Nail fungus, what tests to take
So, let's figure out what tests patients need to undergo for onychomycosis.
- First, a general blood and urine test. These procedures are performed both before the start of treatment and at the end (to determine its effectiveness). They will help identify the stage of development of onychomycosis, minimize side effects from antifungal agents,
- If toenail fungus is observed, the analysis should be microscopic. Simply put, the biological material (in this case, a piece of the damaged nail plate) is examined under a microscope.
- Another type of test for nail fungus is microbiological culture. Biological material with the suspected pathogen is placed in optimal conditions (nutrient medium plus optimal temperature) and the growth of the culture is observed. The advantage of this method is that while colonies of microorganisms are growing, they can be tested for sensitivity to certain antifungal drugs.
- They may also prescribe a PCR test aimed at searching for RNA or DNA of the pathogen.
How to test for nail fungus
The collection of biological material takes place in the dermatologist’s office. Using a scalpel, the specialist removes the top layer from the affected nail plate. Further uses this in microscopic, microbiological and PCR analysis. This procedure will be absolutely painless and will not bring any discomfort.
Sowing for a fungus
One of the types of microbiological research. The material for research is a scraping from the nail plate. It is placed on a nutrient medium and waited for some time for the pathogen to grow. Depending on the type of fungus, growth can take several days to weeks. When a colony of a microorganism is identified, it is examined under a microscope. A laboratory diagnostics doctor identifies the type of organism. It is possible to determine the sensitivity of the fungus to various medications.
Important!
This must be done for effective treatment.
PCR analysis for fungus
The polymerase chain reaction identifies the fungus by its nucleic acid. This method is accurate and highly sensitive. For PCR, a scraping is taken from the nail. DNA is released from the material, and sections of nucleic acid are divided many times. The doctor determines whether there is an infection and what type of fungus this patient has. In laboratory conditions, a fungus is grown using DNA fragments and its type is determined. The technique takes place in four stages. At the first stage, biomaterial is prepared for subsequent copying; sections of nucleic acid are separated. They are filled with special substances. They are different for each type of fungus. At the second stage, the nucleic acid is combined with reagents. This is done at high temperature. If there is fungal DNA in the sample, it is detected and noted. In the third stage, the nucleic acid undergoes multiple copies. At the final stage, the pathogen is determined and a conclusion is made about the type of fungus.
Microscopy for fungus
This study is carried out if mycosis is suspected. The substrate for examination will be part of the affected nail plate. The material is collected at the border of the pathological focus. As a rule, the largest amount of the pathogen is located there. The biological agent is treated with various substances or dyed. Then the doctor examines under a microscope.
Microscopic examination is of two types:
- the presence of opportunistic flora, determining whether it is normal - this is a qualitative analysis;
- The type and amount of fungus is determined, as it looks under a microscope - this is a quantitative analysis .
Microscopy allows you to confirm or exclude the diagnosis. This study is done over three days.
Causes of false positive fungal tests
Errors in analysis results do occur. There are a number of factors for the appearance of a false positive conclusion for the fungus. For example, a person did not properly prepare for collecting material. The result of the analysis will be inaccurate, quite possibly a false positive. A lot depends on the laboratory. Collection of biomaterial should be carried out only with a sterile instrument. The test tube must be original and the packaging must be intact. If one of these items is contaminated with fungi, the test result will certainly be a false positive. The reliability of the research procedure depends on the laboratory assistant. Hands must be wearing sterile gloves. This will prevent contamination of biological material. If you do not violate the procedure for preparing for analysis, there should be no erroneous results. It is better to contact a trusted specialist or a specialized laboratory.
Causes of false negative fungal tests
No one is immune from incorrect results of laboratory tests for fungus. What if the patient takes antifungal medications on his own during the delivery of the material? Then the study will show a negative result, but the fungus will be in the body. On the eve of blood sampling or scraping, the person steamed his nails and used hygiene products. In this case, the result will be false negative.
Remember!
The material must be taken from a specific area where there is a sufficient amount of the pathogen.
It is difficult to take a sample with deep mycosis, when the pathogen is absent in the superficial areas of the nail. Sometimes sampling occurs from an area where the concentration of the pathogen is low. Then the conclusion will be negative for the presence of fungus. Conducting laboratory diagnostics using low-quality reagents also leads to unreliable results.
Taking a blood test for fungus in the body
Mushrooms surround a person throughout his life, and after it too. And there are a huge variety of them, ranging from household mold to severe tropical fungal infections. But what unites everyone is the implementation of the pathological process only in specific favorable conditions. Whether this process has begun and how advanced it is can be found out by taking a blood test for fungus in the body. What kind of analysis - let's figure it out!
Etiology
The etiological factor is fungi, saprophytes and absolute pathogens. The first group exists in the human body in quantities of up to 3 logarithms and normally does not cause discomfort. The second group includes fungi from the surrounding world, which, if they enter the macroorganism, can cause disease.
Infection occurs in the following ways:
- from environmental objects;
- from animals;
- from a person;
- by activating its own opportunistic microflora.
When encountering a fungus, not everyone can get sick. First of all:
- persons with reduced immunity;
- persons with altered immunity.
If local protection is violated, dysbiosis develops (for example, vagina or oral cavity) and candidiasis develops against a pathological background.
With severe immunodeficiency caused by HIV, the use of cytostatics, and oncological therapy, the fungal flora does not stop at damage to the dermis.
Severe visceral mycoses develop:
- aspergillosis;
- histoplasmosis;
- mucorosis, etc.
Chronic diseases deplete the immune system, and they also have a constant source of inflammation. Add here periodic courses of antibiotic therapy and we get ideal conditions for the development of a fungal infection.
Antibacterial drugs kill not only pathogenic bacteria, but also representatives of normal flora. The mushrooms themselves are sensitive to a specific group of drugs. But against a sterile background they grow beautifully, causing an inflammatory process.
Patients with diabetes are a tasty morsel for mushrooms with a “sweet tooth.” In addition to the body's impaired resistance to infection, people with diabetes have permanently elevated blood sugar and altered acidity.
Clinical picture
There are 5 types of fungal infections:
- dermatomycosis;
- keratomycosis;
- candidiasis;
- systemic or visceral mycoses;
- pseudomycoses.
Dermatomycoses
This disease causes skin lesions. The causative agents are a group of dermatophyte fungi:
- favus;
- athlete's foot;
- microscopy;
- trichophytosis.
Infection occurs through contact with soil, animals and a sick person. Rounded areas of hyperemia appear, accompanied by itching. Subsequently, the spots are covered with scab.
With dermatophytosis, the hair follicle is involved in the inflammatory process:
- it is destroyed;
- hair falls out;
- bubbles with cloudy purulent and hemorrhagic contents and crusts appear.
Inguinal dermatomycosis manifests itself:
- pustular rashes;
- redness;
- peeling.
Keratomycosis
With lichen versicolor, pink-coffee spots with scalloped outlines appear, which subsequently become covered with peeling.
Actinomycosis appears upon contact with cereal crops - mill workers get sick, and the following appear:
- cyanotic nodes;
- gummas;
- fistulas
In addition to skin manifestations, visceral pathologies are characteristic. Piedra affects the hair, but only causes aesthetic discomfort.
Candidiasis
This disease can be different:
- seizures in the corners of the mouth;
- thrush in women;
- severe systemic diseases (esophagitis, pneumonia and sepsis).
They are united by an etiological factor - “sweet tooth” fungi of the genus Candida. Normally, they exist in the body of every person and do not cause harm.
Visceral and systemic mycoses
Visceral develop:
- when encountering a large number of fungi;
- with decreased immunity;
- in the absence of normal flora - the so-called “good” bacteria.
All fungi are sensitive to the pH environment, and this acidity is controlled by other microorganisms of normal human flora.
Systemic mycoses include:
- histoplasmosis;
- coccidioidosis;
- blastomycosis;
- cryptococcosis;
- geotrichosis;
- chromomycosis;
- rhinosporidiosis;
- aspergillosis;
- penicillinosis;
- mucorosis
Their main symptoms are associated with pathology of the lungs, heart or gastrointestinal tract, and skin lesions are not the main symptom.
At the same time, they develop:
- pneumonia;
- enteritis;
- sepsis.
All of them are difficult and difficult to diagnose and treat.
Pseudomycoses
This disease occurs under the guise of fungal infections, but the etiological factor is bacteria.
Diagnostics
This section describes 4 methods for diagnosing fungus in the human body.
Microscopic method
It is aimed at detecting fungal elements:
- yeast cells;
- pseudomycelium;
- mycelium;
- conidiophores;
- conidium;
- tissue forms of deep mycoses.
Smears are made on glass and examined under a microscope by a medical specialist. Material for microscopy is taken from the lesion or at its border.
Culture method
A blood test for fungus in the body is necessary to determine the antibiotic sensitivity of fungi. The culture grown in a Petri dish is examined in an analyzer with various antibacterial drugs.
For fungal infections, blood culture tests are performed using:
- the blood itself for the fungus;
- cerebrospinal fluid;
- sputum;
- urine;
- feces;
- washing fluid from the bronchi, maxillary sinuses;
- bile;
- discharge from fistulas and ulcers;
- mucous discharge;
- pieces of fabric;
- scales of nails and hair.
Serological studies
These studies are aimed at determining specific antibodies to fungi in human blood. Immunoglobulins M and G are detected.
The following mycoses are diagnosed using this method:
- Aspergillosis;
- Histoplasmosis;
- Penicillinosis;
- Mucorosis;
- Cryptococcosis;
- Blastomycosis, etc.
PCR method
Detection of fungal DNA by PCR is an accurate analysis that allows you to quickly determine the presence of a fungus in a person’s blood or other environments of the body.
Treatment
Fungal infections are often more difficult to treat than bacterial ones. Treatment is divided into:
- etiotropic - aimed at destroying the fungus;
- symptomatic.
Antifungal drugs include:
- Ambizome;
- Amphoglucamine;
- Ampholip;
- Amphotericin B;
- Levorin;
- Levorina sodium salt;
- Mycoheptin;
- Nystatin;
- Pimafucin;
- Travogen.
The drugs are used externally and internally, for systemic mycoses (histoplasmosis, aspergillosis, mucorosis) intravenous and inhalation.
Treatment of fungal diseases takes a long time - from 2 weeks to a year - depending on the identified pathogen and the clinical picture.
Symptomatic treatment of the fungus is aimed at:
- to maintain life;
- reducing symptoms of organ dysfunction.
Appointed:
- glucose-saline solutions;
- antihistamines and decongestants;
- antidiarrheal drugs;
- corticosteroids, etc.
Surgical treatment is used for aspergillosis - lesions in the lungs are excised. If the vessels are affected by the fungus, arterial embolization is performed.
Prevention
Personal prevention is as follows:
- compliance with personal hygiene rules;
- use of individual manicure and pedicure accessories;
- wearing personal shoes when visiting swimming pools, baths, saunas;
- lack of contact with unknown and homeless animals without protective equipment;
- use of a respirator, gloves and protective suit in hazardous work;
- treatment of chronic diseases;
- blood sugar control;
- maintaining a normal weight and physical activity;
- adequate antibiotic therapy;
- treatment of sick family members.
Conclusion
Fungal infections cause discomfort and harm to human health. Timely prevention will help avoid infection. And if the disease does begin, adequate treatment prescribed by a specialist is necessary. And then you can say goodbye to the fungus forever!
gribokbolezn.ru
Decoding tests for fungus
Different types of tests can confirm or deny the presence of infection in the body.
Important!
The result depends on the chosen research method.
Microscopy identifies the pathogen and determines whether there is a fungal infection. A quantitative culture test can be performed and a colony of fungi grows on the medium. In this case, the conclusion will be expanded. It is determined what type of fungus caused the disease - mold, ray, yeast. Its quantity is determined, which parts of the fungus are found. The polymerase chain reaction reveals the presence or absence of a particular fungus. If an enzyme immunoassay was performed, antibodies to the pathogen are detected in the blood.
results
If the test result is positive, this indicates that a laboratory test found fungal spores or mycelium in the provided biomaterial. The scraping result can provide only narrow information about the presence or absence of the pathogen. If the result is positive, then the dermatologist prescribes a wider examination of the sample, taking into account the patient’s symptoms and complaints.
To identify the DNA of a pathogenic organism, the biomaterial is placed in a special nutrient medium. As a result of cultural analysis, it is possible to more accurately determine the type of fungus and confirm the assumption with PCR results. In order to confirm the diagnosis, the doctor can confirm the result with multiple tests, which are carried out after a certain period of time. Depending on the analysis, the research result can be obtained within 2-3 days after collecting the biological material.
Lead times for analysis
Direct microscopy usually takes three to five days in a regular clinic. In a private center - no more than a day. The patient then receives the test result. In our specialized clinic, microscopy can be performed by a doctor during an appointment. Sowing biological material onto nutrient media takes a longer time. The fungi need to multiply and grow. Typically this procedure takes from a week to two. An undoubted advantage of the study is the ability to determine the sensitivity of fungi to antifungal drugs. With this method in mind, the doctor can easily prescribe an effective drug. The usual time to obtain results from polymerase chain reaction is three to five days. In our center - a day. The pathogen is almost unmistakably detected when its quantity is small in the material under study. This is an undeniable advantage. The method is modern, accurate, and has significant sensitivity. The enzyme immunoassay takes up to five days to prepare. During this time, it is determined whether there is an increase in antibody titer. In this case, there is an active infectious process in the body. It is caused by fungi.
How to test for fungi
In case of a fungal infection of the nails, material is taken for further research in the laboratory. For examinations, a small part of the nail plate and the skin next to it is sufficient. This manipulation is performed only in medical institutions by a dermatovenerologist. To collect material, use a scalpel, needle or scissors. Sometimes a sterile spatula is suitable if the nail is very crumbly. The biological substrate is taken from the places where the fungus had the strongest impact. To detect fungal spores, scales are collected using a spatula. The material is placed in a test tube with saline solution or a special container. Solid particles are dissolved in special substances. Then everything is sent to the laboratory department for further research. The procedure for collecting biomaterial is completely painless and is performed by a highly qualified specialist. To cure mycosis, the best option is to see a doctor early and get tested. Then effective therapy is possible, it will completely eliminate the disease.
Blood test for fungus in the body, how to decipher the analysis?
Blood in the human body never stands still, it is constantly in motion, under the action of the heart, like a “pump”, spreading throughout the body, ensuring its vital functions (breathing, nutrition, etc.).
This unique substance, with a unique composition, provides vital functions for the body.
The science that studies blood is called hematology (the study of blood), which, in the literal sense, began its development after the invention of the microscope in the 17th century. Scientists and anatomists began to discover the constituent particles of blood in this “red” substance.
Theories about blood circulation began to emerge in the same century, but before, with the help of a microscope, medicine began to study blood cells. The paradox of science is that it developed separately in each part of the world, since in China they knew about blood circulation back in the 5th century, to give a trivial example.
This is how a medical breakthrough in Europe occurred in the field of studying blood and the human body as a whole.
But hematology only began to study blood diseases themselves, and began to suspect the causes of diseases in its composition only after several more centuries. And only at the end of the 19th century, Ilya Mechnikov (a native of the Kharkov province) discovered to the world such a concept of medical science as phagocytosis - the absorption of viruses, bacteria and fungi by cells and tissues.
Fungi “feel” comfortable in the human body, and if suddenly an environment favorable for their development arises (negatively affecting human health), then they actively begin their development, growing and spreading throughout the body, starting from the place where they began their development, gradually expanding the habitat, transferring to neighboring organs located next to those already affected by them. The fungus is dangerous because it releases its spores, which are quite resistant, even with treatment. Therefore, mushrooms need to be fought, but first they still need to be detected.
Thanks to blood tests, it is possible to determine the general condition of the human body (hemoglobin (hemo and globin) and blood sugar (level), many pathologies, changes in composition, deviations, it is important to establish with the help of tests - blood clotting, because this is vitally important to know when carrying out operations, if not for the tests, many people might not have been saved).
The role of a blood test cannot be overestimated, but science still does not know much, but suspects a lot; scientific research continues “its life.”
A blood test for fungus in the body makes it possible to see the picture of both the damage to the human body by a fungal infection and to determine the condition of the body and the stage of development of the fungus.
An analysis for the fungus must be carried out in order for the doctor to prescribe further adequate treatment.
Fungus symptoms
Fungal infections can affect the skin, brain, internal organs, nails, and can spread their foci to new (neighboring organs) territories of the human body, as a favorable habitat for them.
For the human body, some types of fungi are conditionally pathogenic, since they exist in the normal microflora of every person and play a role in certain functions of the body.
As soon as a person creates favorable conditions for them (diabetes mellitus, low immunity, pregnancy, genetic predisposition, etc.), the fungi begin to behave quite aggressively and develop quickly. There are other types of fungi that live outside the human body, but they don’t mind getting there and developing at the expense of human health, “eating” his health.
The symptoms of fungal diseases bring a person discomfort and stress, in advanced stages – itching and burning, and the rapid development of the disease with relapses.
- Itching.
- Burning.
- Peeling, peeling (nails, skin).
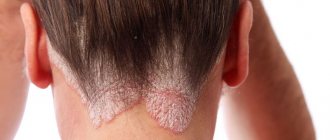
- If the fungus affects the scalp (seborrhea), it also affects the hair, it becomes either oily or dry, and may fall out.
- With thrush, extremely unpleasant symptoms also occur: discharge, itching, burning of the genitals. It is necessary to treat both yourself and your partner.
Diagnosis of nail fungus
A mycologist or dermatologist, after an appointment, and if there is a suspicion that the patient’s body has been infected with a fungal infection, will first of all refer you for tests (blood, urine).
A fungal test will give the doctor all the necessary information for further treatment.
Also, for fungal infections, they can take a scraping for the fungus, for example, a skin scraping for the fungus; you can also detect the fungus in a smear; there are also other tests for fungi.
Skin scrapings are taken to determine skin fungus, smears are taken to detect gynecological diseases, and other cultures are also taken to detect fungus.
Once you have been tested for fungus, your doctor can provide you with expert treatment assistance. Fortunately, fungal diseases are treatable, but they must be treated carefully following the instructions of the attending physician, and best of all, in a comprehensive manner.
Treatment of fungal diseases
To treat fungal diseases, medical science has come up with micro-preparations. For the treatment of fungal infections, attending physicians prescribe drugs that are new and high-quality (often expensive) according to the latest medical research.
Often prescribed: lamisil, mycaltin, miconazole, exoderil, for fungal infections of the scalp - nizoral shampoo, tar soap, there are many drugs and treatment methods, do not forget about analogues if prices are high.
Our wise folk medicine came up with many tools and techniques, using the knowledge of our ancestors, which was passed down from generation to generation for centuries; herbalists have been writing for centuries, describing herbs and their purpose in treatment.
It is important to adhere to the rules of personal hygiene in order to prevent the infection from spreading and infecting loved ones living under the same roof with you. It is also necessary to lead a healthy lifestyle, eat right (vegetables, fruits, cereals, less fat and carbohydrates) and increase your immunity, walks in the fresh air are useful, hardening and other procedures.
The main thing is not to delay it and not to self-medicate, both of which are dangerous to health.
gribok24.ru
Analysis for nail fungus in children
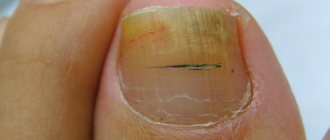
Nail fungus or onychomycosis is an infection of the nail plate by pathogenic fungi. Fungal spores enter the child’s body through a damaged nail plate. There is a high probability of infection when bare feet come into contact with a contaminated surface in the pool, shower and other common areas. The infected nail becomes cloudy or white, flakes, crumbles, and a white coating is visible on the plate. Striations, unevenness, and deformation of the plate appear without previous trauma. If you suspect onychomycosis, you should contact a dermatovenerologist. The clinical diagnosis is confirmed by the presence of the pathogen.
How is a scraping taken for fungus in newborns? To diagnose fungal infections, the KOH test is used. The laboratory technician takes material from the newborn from three areas:
- nail surface;
- hyponychium region - the lowest layer of the nail plate;
- subungual zone.
After which the drug is treated with a 10-30% solution of potassium hydroxide. Microscopy allows you to confirm the fungal nature of the pathogen. Using a culture test, the type of fungi is determined.
What fungal tests should a schoolchild take? The main method for diagnosing onychomycosis in school-age children is scraping from the nail plate and the KON test. Not only a piece of nail, but also hair and scrapings from the surface of the skin are used as biological material. If infection spreads, enzyme immunoassay can be used. ELISA determines the titer of antibodies in the blood of each type of fungus. Polymerase chain reaction is also an additional diagnostic method. Allows you to determine the presence of specific antigens in the body.
When should a child be tested for fungus?
If the color of the nail plate, the shape of the nail, or the presence of deformities change, you should contact a dermatovenerologist. If there is a case of the disease in adults in the family, the child should be tested. Onychomycosis at an early stage responds well to treatment. Treatment of nail fungus includes systemic and local therapy. Consists of trimming the nail plate and 2-3 courses of antifungal medications. After completion of treatment, follow-up after 1 year. Prevention is easier than cure. The best method is individual house shoes for each family member.
Types of pathologies
Fungal spores are able to withstand any temperature fluctuations from -60 to +100 degrees and retain their viability even when exposed to acids and alkalis. Therefore, when the fungus gets on the skin or into the body of a healthy person, it does not make itself felt for a long time and can remain dormant for several years.
But, as soon as a failure occurs in the immune system, microorganisms begin to activate on the mucous membranes, in the folds of the skin, scalp, and nails. Fungal pathology is classified into the following types:
- Dermatomycosis - affects the skin with an infection that feeds on dead epidermis, manifests itself in the form of flaky itchy spots and cracks. The nail plates change color, become deformed and split. Ringworm includes pathologies such as lichen, seborrheic eczema, and athlete's foot. The main pathogen is dermatophyte. Read more…
- Candidiasis – damage to the mucous membranes, nail plates, folds (for example, in women under the breasts), and the surface of internal organs. It appears as thrush - a white coating. The fungus can be detected in a smear from the affected mucous membranes.
- Aspergillosis is a fungus that affects the respiratory system. The symptoms are similar to those of tuberculosis. May be fatal.
- Histoplasmosis is a lesion of the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, pharynx, and surface of the ears. As the infection progresses, it spreads to the internal organs - liver, intestines, spleen. Manifests itself in the form of ulcers, continuous dry cough, pneumonia.
- Sporotrichosis is a fungus that affects the skin, lymph nodes and mucous membranes. May spread to internal organs and bone tissue. Symptoms are itchy ulcers, decreased sense of smell, sneezing, nasal congestion. We have already written on the site about how fungus manifests itself in the mouth and how to eliminate it.
Which doctor collects material for fungus?
You can get tested for fungi yourself in private laboratories. But this is not a convenient way, since the result should be visited by a doctor. The dermatovenerologist himself carries out the sampling and sends the material to the laboratory. As a rule, medical clinics have a laboratory department. On the day of delivery, the doctor will collect anamnesis, conduct an examination and conduct an initial consultation with the patient. Then you need to come straight to a dermatovenerologist for the result. In this case, you can do without unnecessary visits to laboratories. After receiving the results, the doctor will immediately make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment. The earlier therapy against the fungus is prescribed, the greater the chance of getting rid of it. Treatment is carried out until the pathogen is completely eliminated.
Where to get tested and which doctor to contact after
If you suspect nail fungus, your first step should be to see a doctor. A dermatologist deals with this problem. After a visual examination, the specialist will be able to make a presumptive diagnosis and write out a referral for the necessary examinations.
Tests can be taken either in a public medical institution or a private laboratory. The problem is that not everyone everywhere is involved in the specific diagnosis of mycoses. For example, identifying the pathogen using PCR is possible only in commercial structures. This is due to the need to purchase special equipment and reagents, which requires large material costs. Accordingly, the cost of this procedure is quite high.
Public tests, such as a general and biochemical blood test, are usually taken at a local clinic. Urine for testing, collected the day before at home in a sterile container, can also be taken there.
When the causative agent of the disease is identified, the doctor will prescribe specific treatment. After its completion, the tests are usually repeated. This is done to ensure that fungal nail infections are completely cured.
Where to get tested for nail fungus
To solve this issue, you can turn to the Internet for help. There are specialized resources that contain descriptions of clinics, their ratings, and comments about them left by real people. Also, if you are a resident of a big city, you can contact specialized agencies. They will immediately find you a laboratory or clinic to suit any budget.
If you need to get tested for nail fungus, contact the author of this article - a mycologist, dermatologist with 15 years of experience.
How to prepare for tests
Before you begin research, you need to figure out how to properly get tested for nail fungus. In order for the result to be as accurate as possible, you need to follow a few simple rules. It is important that three days before collecting biomaterial from the surface of the affected area of the body, no liquids come into contact with it. During the same time before the study, the use of local and general antifungal agents is prohibited. 10-12 days before the analysis is taken, cutting the edge of the nail with scissors is prohibited. From the moment the disease is detected until it is completely cured, the use of nail polish is not recommended!
As for the additional requirements for the patient before undergoing tests, they are as follows:
- biomaterial for research is given on an empty stomach in the first half of the day;
- the day before the test, alcoholic beverages are completely excluded;
- You must stop using any medications 72 hours in advance (if a person is forced to take vital medications every day, you should immediately notify your doctor);
- On the day of taking a clinical and biochemical blood test, you should refrain from smoking tobacco products, and also not drink coffee and tea.