HPV or Human papillomavirus is a disease that represents a group of viruses. Includes more than 25 species and 150 strains.
Human papillomavirus is a sexually transmitted disease. Because this is how, in 90% of cases, infection occurs. In the patient's body, the virus can exist in several forms.
In episomal - a benign course of pathology, often without pronounced symptoms. And in an integrated way, it can degenerate into malignant processes.
The incubation period is the time from infection to the appearance of the first signs. Lasts from several weeks or months to 2-3 years.
In practice, a latent course of the disease is often encountered, and the patient is diagnosed with several types of the virus. Under the influence of certain factors, most often a decrease in immunity, the virus is activated, which is accompanied by the development of symptoms.
Many people believe that papillomavirus is a disease that is only common among women. However, a man is no less prone to infection and can act as a carrier of the disease.
A man is infected with HPV in the same way as a woman: through direct and intimate contact with the skin or genitals. The virus can spread through anal, vaginal or oral intercourse, whether with a member of the opposite sex or with another man.
HPV is an umbrella term for more than 150 strains of viruses, most of which are relatively harmless.
About 40 of them can affect the genital area and are accompanied by the development of warts and condylomas. However, some strains of HPV are oncogenic and can cause cancer.
Most of the time, the patient is unaware of the infection because many types of HPV are asymptomatic (except those that cause warts). In 90% of cases, the immune system naturally stops the virus and cleanses the body within 6-24 months.
According to April 2020 data from the National Center for Health Statistics, the prevalence of HPV among adults 16 to 60 years of age was 42.5% in 2013 and 2020. Among men, the prevalence reached 46.3%, and among women 39.9%. Men who have sex with men and people with weakened immune systems, including those with HIV, are most likely to become infected with human papillomavirus.
A study published in June 2020 in JAMA Oncology reports the following data.
Genital HPV infection in male patients was responsible for 63% of cases of erectile tissue malignancy (penile cancer). In other cases, HPV 6 and 11 of low oncogenic risk were diagnosed.
With the simultaneous development of genital warts and condylomas. These same types of HPV can cause a condition called recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. A rare but life-threatening disease accompanied by the formation of papillomas on the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract.
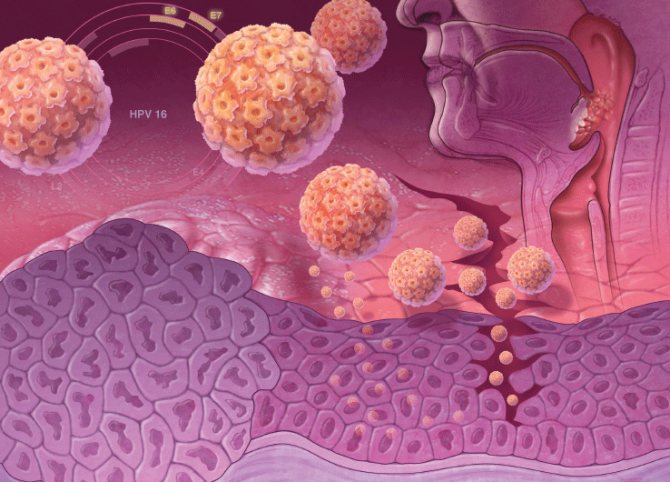
Symptoms and classification of papillomas
Quite often, HPV occurs without a pronounced clinical picture or is completely asymptomatic. As a rule, the appearance of signs of the virus is associated with a decrease in the functioning of the immune system.
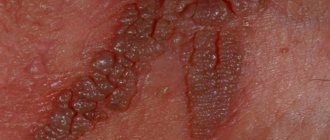
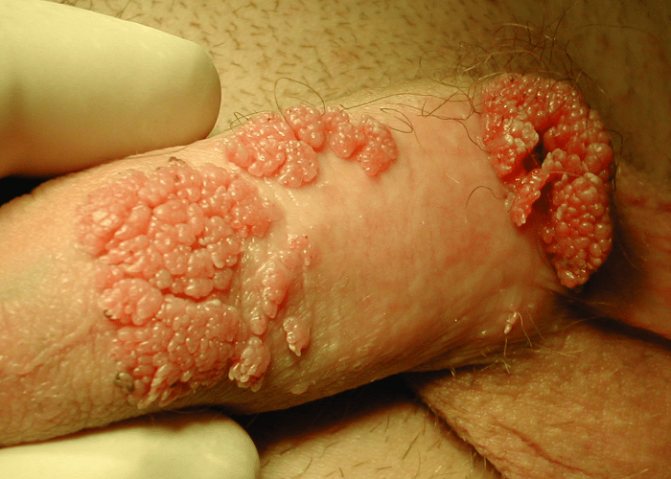
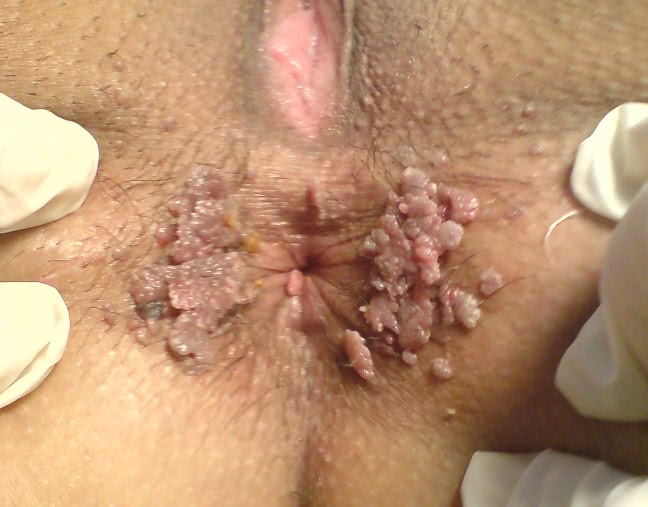
The main symptoms of HPV in men are papillomas in the genital area. Localization of formations can be inside or around the anus, on the upper thighs, in the groin area. On the scrotum and penis, including under the foreskin, and on the mucous membrane of the urethral canal.
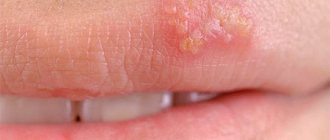
In some cases, such as men who engage in oral sex, warts may appear on the back of the throat.
Research shows that men and women have the same risk of contracting HPV. Moreover, the most important factor is sexual contact with multiple partners. Genital warts can have a different appearance: flat, pointed, or in the form of a small growth on a stalk.
If warts are localized on the mucous membrane of the urethra or rectum, the following symptoms are observed:
- pain, burning, discomfort when urinating;
- disruption of the defecation process;
- erectile dysfunction, pain during sexual intercourse.
In addition, papillomas are often accompanied by severe itching and can bleed due to injury. More than 150 different strains of HPV have been identified, each identified by a number known as the HPV type. Some types, such as HPV11 and HPV6, are associated with the appearance of warts.
Read also: Why does my penis fall during sex?
Meanwhile, HPV types 16 and 18 are among those that do not cause the development of such formations, but at the same time have a high oncogenic risk.
Warts, papillomas and similar formations are usually distinguished by appearance and location:
- Flat warts. Slightly darker in color than the base skin tone, flat and slightly raised in appearance. In men, it is more common on the face, in the beard area, as this place is prone to cuts during shaving. In women, most often on the thighs.
- Plantar warts. They are hard, granular growths that grow on the heels of the feet. They can cause discomfort and pain when walking. Diagnosing this form of HPV is not difficult.
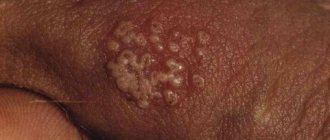
- Papillomas. The growths, slightly raised above the surface of the skin, may have the appearance of a lump, localized one at a time or in entire groups. They are benign formations from light beige to brown.
- Genital warts. They can be caused by any of the 40 types of HPV strains. They are contagious and can be transmitted through sexual contact. They appear in the form of small growths, similar to cauliflower or cones. In women, the main location is the vagina, cervix, vulva and anus; in men - the penis, scrotum or around the anal area. Although they rarely cause pain, they are often accompanied by itching and discomfort during intimacy.
During oral sex, it is possible to develop formations on the mucous membrane of the throat (oral HPV), the following consequences are observed:
- Hoarseness.
- Ear ache.
- Sore throat that doesn't go away.
- Pain when swallowing
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
- Unexpected weight loss.
What is HPV?
Human papillomavirus or HPV is a whole group of different viruses that has long been known to scientists. It is these pathogens that cause the appearance of warts and papillomas on the human body. About 40 varieties of this virus are capable of causing growths on the genitals and anorectal area. According to medical statistics, the level of infection with human papillomavirus infection among the population reaches 80%. But for most people, the disease does not make itself felt.
Most types of HPV are considered relatively safe; they can lead to the appearance of unwanted growths on the body, but such papillomas and warts can only be a cosmetic defect. However, some types of virus can cause cancer.
Oncogenic type pathogen
Some types of pathogens are considered dangerous from the point of view of malignancy - they can cause the appearance of malignant tumors. In men, condylomas can lead to cancer of the anus and penis, and scientists have also proven the relationship between HPV infection and the occurrence of squamous cell carcinoma of the larynx.
Among the pathogens of the oncogenic type are HPV 16 and 19 - they are the most common and occur in 70% of patients with manifestations of human papillomavirus infection. Potentially dangerous types of the virus also include HPV 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59 and 68.
Those strains of the virus that are potentially safe may also have oncogenic qualities. But it is not possible to predict such a transformation, so manifestations of HPV are a clear indication for targeted treatment.
Causes
The human papillomavirus can enter the body in several ways. Most often, infection occurs during sexual contact with a partner infected with HPV. Thus, up to 70% of men who have sexual relations with women who test positive for HPV are also infected with this infection. However, their disease can occur without obvious clinical symptoms. Therefore, many men may not even be aware of their own HPV infection, but at the same time become carriers of the virus. The pathogen can also enter the body:
- During childbirth. The infection is easily transmitted from mother to child.
- In everyday life, including through simple touch. The pathogen can remain viable for some time in public places, and then enter the body through abrasions and scratches.
- During medical procedures. This route of infection is very rare.
There are cases where a person infected with HPV transferred the pathogen to different parts of the body while shaving. In this case, doctors talk about autoinoculation. Infection with several types of HPV can occur at the same time.
After entering the body, the virus penetrates into the lower layer of the epithelium, where it can exist in two forms:
- Benign. In such a situation, the pathogen lives outside the chromosome of the carrier.
- Malignant. In this case, the DNA of the virus is integrated into the genome and provokes tissue degeneration (the appearance of growths on the body).
It is worth noting that in almost 90% of cases the body can get rid of the virus on its own. This may take about 1 year. However, in the presence of certain provoking factors (lowered immunity, somatic and infectious diseases), the pathogen can be activated, which is accompanied by the development of HPV symptoms.
HPV 16 and other types of virus in men
While most HPVs usually do not cause any problems, there are other types that can cause atypical symptoms. Papillomaviruses are usually classified into three groups: low-risk, medium-risk and high-risk oncogenic.
There are about 12 types of low-risk HPV, namely HPV: 6, 11, 40, 42, 43, 44, 54, 61, 72, 73, 81. The most common low-risk types are 6 and 11.
In 90% of cases, these species provoke the development of genital warts and papillomas. Average oncogenic risk (HPV 30, 35, 45, 52, 53, 56, 58).
At average risk, the development of atypical cells is extremely rare. But under the influence of type 35, the development of Bowen's dermatosis is possible. This rare disease is intraepidermal cancer - neoplasms on the skin of the penis.
High oncogenic risk (HPV 16, 18, 31, 33, 39, 50, 59, 64, 68, 70).
Most cases of high-risk HPV do not show any symptoms.
They go away within one or two years without causing any complications. However, some of them can persist for many years, leading to abnormal cell changes.
The most dangerous viruses are types 16 and 18. Since they account for about 70 percent of all cases of cancer due to papillomavirus.
What drugs can be prescribed
To combat papillomavirus, antiviral agents, immunomodulators and topical treatment agents are prescribed. All this will be described in more detail below.
Antiviral tablets
Therapy with antiviral drugs is especially relevant in the treatment of viruses of high oncogenic risk - strains 16 and 18.
These products help not only prevent the appearance of new formations on the skin, but also significantly reduce the number of viruses in the body.
- Amiksin is an antiviral agent with an immunomodulatory effect. Take 1 tablet per day for 3 days, then the product should be taken every other day. The course of treatment is 10 days.
- Cycloferon. It has a complex effect, suppresses viral activity, strengthens the immune system, and reduces inflammation. The daily dose is 3-4 tablets, a total of 40 tablets should be taken, after which it is recommended to take a break for a month and repeat the course of treatment.

Medicines in the form of suppositories
This group of drugs is usually prescribed for the presence of growths in the anal area. This type of medicine is indicated when it is impossible to use antiviral drugs orally.
Local ointments and talkers
3% oxolinic ointment is a very common remedy in the treatment of papilloma.
The ointment is applied to the affected area three times a day for 2–8 weeks. Particularly severe cases require the use of ointment for a longer time. After applying the drug, wax paper is placed on top.
Viferon ointment is no less popular . Its active ingredient is human interferon, which has not only an antiviral, but also an immunomodulatory effect.
The ointment can be safely used on young children and pregnant women. The product is applied to the tumors for 7 hours 3-4 times a day. The maximum duration of the therapeutic course is a week.
Another good remedy for local control of the papilloma virus is 60% salicylic ointment. Since its use may cause a burning sensation, it is not recommended for use on the face.
Apply the ointment morning and evening. During treatment, the growth will dry out, but it is strictly forbidden to rip it off - you should wait until it falls off on its own.
Clearol ointment is currently recognized as the best remedy for the local treatment of papillomatous neoplasms. Positive results are noticeable after just a few days of use - the papilloma dries out and then disappears, leaving no trace. Therapeutic course – 10 days.
Vishnevsky ointment is a time-tested drug. To get rid of papilloma with its help, the ointment is applied to the affected area 2-3 times a day, covered with a clean bandage.
Acyclovir ointment also has an inhibitory effect on papilloma viruses. It can rid a person of an unpleasant growth in two weeks. It should be used 5 times a day with an interval of 4 hours.
Panavir gel is a natural product based on herbal ingredients. It is recommended to treat skin growths up to 5 times a day. Depending on the positive effect, the course of treatment is 5–10 days.
What does HPV look like on the head of the penis in men?
With an active viral infection, formations of the papillomatous type are observed on the glans penis, the surface of the frenulum, on the foreskin and the circular groove. The formations can be solitary or localized in groups, have a flat appearance or resemble cauliflower. As a rule, papillomas grow only on the head of the penis.
Spread throughout the penis is possible in extremely advanced cases. For a long period of time, education remains unchanged, but against the background of certain factors they begin to grow rapidly.
Formations on the penis are accompanied by a number of uncomfortable sensations and are often injured and bleed. The main treatment is to remove the growths to prevent permanent injury. Next, the doctor selects an antiviral drug and a means to restore immunity.
Human papillomavirus infection in men: alternative treatment, prevention
Not everyone knows that human papillomavirus infection in men is a rather serious pathology that can lead to a number of complications in men and cervical cancer in women (if infected from a partner). That is why traditional treatment can be practiced in this condition only after the doctor’s permission.
Potato juice helps eliminate HPV very well. To do this, you need to take chopped raw potatoes, which have been passed through cheesecloth, twice a day. This treatment method is contraindicated for acute stomach diseases and diabetes mellitus.
Another effective method of folk treatment involves smearing papillomas with celandine juice. It will cauterize the warts and help them disappear quickly. The course of such treatment should not exceed two weeks.
In addition, human papillomavirus infection in men is well treated by lubricating warts with the following means:
- There is little castor.
- Freshly squeezed juice of the aloe plant (can also be used as a lotion).
- Garlic juice.
- Ammonia alcohol.
It is important
If warts are localized in the intimate area (on the head of the penis), it is prohibited to apply aggressive agents in the form of undiluted garlic juice to the mucous membrane. Otherwise, it may cause burns.
Disease prevention

Prevention of human papillomavirus infection in men, first of all, consists of protected intimate relations, namely, the use of barrier contraception during every sexual contact. Moreover, due to the fact that HPV in women can be completely asymptomatic, it is also impossible to practice unprotected oral sex.
The next mandatory criterion for preventing HPV is vaccination against the papilloma virus. It includes a course of three injections that are injected into the muscle. Despite this, you need to understand that for some types of virus, even vaccination cannot develop complete protection and lasting immunity.
To prevent the progression of the disease and detect it in time, every year men are recommended to undergo the entire list of tests for HPV, as well as sexually transmitted diseases. This will help not only to detect pathology in its initial form, but also to significantly simplify the further treatment process.
Moreover, preventive testing will protect a man’s potential sexual partners from infection.
Reviews
To better understand the characteristics of the course and treatment of HPV in men, we present the following reviews about this problem:
- Valentin “Quite by accident I discovered several condylomas in my intimate area. At first I didn’t even understand what it was, but after several minutes of searching for information on the Internet, I literally saw the light. Of course, the first reaction was shock, because I didn’t even know where it came from (I’ve been successfully married for several years and don’t have any outside connections). It turned out to be much more complicated, because after undergoing a series of tests, the doctor said that the primary source of HPV was not me, but my wife. Now we are both undergoing treatment and I’ll be honest, this is a very serious disease that is dangerous for both men and women.”
- Mikhail “In fact, I didn’t know about HPV for a long time until I experienced first-hand what it was. I discovered the disease by accident when I found warts in the intimate area, as well as on my hands. A series of tests only confirmed the disease. Since at that time I was already planning to start a serious relationship and even planned to have children, I approached treatment as seriously as possible. First I took a course of medications, then completely eliminated all the warts with a laser. So far everything is fine, I don’t think HPV will bother me anymore.”
HPV testing in men
The first stage of diagnosis is a visual examination of the patient.
If neoplasms are detected, the following types of tests may be recommended:
- PCR research;
- ELISA diagnostics;
- papilloma/wart biopsy;
- smear cytology.
PCR (polymerase reaction) remains the most informative method for diagnosing HPV. It makes it possible to detect the virus itself directly, without a clinical picture and at the earliest stages of infection. To carry out a polymerase reaction, a small amount of biological material is sufficient: blood, pathological discharge, a smear from the urethral canal.
Read also Incubation period of STDs
ELISA is also often prescribed for suspected HPV, but is a less informative method for diagnosing the disease. The analysis is aimed at identifying waste products of a pathogenic agent. But he cannot identify its presence in the body.
During a biopsy, a sample of the growth is taken intravitally. The analysis is prescribed if the color or shape of the formation changes and if the doctor suspects the presence of an atypical process. It is mandatory when diagnosing HPV with medium and high cancer risk. Additionally, a cytological examination of a smear from the urethra is performed. To detect or exclude concomitant sexually transmitted infections.
Human papillomavirus in men: manifestations, diagnosis
All the main symptoms of human papillomavirus in men can be divided into four separate categories, which manifest themselves differently and affect the patient’s health.
These types of diseases are:
- Warts.
- Condylomas.
- Papulosis.
- Bowen's disease.
Warts are the most common and surest sign of human papillomavirus in men. Externally, these formations are round in shape and in the initial stages of the disease do not bother the person at all. They may not differ in color from the rest of the skin, so sometimes it is not so easy for a man to identify them in the intimate area, on the eyelids, hands or other parts of the body.
Condylomas are also warts, but they have a characteristic pointed shape. Typically, these formations are localized in the groin of a person and on the mucous membrane of his genital organs.
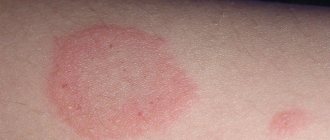
Papulosis is a type of disease that manifests itself in the form of rashes that appear on the penis. Externally, these formations have the form of pink plaques. It rises slightly above skin level.
Bowen's disease is another type of HPV. It is accompanied by the formation of a large round plaque on the human penis. This symptom will definitely indicate that there is an HPV virus in the body.
In the absence of timely treatment, this disease can lead to a narrowing of the foreskin, which in turn threatens problems with potency and even infertility.
It is important
If the patient does not get tested on time and does not start taking prescribed medications, he will put his sexual partner, and subsequently his children, at risk of infection. That is why, when the first signs of HPV are detected at home, a man should immediately consult a doctor.
Diagnostics
Human papillomavirus in men is diagnosed after examining the patient by a doctor, taking a medical history and performing a biopsy of papillomas. Also, the patient must undergo blood tests to detect the DNA of the virus, thereby confirming its presence in the body.
The most accurate and fastest method for detecting HPV is the Digene-Test. Its peculiarity is not only that it can detect the virus in the body, but also that it is able to accurately determine the specific type of papillomavirus.
How to treat HPV in men?
Genital warts pose a significant challenge to dermatologists.
Firstly, due to the reluctance of patients to consult a doctor regarding the correct treatment.
Secondly, due to the tendency of the pathology to relapse.
There is a standard treatment regimen for HPV. It includes taking antiviral drugs to stop the infection and immunomodulators. It is impossible to completely eliminate HPV from the body. Therefore, the main goal of therapy is to deactivate the virus and put the pathogen into “deep sleep.”
If there are growths on the skin, the first stage of treatment is to eliminate the formations using the following methods:
- Cryotherapy. Involves the use of liquid nitrogen to freeze abnormal growths. Cryotherapy can be performed to remove genital warts in men, and if necessary, to excise cervical papillomas that are diagnosed in a woman during a gynecological examination.
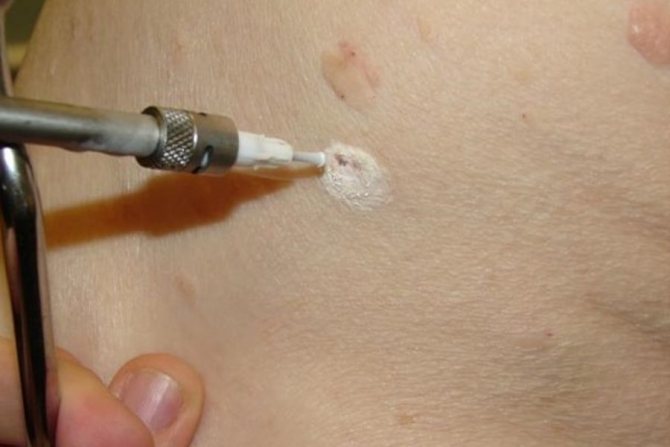
- Laser therapy. The method involves the use of laser radiation to burn abnormal tumors. The procedure is completely painless and does not require special preparation from the patient.
- Surgical excision. The most cost-effective and traumatic option for removing papillomas is accompanied by prolonged healing of the skin, as well as the possible formation of scar tissue. Many doctors do not recommend this method, especially when removing warts localized to the genitals.
After removal of abnormal tumors, drug treatment is prescribed, which includes taking the following drugs:
| Drug group | Medicine (trade name) | Description and Application |
| Antiviral | Groprinosin Isoprinosine · Novirin Allokin - Alpha | The action of the drugs is directed against the synthesis of viral RNA and stimulation of macrophage activity, which increases the protective functions of the immune system. The medications are well tolerated and rarely cause side effects. Dosage is prescribed strictly on an individual basis; for each patient, the dose and course of administration may vary. |
| Immunomodulatory | Cycloferon (prescribed ointment and tablet form) Gepon · Immuno-tone · Cytovir-3 Cervarix (vaccine) | Immunotherapy has proven itself in solving recurrent and resistant papillomas. Immunomodulatory drugs modify the immune system's response by increasing (immunostimulation) or decreasing (immunosuppression) immunoglobulin production. They have the effect of enhancing the immune response against infectious diseases, viral, primary and secondary immunodeficiency. |
| Vitamin complexes | · Alphabet · Multitabs · Complivit | In the treatment of HPV, they are additional drugs aimed at improving the general condition of the body and accelerating the healing process. They have an antioxidant effect and have a beneficial effect on the functioning of the nervous and cardiac systems. |
Prevention
HPV is considered a rather insidious disease, due to the fact that it can remain silent for a very long time, without causing characteristic symptoms and lead to the development of a cancerous tumor. Therefore, doctors recommend that men follow some preventive measures:
- Avoid casual sex and always use a condom in such cases.
- Get vaccinated against the papilloma virus. This vaccine appeared recently, so few people know about it. Vaccination consists of 3 injections at certain intervals. However, the vaccine can only protect a man from certain types of the virus.
Urologist Karaman Sergeevich Abramov talks about men's intimate hygiene:
- Get tested for HPV periodically.
- Maintain intimate hygiene, do not use other people's objects: towels, underwear, sharp objects.
It is almost impossible to completely cure the disease, but getting rid of its main manifestations is quite possible. To do this, you need to strengthen your immune system, avoid casual sexual intercourse, give up bad habits and promptly consult a doctor if you find any tumors on your body.
Papilloma is a neoplasm that appears on the surface of the skin or mucous membrane. The causative agent of the pathology is the human papillomavirus.
It is present in the body of almost all people, but is activated only if the immune system fails. It is not yet possible to completely destroy the papilloma virus in the human body, and treatment is aimed only at inhibiting its activity.

Preventive actions
There is no medicine that can completely eliminate the human papillomavirus from the body. But there are ways to minimize the risk of developing HPV.
Prevention is as follows:
- Reducing stress levels. Prolonged exposure to stressful situations can have a significant impact on the immune system. As a result, HPV recurrence is possible.
- Healthy diet. A healthy diet has a beneficial effect on the functioning of the immune system, making it resistant to viral and infectious diseases.
- Avoid drinking alcohol and smoking. According to the American Cancer Society, smoking and alcohol abuse have a negative impact on the functioning of the immune system. Men who smoke and drink heavily are twice as likely to develop acute HPV.
The best prevention remains staying in a monogamous relationship and limiting yourself from numerous sexual partners. Using protection such as condoms during sexual intercourse can also reduce the risk of contracting the virus.
Getting rid of the problem
Treatment of human papillomavirus infection in men is not able to get rid of the cause of the disease. Modern science is successfully fighting the external manifestations of the disease, especially in the genital area in both sexes. Two approaches are used: medical and surgical.
Recommended Medicines
When prescribing immunostimulants and antiviral drugs, a treatment regimen is developed that uses an integrated approach to the problem. This allows you to live without external manifestations of the disease.
Popular medications to boost immunity:
- "Tymosin";
- "Levamisole";
- "Groprinosin";
- "Immunomax";
- "Isoprinosine."
Antiviral drugs are taken together with these drugs. Depending on the form of release, these can be injections, tablets or ointments.
Recommended medications:
- "Amiksin";
- "Podophyllin";
- "Viferon";
- "Kondilin."
The treatment regimen, in addition to basic medications, contains maintenance therapy, as well as drugs that stop the exacerbation of chronic diseases.
Removal of papillomas
External manifestations of HPV are successfully removed by surgery. The procedures are carried out for a fee, and their prices are quite high.
How to treat human papillomavirus in men using surgical methods:
- Laser surgery – cauterization of papillomas with a laser beam is performed under local anesthesia.
- Creodestruction methods - liquid nitrogen is used, which minimizes pain.
- Chemical coagulation – cauterization of growths using medical means.
- Electrocoagulation - papillomas are destroyed using electric current under local anesthesia.
- Cutting papillomas using radiosurgical equipment in a non-contact manner.
- Surgical removal - used for large tumors that are cut off with a scalpel.
After using any method, a mandatory course of immunostimulating therapy is carried out. In some cases, depending on the severity of the symptoms, drug treatment is repeated after a month.
Folk remedies
Not all visible symptoms of HPV require radical treatment methods. Traditional methods of getting rid of warts on the body are very helpful. Doctors believe that only vulgar and hanging growths can be destroyed at home. If you find genital warts on your genitals, you should definitely consult a doctor.

Popular inexpensive folk remedies:
- milkweed juice;
- celandine;
- compresses of onion plates soaked in vinegar;
- dandelion juice;
- thuja essential oil;
- aloe;
- raw potatoes;
- propolis;
- hydrogen peroxide.
The program for the use of folk remedies is designed for a monthly course. It is recommended to apply compresses or applications in the morning and evening for 20 minutes. According to patient reviews, warts begin to change color and dry out no earlier than after a week of constant use of the medicine.
The effectiveness of treatment for human papillomavirus in men depends on the patient’s age and the state of his immune system.
Effective pharmaceutical medicines
Certain medications are used to treat HPV. The most effective of them will be described below.
Isoprinosine
It is well absorbed into the gastrointestinal tract, since the structure of the active substance is similar to purines. This makes the drug highly effective.
Isoprinosine pushes the body to produce its own interferons - cells that actively fight papilloma viruses.
In addition, the drug supports immunity and stimulates the synthesis of immune cells. Take 2 tablets three times a day, course – 2-3 weeks.
Allokin-Alpha
It starts to work very quickly. After injection, the maximum concentration in the blood is observed after 8 hours. The drug eliminates the manifestations of HPV, has an antiviral effect, increases the production of interferon, has an antibacterial effect, and stimulates the defenses. Subcutaneous injections are given at a dose of 1 mg once every two days. As a rule, 6 injections are prescribed.
Immunomax
This is an immunomodulatory drug that forces cells to give an adequate response to the invasion of foreign agents. The drug is introduced into the body through intramuscular injections of 100–200 units. 1 time per day every other day. The duration of treatment is 6 injections.
Lycopid
The active ingredient of these tablets is glucosaminylmuramyldepeptide. Prescribed to stimulate the cytotoxic and bactericidal activity of phagocytic cellular structures.
Increases the synthesis of antibodies to the papilloma virus. Contraindicated in case of exacerbation of autoimmune diseases, fevers, pregnant and lactating women.
Keravort
Topical immunomodulator. The cream is applied to the cleaned affected surface and rubbed in until completely absorbed. It is recommended to use 3 times a week before bedtime. The product should remain on the skin for 6–10 hours.
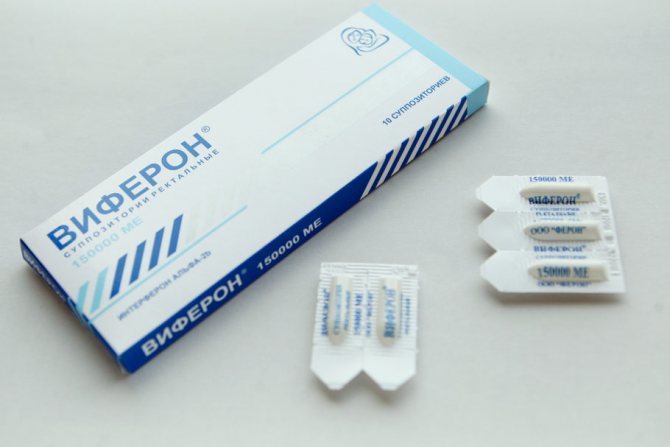
Viferon
This drug is available in the form of rectal suppositories, gel and ointment. It must be used in the course of treatment of papillomavirus as an addition to antiviral tablets. Has no contraindications.
Epigen intimate
This is a spey whose active substance is glycyrrhizic acid. The drug relieves itching and inflammation, actively restores the immune system, prevents the multiplication of the virus, destroying its chains.
Epigen Intim is often positioned as a drug for women, but it can also be used by the male population without restrictions.
The product is well suited not only for the treatment of viral infections, but also as a preventive measure for the activation of HPV. The affected areas should be treated with the product three times a day until the growths disappear.
Antiviral agents
Genital warts and other growths on the skin are easy to diagnose, since their presence is determined by visual examination. It is much more difficult to identify pathology at an early stage, because the disease is characterized by a long latent period, during which the virus lies dormant and does not attempt to reproduce. And this is where modern diagnostics come to the rescue.
The use of laboratory methods is aimed at studying biopsy material at the cellular level, detecting HPV DNA, E7 oncoprotein and determining antibodies to the virus. An integrated approach involves the following procedures:
- clinical examination of the external genitalia to identify growths;
- colposcopy to determine the presence of intraepithelial neoplasia;
- Papanicolaou testing (PAP test);
- immunological methods - PIF, ELISA, RSK;
- PCR – polymerase chain reaction;
- DNA probe;
- cytological examination;
- histology and biopsy of tissue sample.
It is important to know! HPV typing and determination of its group membership, taking into account oncogenic risk, are considered important in the research process. This is achieved using the Digene test.
Despite the rapid development of medicine, the creation of progressive diagnostic methods and highly effective medications, a specific cure for papillomavirus to completely destroy it has not yet been invented. Therapy is aimed primarily at eliminating the external manifestations of HPV, as well as treating a number of other problems:
- prevention of reactivation of the virus;
- reducing the risk of complications, including prevention of cervical cancer;
- stimulating the immune system, strengthening the defense mechanism.
What methods the doctor will operate on and how he will treat HPV in women, what kind of drugs he will choose, depends on many factors: medical history, somatic status, size of tumors, their number and location. The woman’s tolerance to prescribed medications is also taken into account.
Local treatment of HPV in women is aimed at removing growths (warts, condylomas) and atypically changed epithelium using cytostatics, chemical coagulants, as well as destructive methods. After this, in order to prevent relapse, therapy with antiviral drugs, nonspecific immunomodulators, and interferon inducers is indicated. Since the virus is transmitted sexually, both partners must be treated at the same time.
"Solcoderm"
A local drug used to remove papillomas and warts on the surface of the skin.
Available in the form of a solution, intended for use in an outpatient setting, under the supervision of a physician. After applying the drug, the formation mummifies, and after some time the wart disappears on its own.
DETAILS: Treatment of uterine cancer with folk remedies
"Nitric acid"
Its action is similar to Solcoderm, it causes necrosis of the formation, as a result of which the wart disappears. Requires a fairly long course of use, often up to 4 weeks or more.
How to cure papillomavirus in men and women? The doctor prescribes any drug for the treatment of human papillomavirus based on the studies performed, test results and the person’s condition. Experts prohibit trying to get rid of the disease on your own or relying on the opinion of those who have previously treated such a lesion with a doctor.
Most often, the doctor prescribes the following medications to the patient:
- "Panavir";
- "Arbidol";
- "Epigen intimate";
- "Viferon";
- "Genferon";
- "Isoprinosine."
All the described antiviral drugs, despite the positive effect in treatment, can provoke an adverse reaction in the human body; an experienced attending physician must carry out an accurate diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment.
How to cure papillomavirus with folk remedies? Some people try to treat the disease using traditional medicine. If the virus manifests itself to a minor extent on the arms and legs, and there are no profuse rashes on other parts of the body, then doctors advise using special celandine juice, which is applied to the affected areas of the body several times a day.
How to cure papillomavirus at home? You can also use garlic juice to effectively treat papillomas, which quickly kills the virus. It is applied to the condyloma several times a day, and the garlic clove itself is cut in half and applied to the affected area of the body at night. It is important to remember that only the treating specialist can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe correct and effective treatment, since such forms of formations on the surface of the body can indicate the presence of a dangerous disease in the body.
Many patients do not take this form of damage seriously and underestimate the level of its danger. The human papillomavirus can be transmitted sexually, and even contraceptives cannot provide 100% protection against infection. Infection, as a rule, occurs after direct contact of the skin or mucous membrane of a healthy person with diseased areas of the patient’s body.
For the female half of the population, the HPV virus poses a particular danger, as it can lead to a very serious disease - cervical cancer. If men do not show any external signs of the disease or special symptoms of infection, this does not mean complete safety, since in most cases men are asymptomatic carriers of the infection.