Papillomas in the vagina are a consequence of infection of the body with HPV. They can occur approximately 3 months after sexual intercourse or several years later. Immunity plays a decisive role in this. Papillomas in intimate places in women must be removed, even if they do not cause discomfort. Neoplasms of high or medium oncogenic type can degenerate into malignant ones and become the cause of cancer.
What is HPV in gynecology
HPV in gynecology unites one of the largest families of viruses. More than 100 types of this virus have been identified, and 80 of them are dangerous. Currently, each strain was given a serial number and divided into 3 groups.
- Non-oncogenic. Viruses of genotype 1,2,4,5 cannot degenerate into malignant formations. They cause warts on the hands, feet and other parts of the body.
- Low oncogenic. In rare cases, genotypes 6,11, 43 and 44 are detected when examining patients with precancerous diseases. They form pointed papillomas in the perineum.
- Highly oncogenic. This group includes more than 13 types of viruses, but the most dangerous are 16 and 18. They were identified in women who were diagnosed with cervical cancer.
It is believed that HPV is the cause of cancer. It disrupts the normal division of cells in a certain area, which provokes their degeneration into malignant ones.
How have HPV diagnostic methods advanced?
There is no single technique that can accurately make a diagnosis. To do this, an experienced doctor prescribes a set of diagnostic procedures – usually two of them. This helps eliminate the possibility of error when making a diagnosis. Modern medicine provides the following types of diagnostics:
- Anamnesis is a detailed dialogue with a doctor, where the patient honestly answers the questions asked. This helps to identify the cause of infection, prevent cancer of the cervix, vulva, etc.;
- PCR diagnostics a highly accurate procedure aimed at identifying the pathogen strain. This way you can find out how much the virus has spread throughout the body;
- Anoscopy - used to detect papillomas in the anal area. Since formations tend to grow, it is better to resort to this procedure - this way you will protect yourself from unexpected problems in treatment;
- Histology – using a sample of damaged tissue, you can study the structure of the neoplasm and identify the strain of the disease;
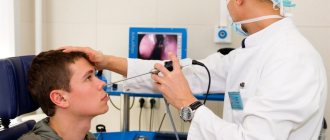
- Colposcopy – warns of any damage to the vaginal wall. A colposcope is used to examine the vagina, previously treated with a special iodine solution;
- Oncocytology – helps identify pathogenic cells. For analysis, scrapings are taken from the vagina, cervix and cervical canal.
The reason for the appearance of the tumor
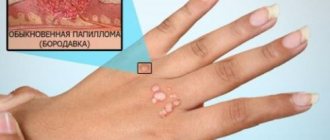
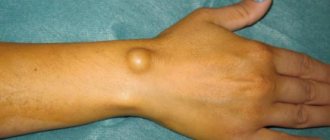
Papillomas in the vagina appear unexpectedly and are usually discovered during a gynecological examination. Papillomas on the labia can also be seen independently. Vaginal papillomas come in several types - pointed on a high stalk and flatter, merging with the mucous membranes. The latter are more dangerous - they cause dysplasia and cervical cancer.
Papillomas on the genitals appear due to HPV infection. This viral disease is easily transmitted through sexual contact. Women are more susceptible to HPV than men due to the structure of their genitals. Moreover, in women, papillomas in the vagina more often degenerate and become malignant than those located on the genitals of men.
With unprotected sexual intercourse, the risk of infection is 80%. Women who have a strong immune system that will prevent the virus from entering the body remain healthy. Papillomavirus is transmitted through any type of sex and even kissing. To do this, contact of skin or mucous membranes with infected people is sufficient. Even when using a condom, the risk of infection is 30%.
Papilloma in an intimate area can occur not only after sexual intercourse with men who are infected. The human papillomavirus in gynecology is almost as common as genital herpes, but is slightly inferior to it. The disease is transmitted through household and household contact. Using other people's towels, visiting bathhouses, shaking hands and wearing other people's clothes can provoke papillomas in the vagina.
Symptoms of vaginal papilloma
The virus infection scheme is as follows: first, the pathogen enters the dermis layer, affecting the membrane of healthy cells, then the infected DNA is introduced into the cell, after which the virus waits for favorable conditions for activation.
In this situation, if the infected girl has a strong immune system, papillomas in the vagina may not form for a long time.
There are 3 stages of the disease in total. The first is characterized by the absence of severe symptoms. Depending on the general physical condition and the state of the immune system, this stage can occur over a long period of time, and in the absence of provoking causes, symptoms may not appear for several years. Despite this, the girl is already a carrier of the virus and can infect her sexual partner.
The second stage is characterized by changes in the mucous membrane of the genital organs. Neoplasms can be localized deep in the vagina, so it is not possible to identify them independently.
Papillomas at the entrance to the vagina or on the labia can sometimes be detected by touch. Also, due to regular contact with clothing or during washing, they may bleed, which is a serious reason to consult a doctor.
At the third stage, diagnosis does not cause problems.
Symptoms become more pronounced and include:
- the appearance of severe pain during sexual intercourse;
- itching and burning in the intimate area;
- the appearance of purulent discharge.
Many girls are interested in what papillomas in the vagina look like. Unfortunately, you won’t be able to detect these growths on your own; to do this, you need to undergo a thorough diagnostic examination.
How does the virus manifest itself?
Papillomas on the labia after infection may not appear for a long time. In the latent form of the disease, the virus can be detected using laboratory tests. Treatment in this case is necessary, since the human papillomavirus in women can lead to the appearance of tumors in the future.
In the subclinical form, diagnosis is possible by colcoscopy and laboratory tests using special solutions. This form is quite dangerous and requires immediate treatment. It is necessary to remove papillomas from the vagina.
Clinical forms are diagnosed by visual examination. With the naked eye, neoplasms can be seen on the labia minora, vulva and vagina. They are a direct source of infection for sexual partners, as well as self-infection of other areas.
What are genital papillomas
Papillomas (also called “genital warts”) in the intimate area are small single or group growths consisting of epithelial or epidermal cells. They are connected to the circulatory and nervous systems, which is why any injury causes profuse bleeding and severe pain. The cause of pathological neoplasms is the human papillomavirus (HPV). You can become infected with it in several ways:
- contact;
- sexual;
- household;
- hereditary (from mother to baby at the time of birth).
In the case of genital papillomas, the main source of infection is an infected sexual partner. You cannot protect yourself from HPV even with the help of contraceptives. The virus cells pass through the latex pores and penetrate deep into the soft tissue in a matter of seconds. Therefore, if a man is a carrier of a pathogen, then through intimate contact the woman will be infected with a 98% probability.
It is impossible to determine when the infection occurred. From the moment the virus cells enter the body until the first symptoms appear, several months or even years may pass. Sometimes the disease does not make itself felt at all and a woman lives to an old age without even knowing about her diagnosis. But during all this time, she remains a carrier and spreads the pathogen to healthy people.
Disease detection and symptoms
Often, HPV is detected at the time of donating blood during a medical examination or when visiting a gynecologist, who, using special equipment, is able to see even the most minor changes in the structure of soft tissues on the genitals and inside the vagina. If there are no pronounced symptoms (large pathological growths), then the patient is prescribed antiviral and immunostrengthening drugs. They put the virus into a dormant state, since, unfortunately, it is not possible to cure this disease.
Important!
In medicine there is the concept of “micropapillomatosis”. This is a small, flat, light pink rash that appears on the labia minora. It relates to the anatomical features of a woman and is not viral in nature.
HPV activation is promoted by:
- weakened immunity (the first and main reason);
- undergoing treatment with strong medications;
- the presence of bad habits (smoking, alcoholism) that reduce the body’s protective functions;
- hormonal imbalances, for example, during puberty or pregnancy.
Symptoms of the disease
Papillomas in women are most often located on the external genitalia. When there is a large accumulation of them, they can resemble the comb of a rooster. If women have genital warts in the groin, they can be distinguished by their long stalk. Due to increased humidity and sweating, papillomas in the groin are injured and can become inflamed.
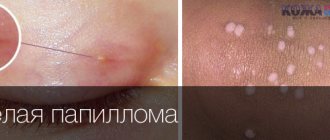
The most dangerous are flat condylomas in intimate places. They are provoked by genotypes of high oncogenic risk. Such a papilloma on the labia slightly rises above the mucous membranes and rarely merges with the rest into large formations. They are quite difficult to notice when they first appear.
Women with HPV may experience the following symptoms:
- Pain and itching in the genital area.
- Nonspecific vaginal discharge.
- The labia are slightly swollen.
- Irregularities and small compactions in the intimate area.
New growths may appear on the pubic area and other areas. Papillomas of the vulva and vagina are observed quite often. Regardless of their location, mandatory removal is required.
When condylomas form on the cervix, the following symptoms occur:
- Pain of unknown origin in the lower abdomen.
- Bloody issues.
- Weight loss and loss of appetite.
- Discomfort and pain during sex.
With these symptoms, a mandatory colcoscopy is required to rule out a precancerous condition, and if so, begin timely treatment. In this case, it is impossible to diagnose the disease yourself.
Symptoms and diagnosis
Of course, in most cases, the appearance of papillomas and warts in the vagina goes unnoticed by the patient. At the initial stage, they are tiny in size, making them difficult to detect on your own. But when the formations reach large sizes, they can be injured during sexual intercourse or during shaving. Because of this, a woman may experience extremely unpleasant symptoms, and blood discharge will be noticeable on her underwear.
Genital warts at their base secrete a clear liquid that smells bad. The disease can be prevented from getting worse if the woman promptly pays attention to the following symptoms:
- Activation of HPV in the body provokes unpleasant, profuse vaginal discharge that smells bad.
- If sexual intercourse becomes accompanied by pain, this may indicate infection with the human papillomavirus. In its advanced form, the pathology can provoke dysplasia and erosion, as well as subsequent rash of condylomas.
- If the papillomas have reached a large size, the woman may feel the presence of a foreign body in the perineum.
- Burning, swelling, itching, irritation and many other uncomfortable symptoms always precede the imminent appearance of dangerous genital warts.
- Minor bleeding during and after sexual intercourse quite often occurs in the process of rubbing and traumatizing the formations.
- Abundant vaginal discharge and nonspecific moisture on the surface of the genital organs may indicate that genital papillomas have merged into multiple foci.
- If the condylomas have spread to the internal parts of the genitals, the patient may experience severe external swelling.
It is worth noting that it is forbidden to independently determine the diagnosis, since each symptom must first be discussed with a gynecologist. Only thanks to modern diagnostic techniques can a specialist confirm or deny the presence of HPV.
Only a qualified specialist can make an accurate diagnosis. Self-medication is strictly prohibited, as this can result in very tragic consequences. For high-quality diagnostics, specialists use several basic manipulations:
- Step-by-step history taking. The doctor must know exact information about how long ago the papillomas appeared, as well as whether there was unprotected sexual intercourse and how long ago.
- A thorough examination and sampling of affected epithelial cells for further PCR research.
- Laboratory determination of the type and number of pathogens.
- Colposcopy. Examination of the condition of the vagina to identify affected areas. A special device is used to carry out the procedure. The cervix must be stained with iodine solution.
- Linked immunosorbent assay. Allows you to confirm the presence of beneficial antibodies to HPV in the patient’s body. Based on the data obtained, the doctor can draw a conclusion about the degree of development of the pathology.
- A universal cytological examination, which is aimed at detecting damaged areas.
- Anoscopy. A qualitative examination of the anal area to exclude the possibility of papillomas.
- Oncocytology. Laboratory study of cells in scrapings taken from the cervical canal and cervix.
HPV during pregnancy
Pregnancy is a time of hormonal disruptions and weakened immunity. This is why papillomas in the groin area and vagina appear during this period if the virus was detected in the body. But it is worth understanding that HPV is not any contraindication for pregnancy. With it you can carry and give birth to a child.
If the appearance of papillomas on the female genital organs is accompanied by dysplastic changes, then the issue of treatment is decided on an individual basis. It is worth knowing that the disease can be transmitted to the baby. Papillomas may later appear in the baby’s larynx area. But in any case, HPV treatment cannot be carried out during this period.
Treatment methods
In laboratory conditions, it has been proven that the risk of developing a malignant tumor in the affected areas increases if the condylomas are repeatedly injured during intimacy, as well as during routine hygiene procedures. The final course of treatment depends on the current symptoms, as well as the intensity of growth of skin lesions. If the patient does not have pronounced degenerative phenomena, then specialists prescribe conservative treatment with the mandatory use of local drugs.
If there are large papillomas on the organs that cause unpleasant symptoms, then, at the patient’s request, she may be prescribed surgical methods to remove the growths. It is worth noting that in such a situation it is strictly forbidden to resort to home therapy and traditional recipes, as this is fraught with serious complications. Specialists try to improve the well-being of such a patient with conservative medicinal gels, ointments, as well as solutions with antiviral and immunostimulating effects.
Positive results have been repeatedly seen after using the following medications:
- Suppositories - Alpizarin, Lykopid.
- High-quality solutions - Condilin, Verrucide, Feresol.
- Ointments - Cycloferon, Viferon, Solcoderm.
If the papillomas are too large, then surgical and hardware treatment may be necessary. The final choice always depends solely on the patient. The following procedures have the greatest effect:
- Universal cryotherapy with cauterization at low temperatures. This is one of the most popular methods for removing warts on the genitals. Depending on the size of the lesion, multiple treatments may be needed.
- Traditional surgical method of excision of benign tumors. Prescribed only in extreme cases. Since this treatment method is invasive, the recovery period takes a long time. Small scars may remain on the genitals.
- The radio wave method with excision with a special knife is used only under anesthesia, since there is a risk of high pain shock. The recovery period may take two weeks.
It is worth noting that the most gentle laser method for removing papillomas in the vagina. In half an hour you can get rid of all growths on the genitals. Recovery takes 24 hours. But this method is ineffective for giant formations.
Diagnostics
In order to prescribe the correct treatment, it is not enough to conduct a visual examination, even if there are papillomas of the vulva and vagina. The HPV genotype plays a major role. It can be established using PCR diagnostics. The analysis is similar to a regular smear in women in gynecology, which is taken with a special brush. DNA testing is carried out to identify the smallest viruses that may be in latent form.
There are other tests, but PCR is the most reliable and is performed in almost all laboratories. Digene has proven itself well - a test that also detects the virus, indicates its quantity and degree of oncogenicity, but it is not performed everywhere and has a high cost.
Prevention
HPV is a dangerous virus that can lead to a number of complications.
To avoid HPV infection and the formation of papillomas in the vagina, women should adhere to preventive measures and recommendations.
These include:
- maintaining intimate hygiene;
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle;
- no abuse of tobacco and alcohol products;
- regular examinations by a gynecologist;
- use of barrier methods of contraception during sexual intercourse;
- increasing immunity (regular consumption of vitamin complexes, minerals and trace elements);
- maintaining a proper balanced diet.
Remember, at the first sign of unwanted growths, you should consult a doctor. Visit the nearest dermatovenerological clinic to prescribe the correct treatment.
Treatment
Treatment of papillomas on the labia consists not only of removing tumors, but also of antiviral therapy and strengthening the immune system. Only the attending physician can prescribe effective antiviral drugs, depending on the individual characteristics of the body.
Most often used:
- Panavir.
- Vikferon.
- Reaferon.
- Gropronosin.
It is necessary to treat HPV with antiviral drugs for a long time. The course of treatment may take several months. In order to evaluate the success of therapy, a study is carried out to quantify the virus. Finding an effective drug is quite difficult, since the virus is too stable.
Removal of genital warts on the perineum is possible using the following methods:
- Electrocoagulation. Removal occurs through electric current. Papillomas on small or other areas of the body receive an electrical burn, after which a crust forms, which heals in about 2 weeks. A rather painful method that can lead to burns of healthy tissue.
- Surgical removal. It is performed very rarely in the case of malignant neoplasms of the vagina. May cause scarring and bleeding.
- Cryodestruction. It is the removal of papillomas on the vulva with liquid nitrogen. Under the influence of low temperatures, the neoplasm is destroyed. The procedure is painless, but if the doctor is inexperienced, it can cause frostbite to adjacent tissues.
- Radiocoagulation. High frequency affects tumors and destroys them painlessly. One of the best ways to remove vaginal papillomas, as it does not lead to scarring or bleeding.
- Laser removal. Allows you to remove papillomas from almost any part of the body. After the procedures, minor discomfort is possible.
Before removing tumors, it is worth eliminating the causes that caused the activation of the virus. It is important to know what papilloma is, since it is simply an accumulation of viral cells on the surface of the skin or mucous membranes. If antiviral therapy is not carried out and the immune system is not strengthened, neoplasms may arise again.
Removal is possible using special alkali solutions. Regardless of the method chosen, viral pathology must be removed by the treating specialist. When independently using chemicals with active chemicals, many people received severe chemical burns.
Products for external use:
- Solcoderm.
- Condilin.
- Verrucacid.
The most effective remedy for removing genital warts is Solcoderm. In most cases, one use of this remedy is enough to get rid of tumors. However, this drug should be applied by a doctor who can avoid affecting healthy areas of the skin.
There are also more aggressive agents, the removal of which is undesirable on mucous membranes. For example, super celandine can be applied to the pubis and other areas of the body. This remedy is a solution of alkalis and acids, and papillomas are removed by cauterizing them. If the chemical is applied to the genitals, you can get burned.
If there is at least one sign of the appearance of HPV in the body, you should immediately contact a specialist. Papilloma in gynecology is not just a cosmetic defect, but a high risk of developing oncogenic neoplasms. Treatment at an early stage reduces the risk of malignant degeneration and helps drive the virus into a dormant state.
How to get rid of papilloma on the genitals
Modern medicine still does not have radical methods to eliminate the disease; it is not capable of destroying HPV. Therefore, conservative therapy coupled with surgery pursues the following goals:
- strengthening the immune system;
- removal of condylomas prone to spreading;
- decrease in the concentration of HPV in the body.
Drug treatment of papillomas on the labia is carried out with ointments or aerosols.
The most effective remedy for vaginal papillomas are suppositories.
Papillomas in the vagina can be removed surgically or using hardware.
Drugs from the pharmacy
Conservative treatment of papillomas on the labia is recommended only in cases where the disease is caught at an early stage or the insignificant activity of the virus does not yet pose a danger to the patient.
- Immunomodulators remain the basis of drug treatment. To prescribe the optimal drug, the patient’s immune status and her sensitivity to certain medications are first checked. They correct immunity with Viferon, Galavit, Immunofan, Isoprinosine, Interferon, Larifan, Neovir, Cycloferon. The concentration of HPV is reduced by antiviral drugs (Alpizarin, Likopid).
- Epigen antiviral aerosol is used to treat the labia and vaginal walls. It can be replaced with Oxolinic ointment, Riodoxol.
- To destroy papillomas cells, an external antitumor drug, Podophyllotoxin, based on plant materials, is prescribed. Feresol is an aggressive agent, so it is used when the growths are single. Otherwise, its effectiveness is low, and the risk of getting a burn is high. They also use salicylic acid, Imiquimod, Cryopharma, lapis pencil, and Supercelandine. It is forbidden to carry out such cauterizations at home - the procedure is performed by a doctor.
- To localize the affected area in the vagina, vaginal suppositories are prescribed. Their advantage over ointments is undeniable: it is difficult for the latter to have an effect without deep application. In addition to the antiseptic effect, these dosage forms help increase local immunity (Betadine, Genferon, Gravagin, Panavir).
- If condyloma is found in the vagina during pregnancy, then Interferon is prescribed, and local drugs include Galaderm, Solcoderm.
Surgical method
Large neoplasms cannot be cured, so removal of papillomas in the vagina is sometimes the only way out. Surgical excision is practiced extremely rarely - only in cases where the use of other methods is impossible. For example, if the area of the vagina where papillomas have grown has a diameter of more than 10 cm, or when it is necessary to save the affected tissue for histological examination.
This is due to a high risk of trauma to the vaginal mucosa and potential wound infection. During the operation, local anesthesia and a regular scalpel are used. After excision, the wound is sutured, it waits for a whole month to heal, and scars often remain in the vagina. Therefore, it is better to choose a method from less traumatic and relatively new methods.
Hardware removal
Genital warts growing in the vagina cause not only pain, but also significant psychological discomfort. Therefore, removal of vaginal papillomas is the best solution when the risk of cancer is high. Such growths must be removed immediately. There are several ways to remove dangerous interference:
- Cryodestruction - freezing papillomas with liquid nitrogen. The procedure does not bring any unpleasant sensations; patients note only a slight tingling sensation. Thanks to freezing, the growths first darken and fall off after a few days. No scars are formed.
- Laser surgery is an effective way to get rid of growths. This beam quickly (in 1 minute) and completely evaporates pathological cells. This operation is completely painless, there are no traces of the intervention left, and the wound heals quickly.
- Radiosurgery. Elimination of papillomas occurs under the influence of high-frequency radio waves. The method is used for small and shallow lesions.
- Electrocoagulation. The base of papillomas (or entire groups) is cauterized with electric current. Not suitable for every type of growth; it is used in advanced cases.
Any hardware removal method requires the use of immunocorrective agents and antiviral drugs, otherwise relapses of the disease will occur again and again.
Destruction of papilloma without special drug therapy leads to relapse of the disease in 50–75% of cases.
The regimen must be selected by a doctor. You need to start taking medications a month before removal of tumors and continue for another 30 days after it. This approach minimizes the risk of encountering papillomas and condylomas in the near future.
Will folk remedies help?
The use of such an alternative method when localizing tumors in a delicate area is strongly discouraged. Additional therapy does not guarantee a cure, but can cause serious harm. Self-treatment of papillomas on the genitals is fraught with dire consequences.
Those products that are used for warts on other, external parts of the body most often contain extremely aggressive active ingredients. These are acids, alkalis, as well as poisonous juices of medicinal herbs. These compositions help to quickly destroy pathology on the skin, which is very dangerous to do on the delicate mucous membranes of the intimate area.
The only remedies that are not prohibited are decoctions and infusions of herbs that increase the body's defenses. But even in this case, consultation with an immunologist is necessary, because a potentially serious disease requires an adequate response.
How to remove papillomas in the vagina
- 01 August
- 0 rating
Often women go to the doctor with a delicate problem - the occurrence of papilloma in the vagina. However, not many people know what it is and how dangerous such growths are. Therefore, it is worth considering the characteristics of vaginal papillomas, as well as understanding what methods of treatment and removal of tumors in intimate places exist.
Development of papillomas
The appearance of papillomas on the human body is provoked by a specific papillomavirus, which is transmitted from a sick person to a healthy one. It manifests itself in the form of growths localized on the skin or mucous membranes. Vaginal papillomas, as well as neoplasms on other genital organs and the anus, are called condylomas. They come in 2 types:
- Pointed (exophytic). Genital warts are most often benign formations. They rise above the surface of the skin and look like a sharp papilla.
- Flat (endophytic). Such papillomas grow inside the epithelium, which causes changes in it that can provoke the transformation of a benign growth into a cancerous tumor.
HPV, which causes vaginal papillomas, has more than 100 strains. Some of them are relatively harmless and appear as benign formations, others have oncogenic properties. Depending on the degree of risk of cancer cells, papillomaviruses can be divided into the following groups:
- low-tumorigenic;
- moderately oncogenic;
- highly oncogenic (strains 18 and 16 are especially dangerous for women).
That is, all strains of the virus that cause vaginal growths are potentially dangerous and can lead to the appearance of cancer cells in the absence of appropriate treatment. Therefore, if vulvar papilloma appears, you should consult a doctor.
How does papilloma occur in the vagina? First of all, a person must become infected with papillomavirus. There are several ways of transmission of infection:
- Contact. Often papillomas at the entrance to the vagina occur as a result of unprotected sexual intercourse with a carrier of the virus. The papilloma virus is also transmitted through anal and oral sex.
- Domestic.
This method of infection involves the use of personal belongings, underwear, hygiene items (soap, towels) that belong to the carrier of the virus. - From a mother to her child. If the mother has condylomas on the mucous membranes of the genital organs, then there is a high risk of infection of the fetus during childbirth.
- Autoinfection.
This method involves getting infected during depilation or shaving if there are microdamages in the vagina.
Vaginal papillomatosis is manifested by the appearance of neoplasms in the following places:
- inside the vagina;
- on the vulva;
- on the walls of the vagina;
- in the area of the vaginal vestibule;
- on the uterine cervix.
Once HPV enters the body, it remains there forever. The incubation period lasts from several weeks to several years. Only in the presence of certain factors does it become activated and manifest itself in the form of growths in the genital area.
Main characteristics
How to determine the presence of papillomas in the vagina? To do this, you should pay attention to specific symptoms. First of all, you need to figure out what papillomas in the vagina look like. There are several characteristic signs:
- The size of genital warts is small (up to several millimeters).
- As a rule, vaginal papillomas appear not one at a time, but in whole families at once.
- They are localized in the vaginal area (on the labia minora and majora, on the clitoris), on its walls, and also on the cervix.
They can also be located in the anus and rectum. - The color of the formations ranges from light (skin color) to red and dark brown.
- The surface of the papilloma is lumpy and rough. Externally, the growth resembles a cauliflower inflorescence on a thin stalk.
- Condylomas tend to merge, forming one large growth.
If there are papillomas in the genital and anal areas, the following unpleasant clinical signs are possible:
- itching and burning sensation;
- discomfort;
- when the growths are damaged, pain occurs;
- there is a smell of rot;
- white discharge occurs, sometimes with blood or pus;
- discomfort and pain during bowel movements, urination or sexual intercourse.
If such signs appear, you must urgently seek qualified help. If treatment is not started on time, complications may occur.
For women, the most dangerous are papillomas on the cervix, as they can cause cancer of this organ.
Genital papillomas may not appear even in the presence of a virus. To do this, you should monitor your health, eat right and improve your immunity.
Why do papillomas appear on a woman’s genitals, what are the reasons for the activation of the human papillomavirus? It can remain in the body for many years without manifesting itself.
But in the presence of certain factors, the papillomavirus begins to multiply, manifesting itself in the form of genital growths. When papillomas appear in the vagina, the reasons may be as follows:
Weakening of the immune system. This may be affected by:
- long-term treatment with antibiotics;
- poor nutrition, starvation, irrational diets;
- stress;
- hypothermia;
- overwork (physical or emotional);
- infectious (including venereal), metabolic diseases;
- presence of cancerous tumors.
- Hormonal imbalances.
Most often they are observed in adolescents during puberty, women during pregnancy, lactation and menopause, with long-term use of drugs containing hormones. - Hypovitaminosis. Most often it occurs due to poor or improper nutrition.
- Neglect of personal hygiene rules.
- Venereal diseases.
Papillomas in the vagina: causes, symptoms, treatment
Papillomas in the vagina are benign formations (condylomas) localized on the vaginal mucosa, caused by the activation of the human papillomavirus (HPV), which provokes tissue proliferation.
Factors of occurrence
The virus can enter the human body through microtraumas on the mucous membranes and skin. Microscopic cracks are invisible to the human eye, but for the virus they can be the best way to penetrate.
The main methods of infection with HPV:
- Contact-household way. Infection occurs through contact with an infected person through the use of shared hygiene items. These could be towels, a sponge for washing;
- Unprotected sexual intercourse. Transmission of infection occurs through the natural secretions of an infected partner that fall on the mucous membrane of a healthy person, microtraumas resulting from external influences. Infection can occur through traditional sex, as well as oral and anal sex.
Having penetrated the body, the virus can remain dormant for a long time. The following factors can trigger its activity:
- Decreased immunity. The weakening of the body's defenses can be facilitated by exacerbation of chronic diseases, long-term use of medications, disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract, addictions, physical and nervous overload, improper diet, vitamin deficiencies;
- Hormonal disorders that may occur due to age-related changes (menopause), pregnancy, pathologies of the endocrine system;
- Infectious and inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system:
- Vulvovaginitis;
- Endometritis;
- Adnexitis;
- Chlamydia.
Types of vaginal formations
Microgrowths localized on the vaginal mucosa are represented by 2 types:
- Exophytic form. The growths of this species have a pointed shape with a papillary surface. Exophytic growths have a low risk of degeneration into cancer;
- Endophytic. The formations have a flat shape, growth occurs deep into the mucosal epithelium. Endophytic microscopic warts can change healthy tissues; if not treated in a timely manner, they can provoke the development of pathological processes in tissues and the occurrence of cancerous tumors.
Symptoms of papilloma in the vagina
Multiple growths and a single papilloma in the vagina often develop asymptomatically. In most cases, they are diagnosed during a random examination by a gynecologist. You can independently identify only vulvar papillomas, which are located on the surface of the mucous membrane of the external genitalia.
Symptoms indicating the presence of condylomas are as follows:
- Painful sensations during sexual intercourse. There is an active effect on papillomas, due to which they are injured, irritated, and pain appears;
- Copious mucous discharge, often streaked with blood;
- Small blood spots on underwear that occur when tumors are injured;
- Swelling of soft tissues.
The occurrence of one of the symptoms of vulvar condylomas requires immediate examination by a gynecologist.
In the case of uncontrolled growth, microgrowths can appear in new areas of the mucosa, forming islands that can completely close the entrance to the vagina.
Injury to growths can lead to their degeneration into cancer. You can see what papillomas in the vagina look like in the photo.
Diagnosis of papillomas on the vaginal walls
Diagnosis of papilloma virus in the vagina is carried out in stages. Each study is of great importance, allowing a specialist to make an accurate diagnosis.
The necessary diagnostic procedures include:
- Examination by a gynecologist. The doctor determines the extent of vaginal papillomatosis and its location. The characteristics of a particular patient are taken into account: how long ago the growths appeared, lifestyle, the presence of chronic diseases of the reproductive system;
- PCR studies. The analysis confirms the presence and quantity of viral agents in the body. The study provides complete information about the type of virus (oncogenic or non-oncogenic) of papilloma in the vagina;
- Examinations with a colposcope (colposcopy). The procedure allows you to determine damage, lesions, and the condition of the walls of the organ;
- Anascopy. The method involves a detailed examination of the anus for the presence of formations in it. The study allows you to detect lesions, pathogenic cells are studied and their main characteristics are clarified;
- Histology. The study allows us to study in detail the structural changes in areas of the mucous membrane when papillomas occur inside the vagina;
- An oncocytological study, for which it is necessary to scrape an area of the cervix and take a tissue sample of the cervical canal. The resulting materials are studied to detect pathogenic cells.
After carrying out diagnostic measures, the gynecologist will clearly determine a set of therapeutic measures. The doctor will explain to the patient what to do if papillomas in the vagina grow, cause discomfort and interfere with a full life.
Treatment of papillomas in the vagina
Based on the diagnostic results and examination, the specialist will decide how to treat papillomas in the vagina.
Medication will help in the fight against growths and suppress the activity of the virus. For this purpose, antiviral drugs are used in the form of tablets and suppositories. Betadine suppositories, which have an antiseptic effect, are effective in eliminating vaginal papillomas. The drug actively destroys the causative agent of infection, fungi and bacteria.
Vaginal suppositories Viferon, Genferon, Panavir are often prescribed. The active components of suppositories are not absorbed into the blood. Suppositories have antiviral and immunomodulatory effects.
To strengthen the body's defenses, experts prescribe Likopid and Isoprinosine tablets. Medicines are used for relapses and severe infections.
Treatment of vaginal papillomas in expectant mothers is carried out by externally affecting the affected tissues using physical methods and antiviral drugs that suppress viral activity and stimulate the body's immune forces.
In some cases, experts allow treatment of vaginal condylomas with folk remedies used in combination with drug therapy:
- Suppositories with sea buckthorn oil, which is characterized by antibacterial properties and has a wound-healing effect;
- To treat vulvar papillomatosis, a solution based on tar or laundry soap is used. The product has high antiseptic characteristics and is effective in the treatment of papillomas localized on the external genitalia.
Removal of papillomas in the vagina is carried out using innovative hardware techniques:
- Laser, the effect of which is the most painless and safe;
- Cryodestruction - freezing the microgrowth with liquid nitrogen, as a result of which the papilloma tissue is destroyed and the formation dies;
- Electrocoagulation, the essence of which is to burn out papilloma with alternating current;
- Exposure to radio waves (radio knife). The problem of papillomatosis is eliminated as quickly as possible, the recovery period is minimal. Removal with a radioknife eliminates the risk of inflammation in the postoperative period. The sterilizing effect ensures rapid healing of mucosal tissues.