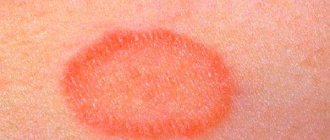
Human papillomavirus (HPV) type 33 in women causes the appearance of genital and flat condylomas on the genital mucosa, erosion, and cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, the development of which leads to cancer. It is impossible to completely get rid of the infection, but after treatment it may recede and not bother the patient for a long time.
Research by scientists has confirmed that HPV type 33 is transmitted only from person to person: the danger is posed by those who exhibit severe symptoms of papillomatosis, and by those whose infection occurs in a latent form.
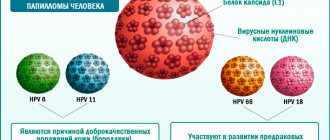
Today, more than 100 strains of the virus have been identified. For convenience, doctors divided them into groups and identified non-dangerous strains that do not cause the growth of tumors that can degenerate into cancerous tumors, and those that have average and high oncogenic activity.
Papillomavirus type 33 belongs to the third group. Its presence in the body of the fair half of humanity greatly increases the risk of developing an oncological process in the cervix and mammary glands. HPV 33 does not always give rise to irreversible phenomena. Its activity and pathogenicity become possible only against the background of immunodeficiency states.
Symptoms
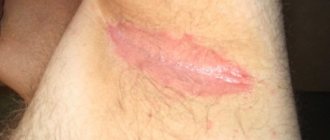
The process can cause irregular growth of abnormal cervical cells. This pathology develops in three stages. Severe neoplasia is already intraepithelial cancer. Often one disease develops against the background of another, so the appearance of pointed and flat warts on the labia minora and majora, on the vaginal mucosa or around the anus should force every woman to undergo a full diagnostic examination.
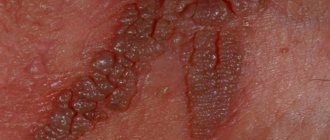
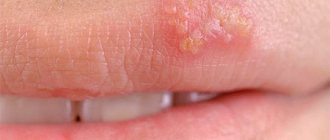
The size of warts may vary. They can have different shapes and look like a head of cauliflower or a rooster's comb. Women can easily detect them by feeling the labia minora, labia majora, and vaginal walls. If there are many condylomas and they are inconveniently located, minor bleeding may occur during sex. Also, the growth of papillomas may be accompanied by itching.
Preventive measures for HPV 33 and other types of virus
Prevention is mandatory to avoid cervical cancer in women and penile cancer in men. Nonspecific preventive measures are aimed at educating adolescents and teaching the younger generation the rules of sexual life. It is important to explain to children that starting sexual activity early is wrong, that you should not change partners too often, and that using a condom reduces the risk of contracting many infectious diseases.
Specific preventive measures include HPV vaccination. After vaccination, stable immunity to oncogenic HPV appears. Today, 2 types of vaccines have been developed and used in medicine:
- Cervarix. The vaccine is used only for healthy girls and women aged 10-25 years. Vaccination is carried out in 3 stages. The vaccine has shown very good results in preventing the development of cervical cancer.
- Gardasil. The vaccine is also used only for healthy people not infected with HPV. Vaccination takes place in 3 stages. The vaccine is recommended for all healthy young women. Prevents the development of cervical cancer.
Vaccination is the only way to prevent HPV infection, however, if a woman or man does become infected, there is no need to despair. HPV can be treated, the main thing is to seek help from a specialist in time, who will prescribe an examination and conduct effective therapy. Some doctors are not against the use of alternative medicine methods in treatment. The most important thing here is to always consult with your doctor.
Prescribing medications on your own, or even more so, removing tumors is strictly prohibited. This can lead to irreversible consequences, including death.
Source: 1papillom.ru
Routes of transmission and reasons for activation
The routes of transmission of HPV 33 infection are well studied and are transmitted:
- sexual intercourse during unprotected sex;
- through the use of general hygiene products (bath towels, washcloths);
- during childbirth from mother to child during childbirth.
The incubation period can last from six months to two years. After its completion, symptoms appear only when immunity decreases.
It can be provoked by:
- poor nutrition;
- vitamin deficiency;
- anemia;
- overwork;
- bad ecology;
- exacerbation of chronic systemic diseases;
- severe pathologies of the blood supply system;
- renal and liver failure.
Exposure to one or more of these factors leads to the fact that the immune system cannot produce as many antibodies as needed to contain the virus. Symptoms of its activation appear precisely in the area where it entered the body.
Main signs of human papillomavirus infection
When penetrating the human body, papilloma 33 virus stimulates the appearance of genital spiky growths. The disease can be detected during an examination by a gynecologist. Let's figure out what HPV type 33 is in women.
Genital genital warts in girls and women begin to appear 2-4 months after infection of the body. Often localized on:
- vaginal wall;
- cervix;
- labia minora.
Important! The problem of detecting HPV is based on the fact that certain types of infection have a long incubation period; from infection to the first symptoms it can take up to 6 months, depending on the characteristics of the organism.
The main signs that will be a “bell” for additional examination can be identified as follows:
- strong discharge, mixed with blood;
- periodic pain in the lower abdomen and discomfort;
- burning after sexual intercourse;
- diagnosing cervical erosion;
- visible vaginal genital warts.
The surest way to diagnose human papillomavirus type 33 is to get tested. After 30 years of age, testing for the presence of the virus must be carried out once every 2 years, regardless of whether there are symptoms or not. This is the only way to avoid possible risks; the earlier the problem is identified, the easier it is to get rid of it.
One of the symptoms of HPV type 33 in women is cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, when the cervix is in a precancerous state. The disease has 3 stages, of which the third stage is incipient oncology, and the first two categories are not dangerous.
Diagnostics
If infection with HPV 33 strain is suspected, the patient must undergo a full examination.
To identify the virus, PCR is performed and the DNA of the cellular parasite is isolated using it. This procedure makes it possible to accurately identify the causative agent of a hidden infection. The reaction takes only a few hours. During this period, it is possible to determine whether it is possible to diagnose the infection during the incubation period. Scrapings from four points of the vagina are used as material for study. If the test is positive, a Digene test is required - a laboratory analysis that determines the strain and oncogenicity of the virus. This indicator then allows you to more accurately interpret the results of cytological tests.
If carriage of HPV strain 33 is confirmed, a colonoscopy is prescribed. If during its implementation the presence of dysplasia, genital and flat warts, or any other neoplasms is revealed, a biopsy, excision of the damaged tissue and its subsequent histological examination are required.
Risk group for HPV infection
When a virus enters the human body, it is usually immediately destroyed by immune cells. If the immune system is weakened, the virus manages to penetrate to a deeper level of the epithelium, where it tries to penetrate the chromosome structure and change the functioning of the body at the cellular level.
In a closed area, cell division rapidly increases, and, growing, they take the form of warts or papillomas.
It cannot be said that the virus poses a serious threat to a healthy body, but there is a so-called risk group of people most exposed to it for a number of reasons:
- weakened immune system;
- past infectious diseases;
- chronic gynecological diseases;
- excessive medication use;
- promiscuous sex life;
- uncontrolled use of oral contraception;
- alcohol abuse;
- smoking.
The virus that lives in the body of women poses a double danger, because during pregnancy it can infect the baby already during intrauterine development.
Danger of HPV 33 during pregnancy
Pregnancy is a factor that causes a sharp decrease in immunity. In this way, the body tries to prevent fetal rejection. If a woman was previously infected with the virus, it will certainly manifest itself during pregnancy.
Exophytic growths may begin to actively grow on the cervix, vagina, and perineum. They rise above the level of the skin or mucous membrane, often accompanied by severe itching. The size of warts and their number depend on the concentration of the virus present in the body of a pregnant woman.
Carriage of the virus does not affect the development of the fetus. Medicine knows only a few cases where the presence of a large number of genital warts in a mother led to the birth of a child with laryngeal papillomatosis. The presence of 33 strains of the virus in a pregnant woman is a condition that requires special attention from a gynecologist. Since the serovirus can provoke the development of oncology, it is important to be alert and not miss the moment.
Virus type 33: routes of infection, diagnosis and therapy
The HPV 33 virus is highly oncogenic. This means that when immunity declines, cancer can develop. If a person is diagnosed with papillomavirus thirty-three, he should consult a doctor. HPV type 33 is expressed on the body in the form of papillomas and condylomas; they form on the vagina in women and on the penis in men.
Type 33 is the most dangerous for females. HPV 33 provokes erosion, inflammation, and if the pathological condition is not treated, then there is a high probability of developing a malignant tumor of the cervix.
HPV type 33 affects men extremely rarely. If the doctor suspects HPV 33, he prescribes a detailed diagnosis. During diagnosis, the question of the appropriateness of therapy is decided.
Typically, patients are prescribed PCR analysis, colposcopy, smear and oncocytology. If the load is not heavy, then healing can occur on its own; usually the process lasts 3 years. If you have been diagnosed with the HPV 33 virus, the main thing is not to panic and not self-medicate.
Treatment
If viral activity is low and there are no severe immune system disorders, you can self-medicate. Within two years from the onset of the first symptoms of growth of genital and flat warts, papillomavirus type 33 loses its activity and goes into a dormant state.
Drug therapy is prescribed only after performing the Digene test three times, if it shows a high concentration of the virus. The patient is prescribed antiviral drugs and immunomodulators. Identified warts are removed surgically or using instrumental installations, radioknife, laser, electrocoagulation, liquid nitrogen.
Cervical dysplasia
Genital warts are an unpleasant, but not the most dangerous disease that can be caused by papillomavirus type 33. This virus also causes another pathological condition – cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. This is a precancerous condition, it will not necessarily result in cancer, but it greatly increases its risk.
Despite the fact that viruses types 16 and 18 are considered the most dangerous for women’s health, type 33 can also cause a cancer predisposition.
In gynecology, the abbreviation CIN (cervical intaepitelial neoplasia) is used to refer to this condition.
CIN degrees:
- Weak degree of dysplasia. There is excessive growth of cervical epithelial cells and partial keratinization. Changes affect no more than 1/3 of the depth of the epithelium. This condition is easily treatable, but is rarely detected during screening studies.
- Moderate degree of dysplasia. Excessive growth takes on a greater volume, keratinization is pronounced. The depth of epithelial damage is about ½. Most often, neoplasia caused by HPV type 33 is diagnosed at this stage.
- Severe degree of dysplasia. The epithelium is affected to more than 2/3 of the depth; there are changes in the external structure of the epithelium and the development of its cells, noticeable at any level - cellular, tissue, organ. This type of neoplasia is a transitional stage between reversible changes in the epithelium and a cancerous tumor.
Men infected with the same virus may develop penile cancer. The likelihood of its development is influenced by the fact that during sexual intercourse, condylomas are often damaged, and this stimulates pathological cell division. Therefore, people who are sexually active are more susceptible to malignant tumors against the background of anogenital warts.
Traditional methods
Traditional methods will not help get rid of the virus, but with the help of some recipes you can successfully combat the symptoms of infection.
For example, using celandine juice, you can cauterize a wart and wait for it to turn black and fall off on its own. To do this, you need to mix the juice with saliva, coat the growth with the liquid and cover it on top with a band-aid. The first results should appear in two days.
Instead of celandine, you can prepare an infusion of chaga or string, make ice cubes from them and wipe the warts with them three times a day.
It is good to cauterize papillomas located on the labia with ointment made from garlic. Grind the clove to a mushy state, mix in equal quantities with cream for intimate places (a clove for two teaspoons of cream). Place the resulting mass in cheesecloth. Apply the compress to the papilloma. The application is removed after five hours. The area is washed with warm water and soap. The duration of the course is one month.
Prevention
There are no ways to protect a woman from the virus in 100% of cases. There are a number of recommendations that you need to follow if you want to minimize the risk of infection. To do this you need:
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- Healthy food;
- have a permanent partner;
- avoid abortion;
- observe the rules of personal hygiene;
- do not use other people’s bath accessories and linen;
- visit a gynecologist regularly;
- promptly identify and treat any viral infections.
Only careful attitude to your health can become a barrier to infection with various diseases.
About the possibility of prevention
Primary prevention of HPV type 33 consists of maintaining body hygiene, responsible sexual behavior, and strengthening the immune system. Considering the high prevalence and contagiousness of papillomaviruses, following the above rules can reduce the risk of infection, but do not protect against infection.
The main value in the life of any person is health. No woman is immune from human papillomavirus infection, but timely diagnosis at an early stage of the disease and adequate therapy will help avoid such a formidable complication as cervical cancer.
Source: UroMir.ru