded. Treatment of malignant pathology is carried out surgically and medicinally.
Breast lipoma in women
Causes of formation of lipomas Types of lipomas Symptoms Diagnosis of lipomas Treatment Prognosis of the disease
A benign neoplasm from breast fatty tissue is called mammary lipoma. You can find synonyms - fatty tumor, wen.
Lipomas account for about 10% of all breast tumors. Its appearance is possible at any age, but more often in women over 40, which is associated with involutive changes in their body.
Reasons for the formation of lipomas
Fatty neoplasias have a polyetiological nature of development. It is often difficult to identify a single mechanism. For convenience, mammologists systematize the reasons into several groups:
- Hormonal. During the premenopausal stage, a woman undergoes hormonal changes. Her body performed the function of conception, birth and feeding of offspring. Now the ovaries are shrinking, the endometrium of the uterus is thinning, and the glandular structure of the breast is changing to fatty. If the restructuring is disrupted, a chaotic accumulation of fat cells is possible, from which a lipoma is formed.
Neoplasms in women of reproductive age can occur against the background of prolonged, uncontrolled use of oral contraception or HRT (hormone replacement therapy), or menstrual irregularities.
- Genetic, hereditary. There are systemic diseases - lipomatosis, in which the formation of pathological foci occurs in various organs, including the breast. The development of pathology is associated with a defect in the HMG IC gene.
- Metabolic disorders, in particular fat metabolism. Some of the fat fractions, low-density lipoproteins, accumulate in tissues and are eventually covered with a connective tissue capsule. Defects in lipid metabolism are provoked by an incorrect diet with an excess of animal products, a sedentary lifestyle, and concomitant endocrine diseases.
- External reasons. This category includes factors of mechanical action on the chest: injuries, operations, inconveniently selected underwear. An unhealthy lifestyle (smoking, frequent stress, alcohol abuse), radioactive radiation also adversely affects the general condition of the body.
The combination of several of these causes stimulates excessive division of lipid cells in limited areas. The conglomerate becomes encapsulated over time and separates from healthy tissue.
Despite the limited nature of the process, many are concerned about the dangers of breast lipoma. Mammologists do not exclude the possibility of transformation of a benign tumor into liposarcoma.
Particular oncological alertness concerns patients with risk factors:
- cases of breast cancer (BC) in the family;
- oncology of other systems in this patient.
Kinds
Lipomas are classified according to several criteria.
By localization:
- Subcutaneous - the formation is located between the dermis and glandular tissue.
- Intramammary - the tumor is located between the milk lobules.
- Deep - formed in the thickness of the gland, closer to the chest.
By degree of distribution:
- Nodular - a clearly demarcated formation.
- Diffuse - with germination into other layers.
According to morphological structure:
- The classic form - the tumor is represented only by adipose tissue.
- Lipofibroma is a combination of connective tissue and fatty structures with a predominance of the latter.
- Fibrolipoma – represented predominantly by a connective tissue structure with small lipid areas.
- Myolipoma is a fatty tumor with penetration into smooth muscle fibers.
- Myxolipoma - formation cells produce a pathological mucous secretion inside the capsule.
The last 2 species are much less common than the others. In menopausal women, wen with a fibrous component is more often diagnosed.
Diagnosis of lipoma
There are no typical signs of breast lipoma. It is important to differentiate the neoplasm from other benign tumors and breast cancer.
Patient examination algorithm:
- Consultation with a mammologist, and, if necessary, related specialists (gynecologist, endocrinologist, oncologist).
- Donation of blood tumor marker CA 15-3 to exclude breast cancer.
- Biochemical blood test. Panel of hormones of the reproductive system, thyroid gland.
- Ultrasound of the breast.
- Mammography is an x-ray of the breast. The nodal form is visualized well. The method is not informative if the growth pattern is diffuse; it is technically impossible to carry out with a small size of the gland.
- CT, MRI according to indications. Tomography determines the exact location and blood flow characteristics of the lipoma.
- Biopsy. The procedure for collecting a tissue sample is carried out using a long needle puncture. The cellular structure of the biopsy specimen is studied. A biopsy is required to confirm the benign nature of neoplasia and determine its type.
Diagnosis and treatment of lipomatous formations
Timely diagnosis can make further treatment quick and painless. It is possible to identify a lipomatous phenomenon in the early stages of development during a profile examination. It is impossible to make a diagnosis on your own, as there is a risk of confusing a wen with a malignant tumor, atheroma, boil or liposarcoma. The palpation method is not reliable in medical practice. To make a correct diagnosis, the patient should undergo an X-ray examination, an ultrasound scan of internal organs, magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography and a biopsy to clarify the nature of the tumor and make a final diagnosis. After diagnosis, the doctor prescribes medication or removal of the wen.
Course of drug treatment
The doctor's further actions depend on the size and type of lipoma. The course of drug treatment includes absorbable drugs, vitamins, hormonal drugs, anti-inflammatory drugs and ointment treatment. Small single wen can be treated with medication. If multiple lipomatosis occurs, large wen should be removed surgically. It is not advisable to treat a tumor exclusively with medication; the use of unconventional methods should be added to the course.
READ ALSO: Caring for problem skin: fighting pimples and acne - online store of natural products 4fresh
Treatment of wen with traditional methods
Celandine, aloe juice, burdock root, potato juice, millennial, onion, honey and Kalanchoe have healing properties in the fight against wen. The herbal decoction should be consumed orally. For better effectiveness, it is advisable to regularly make compresses from honey and pepper, golden mustache, watercress and salt with sour cream.
Despite the confidence of healers in traditional methods of getting rid of tumors, medication and surgical intervention should not be neglected. Doctors are skeptical about this method and at the first signs of lipomatosis recommend seeking medical help. Wen does not go away as a result of using folk remedies. Cases of deterioration of the condition and excitation of inflammatory processes of the tumor after the use of such therapy have been recorded! The consequences of ignoring medical recommendations can be dire.
Methods for removing a bodily defect
Often, removal is the only way to get rid of the tumor.
Cosmetologists actively use the ozone method in the fight against skin defects. From ozone therapy, subcutaneous swelling, scars, scars and burns resolve within five minutes.
A painful tumor with various inflammations in the localized area is subject to surgical intervention.
How to treat?
Treatment of breast lipomas in men and women is determined by multiple criteria. Single small neoplasms without characteristic symptoms and risk of complications are left under observation or drug treatment is prescribed.
Suitable for local processing:
- Ichthyol liniment,
- Vishnevsky ointment,
- "Vietnamese Star".
These agents have an antiseptic and absorbable effect and can “pull out” the contents of the tumor, leading to its spontaneous opening.
Conservative treatment is symptomatic, and in the absence of therapeutic results, elective surgery is prescribed.
Surgical intervention
Despite the unanimous opinion of oncologists about the removal of even minor tumors on the body and internal organs of any nature, surgeons often resort to wait-and-see tactics.
Indications for surgical intervention are:
- Fast growth;
- Inflammatory process;
- Formation of new knobby lesions in a short period of time;
- Foci of necrosis.
Often the indication for removal is the patient’s desire to get rid of an aesthetic defect that worsens the quality of life. In women, the tumor is often injured by friction against underwear or bra wires.
There are several removal methods:
- Scalpel removal . Despite the traumatic method of removal, it is widely used in modern surgery. Firstly, opening the lipoma allows you to remove it within healthy tissue along with the capsule. Secondly, the contents of the lipomatous lesion are preserved, which allows for further laboratory examination. All this eliminates the risk of relapse. The disadvantage is a cosmetic defect after suturing.
- Laser removal . The method allows you to remove the tumor without scars and secondary infectious complications. Under the influence of a precise laser beam, the wen is evaporated and completely destroyed.
- Radio wave exposure . The method involves the destructive effect of a radioknife on a fatty tumor. Radio waves destroy fatty tissue, eliminating the risk of bleeding and post-operative scars.
- Needle aspiration . Removal is carried out by puncturing the tumor, and the contents of the wen are removed through a thin needle or cannula. The method is rarely used, since during such removal the lipoma shell is preserved, which significantly increases the risk of its further growth.
The surgeon selects the appropriate removal method depending on the age and clinical history of the patient. Removal is performed under local or general anesthesia.
Important ! The use of alternative methods for treating thoracic lumps is unjustified, since traditional recipes are largely specific and can provoke allergic reactions and complications.
Prevention
Recurrence of lipomatous lesions after removal can be prevented by following the following clinical recommendations and eliminating all predisposing factors:
- eliminating bad habits;
- playing sports;
- adequate diet;
- body weight control, weight loss for obesity;
- maintaining skin hygiene;
- timely treatment of pustular skin diseases.
If you are predisposed to the formation of lipomas and other skin tumors, hormonal correction and the use of statins, which reduce the concentration of fat fractions, may be required.
Treatment of polyps in the uterus is most successful when a woman follows the recommendations after curettage of the endometrial polyp. We wrote about this in a separate article. Read how the operation of intraductal papilloma of the mammary gland is performed here. Here you will find information about the symptoms of the disease, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Does lipoma pose a threat to human life?
Despite the fact that the ICD-10 code classifies this pathology as section D17, the pathology can develop into cancer. The disease transforms into a malignant form if the occurrence of pathology on the body is ignored. It is possible to determine the prerequisites for such a transition based on the following criteria:
- the tumor begins to hurt upon palpation;
- the wen has increased in size and become inflamed;
- the presence of inflammation around the wen;
- the surface of the tumor turns red;
- formation pressure on internal organs.
Doctors recommend radical removal of the tumor at the slightest suspicion of the presence of cancer cells.
In addition to danger, such growths bring a lot of inconvenience and pain. Limitation of movement, constant risk of injury from shoes or clothing, and limitation of physical activity due to the risk of damaging the lipoma worsen a person’s quality of life and suggest radical removal. Doctors do not recommend removing small formations, as they do not cause physical or aesthetic discomfort. Large subcutaneous pathology grows into the muscles, intertwining with nerves and blood vessels, reaching the bone surface. Thus, the wen exerts pressure and causes pain.
Internal wen interferes with the normal functioning of internal organs. The result is frequent constipation, slower metabolism, deterioration of the digestive system, and failure of the liver, kidneys and pancreas. The negative effect on internal organs depends on the location of the wen. Pathologies that occur on the skin of the face, neck and chest area cause aesthetic dissatisfaction among female representatives, which is fraught with the appearance of complexes and depression.
Removal
Is it necessary to delete
A lipoma on the mammary gland must be removed; the sooner surgery is performed, the lower the risk of developing a malignant process. Small tumors are successfully removed using minimally invasive techniques; they are less traumatic than radical surgery.
Surgical method
Today, wen in the mammary gland is treated only with the help of surgery. Minimally invasive and radical operations are used as a surgical method.
Breast lipomatosis is treated radically only in cases where the tumor has reached its maximum size and there is a risk of transformation into a malignant process.
After each surgical intervention, the wound must be sanitized and treated with antiseptic solutions. Antibacterial drugs are used to prevent the development of infectious complications, as well as vitamins and medications that stimulate the immune system of the woman’s body.
Minimally invasive techniques
Minimally invasive methods include:
- Puncture inspection of the wen cavity with aspiration of fluid. The negative point with this technique is that a capsule remains in the mammary gland, which again accumulates fatty tissue and a relapse is possible.
- Removal of a tumor using laser radiation. This operation requires expensive equipment, which is available only in some medical institutions.
Next, we will briefly consider non-invasive treatment methods.
Wen treatment
You need to understand that no drug will give maximum results in the shortest possible time. You can't cure a lipoma in a couple of days. Moreover, most often the cause of the problem remains unidentified, so the selection of conservative treatment options is difficult. This is precisely the problem of neutralizing provoking factors. Treatment with traditional medicine is considered ineffective.
If a woman or child has one lump on the nipple, and it is small in size, then the operation is not performed. To avoid serious complications, you should be examined regularly. Once every six months you need to do an ultrasound and mammography if the disease has already been diagnosed.
If the formation has to be removed, the doctor should discuss everything with the patient in advance. Only a few problems lead to surgical intervention: an increase in the size of the wen, pain, or an immediately large size of the formation.
If a classic operation is performed, the surgeon cuts the skin, removes the wen and applies sutures. It happens that the formation is located deep in the tissues, as well as in body cavities. In this case, general anesthesia is performed.
There is another treatment method: the introduction of a substance that destroys all lipocytes. However, not all doctors support such therapy, since it is difficult to predict how the lipoma will react to it. You need to understand that such medications do not destroy all fat cells, so there is a high probability of relapse. The puncture-aspiration method has the same drawback, when the contents are removed using a needle.
What completely destroys education? Electric current, laser beam and radio wave knife are excellent for these purposes. Anyone who is afraid of losing their attractiveness should understand that modern medicine has treatment methods that minimally damage the skin. They are performed on an outpatient basis. Local anesthesia is required.
Symptoms and diagnosis of the disease
If the formation has arisen in the subcutaneous fatty tissue, noticeably protruding above the breast, then it can be detected independently. This formation is inactive, painless, and its consistency resembles dough. More often, a lipoma in the breast has a diameter of up to 2 cm, less often the value reaches 10 cm.
Superficial formation is a cosmetic problem that is solved surgically. If the tumor is in the mammary gland, a special diagnostic study is indicated. Some forms of lipoma in the mammary gland develop against the background of the deposition of calcium salts in fibrosis. In this case, the woman feels discomfort and pain in the chest. Large lipomatosis causes pain when squeezed. In this case, the mammary gland itself is deformed.
The wen in the mammary gland has the shape of a knot. Less commonly diagnosed is diffuse lipoma, which is presented in the form of diffuse growths of adipose tissue
The disease is accompanied by symptoms characteristic of fibroadenomatosis, fatty involution and lobules. To diagnose the disease, aspiration biopsy is indicated. Differential diagnosis of the disease requires a comprehensive examination. The mammogram shows a homogeneous clearing with foci of calcification. Ultrasound reveals a homogeneous, and in the presence of fibrous tissue, a heterogeneous formation that has a clear contour. A biopsy reveals fat cells.
Causes
The true reasons for the appearance of wen in the mammary glands have not been established. Researchers suggest that neoplasms of this type develop under the influence of internal or external factors.
Possible causes of lipomas include heredity. Overgrowths of adipose tissue occur due to mutations of one gene and several chromosomes.
The second possible cause of lipomas is considered to be hormonal imbalance. The theory explains why the growth of adipose tissue is observed mainly in women over 45 years of age: during this period, a restructuring of the body occurs, caused by the onset of menopause.
On this topic
- Breast
Do lymph nodes enlarge with mastopathy?
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- November 29, 2020
In addition, the possibility of formation of wen due to metabolic disorders cannot be ruled out. In women with lipomas, the concentration of low-density lipoproteins is increased.
Due to poor permeability, these fats accumulate over time in certain areas, provoking the appearance of benign neoplasms with a capsule of connective tissue.
An increase in the concentration of lipoproteins is caused by excessive consumption of animal products, dysfunction of enzyme systems, and physical inactivity.
Among the external factors, the influence of which contributes to the gradual accumulation of fat in the mammary glands, the following are distinguished:
- prolonged wearing of tight clothing;
- mammary gland injuries;
- burn or frostbite of the chest.
With a high degree of probability, the cause of the formation of lipomas in the mammary glands lies in the simultaneous influence of several factors. At the same time, wen does not appear in the breast due to the accumulation of sebum, which is caused by insufficient hygiene.
Classification
Lipomas are classified according to the histological composition of the tumor, location, and degree of involvement of neighboring tissues. The first criterion is considered key. The prognosis for the development of neoplasia depends on this indicator.
Depending on the composition, wen in the mammary glands are classified into the following types:
- Classic lipoma. Consists exclusively of fat cells (adipocytes).
- Lipofibroma. In addition to fat cells, the neoplasm includes connective tissue.
- Fibrolipoma. Most of the tumor is formed from connective tissue, but adipocytes are also present.
- Angiolipomas. In such tumors, adipose tissue is penetrated by multiple blood vessels.
- Myxolipoma. The fatty tissue of the tumor produces mucus, which accumulates in the tumor, causing it to increase in size.
- Myolipoma. The neoplasm consists of smooth muscle fibers and adipose tissue.
The last two tumors are rare. More often lipomas and fibrolipomas form in the tissues of the mammary glands. Usually wen are single in nature. If the mammary glands are affected by many lipomas, when one is removed, the rest begin to grow actively.
Sometimes neoplasms that contain connective tissue are prone to calcification. Due to the new elements, the pressure that neoplasia puts on the nerve fibers increases, which provokes painful sensations.
Depending on the degree of involvement of neighboring tissues, neoplasms are divided into nodular and diffuse. The first type of tumors is characterized by the presence of a capsule of connective tissue. Diffuse wen grows into adipose tissue.
Depending on the location, lipomas are divided into subcutaneous, intramammary and deep. Tumors of the second type are located between the lobules of the breast, and the latter - behind the mammary glands.
Reasons for appearance
The appearance of a wen on a child’s face can be due to a wide range of different reasons, which can be both physiological and pathological in nature. Etiological factors can vary significantly depending on the gender and age of the child.
In older children, the appearance of lipomas may be due to a number of the following reasons:
- Leading a sedentary lifestyle, low level of physical activity.
- Diseases of the urinary or reproductive systems.
- Early puberty.
- Excess body weight.
Violation of the rules of a healthy diet, consumption of large amounts of fatty, sweet foods, and those rich in chemical additives can also lead to the appearance of neoplasms.
In newborns
Wen in newborns, most often localized on the skin of the nose and cheeks, are often the result of improper functioning or insufficient maturity of the sebaceous glands. Neoplasms of this kind do not require therapeutic procedures and are completely eliminated within a few weeks after birth. If this does not happen or the number of lipomas increases, you need to consult a specialist. Such signs may be the first symptoms of pathologies and diseases of the endocrine system.
Pathogenesis
The mechanism of tumor formation is the increased growth of breast adipose tissue cells. At the same time, atypical cells do not develop in the formation. It consists of mature fat cells enclosed in a capsule of fibrous tissue. The tumor arises from one fat cell by division. Therefore, tumors have a lobular structure. In addition to adipocytes, the process may involve blood vessels, muscle and connective fibers.
The reasons for increased division of fat cells are:
- blockage of the fat cell outlet;
- disruption of the menstrual cycle in women of reproductive age;
- hormonal disorders in the body at the time of menopause;
- dysfunction of the pancreas, pituitary gland or thyroid gland.
Tumors can be diagnosed not only in women, but also in men and children.