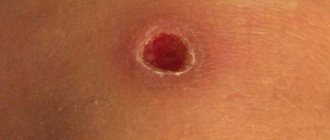
Histology of the mole
Moles are very popular formations on the body of a congenital or acquired type. They arise due to the accumulation of melanocytes in the skin, which, in turn, is due to the cells being overfilled with pigment. Moles can be localized in various parts of the body, and sometimes they pose a threat to health and life. In particular, the aggressive influence of ultraviolet radiation or mechanical damage can lead to the degeneration of such a benign formation into cancer.
Histological analysis of a mole allows you to determine the presence of cancer cells in it. Thanks to this study, it is possible to remove the tumor in a timely manner and undergo targeted treatment to prevent the progression of cancer.
Indications
Histological examination of nevi is indicated for patients:
- Which accidentally injured the mole, especially if the formation protruded above the skin.
- If a mole changes its size.
- When plaque-like spots appear in the area of the nevus.
- If you experience unpleasant sensations in or near a mole.
- When you feel itching in the nevus.
- With visual wrinkling of a mole.
- When peeling formation occurs.
- If the nevus bleeds.
- When the color of a mole changes.
- If a mole changes its structure.
Each of the described conditions should be considered as an indication for mole removal. However, before such manipulation it is extremely important to undergo an examination by a dermatologist-oncologist and do the necessary tests.
Which specialists should check?
So, if such a problem is discovered, the first thing you need to do is visit an oncologist or oncodermatologist. If you are unable to make an appointment with these specialists, you can contact a dermatologist.
If the doctor deems it necessary, he will write out a referral to the necessary specialists, who will make a preliminary diagnosis at the first examination of the problematic mole.
The specialist will definitely prescribe a histological examination.
After the doctor receives the test result, he decides which treatment is suitable in each specific case.
Without histology
Many patients are interested in whether it is possible to get rid of an unwanted nevus without performing a histological analysis. However, experienced dermatologists warn that the decision to remove a mole without histology can be risky, especially if the formation looks potentially dangerous in terms of cancer development. In principle, ordinary nevi that do not show signs of a tumor can be eliminated without a prior biopsy. Doctors usually recommend removal using methods that allow a portion of the material to be sent to the laboratory after resection of the formation. In this case, histology is carried out after removal.
However, if there are any alarming changes in the mole, it is necessary to consult with an oncologist before surgical removal and follow his recommendations regarding tests. The specialist will analyze the research results and select the safest and most effective removal method.
Many doctors prefer to cut out suspicious tumors and then subject them to a full histological examination. After all, when performing a biopsy, there is a risk that it will not be possible to capture the cells of a tiny malignant tumor and miss progressing cancer.
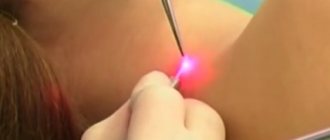
The popular and progressive method of laser treatment of moles does not allow examination of the removed nevi after the intervention, since their cells are simply burned out. Therefore, oncologists often do not advise getting rid of moles in this way.
If a mole was removed without histology, and there were malignant cells in it, there are two possible scenarios:
- If the intervention led to the destruction of all tumor cells, it is possible that the patient will continue to live calmly and for a long time, without even knowing that he had a melanoma removed. Tiny tumors can be completely removed using laser destruction and other surgical treatments, but there is still a risk of developing cancer.
- If the operation does not result in the removal of all the cells of the malignant neoplasm, it will continue to develop under the scar tissue that has formed at the site of the mole. At the same time, there is a risk that metastasis processes will occur more actively, provoked by the intervention. The danger of such melanoma is that external symptoms of the tumor may appear an order of magnitude later than the neoplasm has grown into the underlying tissue and begins to metastasize.
Doctors insist that moles must be removed in accordance with generally accepted protocol. This allows you to avoid cancer and prevent psychological trauma associated with panic after surgery.
Diagnostic methods
Histological examination of a growth on the skin is carried out on the basis of a referral issued by a physician, or on the basis of the personal will of the patient.
The procedure is only permissible within the walls of the clinic. For analysis, preliminary collection of biomaterial from the growth area is required. There are 3 examination methods:
- using a needle (in this case, part of the tissue structure is excised using a specialized instrument, anesthesia measures are preliminarily carried out),
- incious method (a part of the material being examined is taken and several fragments of it are sent to the laboratory),
- excision method (used during surgery, however, to the full depth of the skin with excision of healthy elements that are located near the growth, the subject of study is the complete body of the nevus, which was surgically removed).
Small in size and regular in shape, moles do not pose any threat. At least this lasts until changes occur in them. If the slightest abnormalities are noticed, you should not delay a visit to a doctor, as they may indicate the initial stage of a dangerous pathology - melanoma. It is a skin cancer. If detected early, it responds well to treatment (traditionally removal is used).
The lion's share of medical institutions conduct histological examinations free of charge. As a result, it becomes possible to make a final verdict and confirm or refute the fact of cancer or glomus angioma. The procedures are carried out within the walls of the laboratory according to classical schematics.
It looks like this.
- The doctor removes the problematic tumor.
- After removal, he takes the biomaterial for himself.
- The growth is put into a special solution and taken to the laboratory.
- The material is applied to the glass and must be painted.
- After a certain period of time, the doctor examines the cells under a microscope.
The research process can be carried out in several ways.
- Freezing the medication. This method is appropriate in a situation where an urgent study of a mole is required. For example, during surgical treatment. If the results of the analysis do not correspond to the doctors’ assumptions, it remains possible to change the course of the operation.
- Paraffinization of biomaterial. This technique makes it possible to preserve the removed growth for a long time. This is required for it to be studied by several specialists at once.
The classic scheme of an event consists of a number of stages. Let's look at them in more detail.
- Sampling (direct excision of biomaterial).
- Fixation (placing the sample in a container with water, which is subsequently replaced by ethanol, formalin). This measure helps prevent cellular decay and preserve the intravital structure of the mole.
- Wiring. In order to give the taken “raw material” the optimal shape and structure for examination, it must be dried and filled with paraffin.
- Cutting. When the material hardens, it is cut using special techniques until thin plates are obtained. Excess paraffin must be removed.
- Coloring. At this stage, the plates are lowered into a special solution with dyes that were prepared in advance. This helps determine the cellular structure.
- Microscopic examination. The most important stage of the entire procedure. Modern optical instruments are taken, and the laboratory assistant uses them to obtain a series of data that subsequently needs to be transferred to the attending physician.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Red moles on the body: what does it mean, the reasons for their appearance, redness around the mole.
Carrying out the technique requires about 7 days of time.
If a physician suspects aggressive types of pathology, urgent surgical treatment is necessary in order to save human life. For this purpose, an accelerated method is relevant.
Moles are small and regular in shape and do not in themselves pose any threat to human health until they begin to change.
The disease that doctors are trying to prevent in this case is called melanoma.
If you experience discomfort in the area of the mole or it begins to increase in size in a short time, you should consult a doctor and get tested for histology.
This study must be carried out in the following cases:
- the mole is growing rapidly;
- plaque-like smooth formations appeared against the background of the spot;
- soreness of the nevis, wrinkling or peeling appeared;
- the mole bleeds periodically;
- uneven coloration of the spot appeared;
- The structure of the mole has changed.
Only after an analysis has been carried out will a specialist determine what it is.
Histology is done in a laboratory after surgical removal of a mole.
Material collection
When performing histology of a nevus before resection, doctors use a biopsy technique. The skin at the site where the material is taken is anesthetized (most often with an injection or spray) and a small amount of mole tissue is pinpointed with a special needle. After this, the resulting sample (biopsy) is sent to the laboratory, where it is carefully examined for the presence of cancer cells.
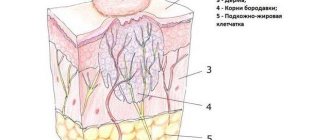
If an already removed nevus is used as material, it is all sent for histology and is also examined in detail under a microscope. At the same time, it is possible to examine the mole layer by layer and see even tiny pathological changes.
In some cases, it is possible to perform a cytological analysis of the formation. For this, the doctor performs a light scraping from the top of the nevus or presses a special laboratory glass against it. Next, the collected material is examined under significant magnification. The fundamental difference between cytology and histology is that in the first case, laboratory assistants analyze a separate accumulation of a limited number of cells, and in histological analysis, the formation tissue.
Cytology is carried out if there is oozing or ulceration on the mole. If the nevus is intact and intact, preference is given to a biopsy and further histological analysis.
Which doctor should I contact?
If such a difficulty is discovered, you should contact a dermatologist or oncologist. If it is not possible to make an appointment with them, you should contact specialized doctors who can make a preliminary diagnosis. But only an analysis will allow us to say 100% that we are dealing with melanoma. To make a final verdict, histology is prescribed. After the doctor receives the results of the analysis, he also makes a decision on the method of therapy.
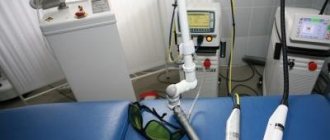
Performing histology
Histological analysis is done in specially equipped laboratories. The doctor must place the collected mole tissues in a special solution (formalin), which preserves their structure. After this, the material is sent for research. Already in the laboratory, a specialist removes nevus tissue and cuts it into tiny plates. The material under study is sent for staining and after some time the tissue is examined under a microscope. Such manipulations allow you to carefully examine the tissue of the mole and highlight possible signs of skin melanoma.
As a rule, histology is done within a week. The results of the study are given to the patient, but only a qualified doctor can interpret them.
What does it show?
Carrying out histological analysis provides information not only about the presence of cancer cells, but also about the features of the detected neoplasm:
- Allows you to determine the type of cancer.
- Detects the thickness of the tumor.
- Allows you to determine the presence of ulceration.
- Provides information about infiltration (growth into surrounding tissues).
- Allows you to determine the presence of vascular invasion (penetration of the tumor into the vessels) and its degree.
- Provides information about the exact size of the tumor (its edges).
- Determines the mitotic rate (the growth rate of abnormal cells) or Clark levels (how deep the tumor has grown into the skin).
Even in the laboratory, they can make assumptions about possible damage to the lymph nodes, the presence of necrotic changes, cell regression and the level of neurotropism (features of the growth of the formation relative to the nerves).
Performing an in-depth histological analysis to identify all of the above points is possible only when examining a removed nevus. Studying a biopsy is not so informative.
Histological examination of a mole after removal: methods of analysis and interpretation of results
Mole histology is a microscopic examination of tissue. It is used to diagnose cancer and other diseases that require similar tests. The study is indicated for all patients who consult a dermatologist for removal of a suspicious, often traumatic or bleeding nevus.
The value of histology after removal
Histological examination is carried out after resection of the birthmark, any suspicious formation on the skin. No preliminary biopsy is taken; oncopathologies of the dermis are classified as aggressive neoplasms. And when the body is damaged, the tumors begin to actively metastasize.
Indications for the study:
- permanent nevus injuries;
- intensive growth of the birthmark, deep penetration into the dermal tissue;
- the appearance of plaques;
- burning, itching, inflammation, presence of nodules;
- peeling, reduction in the size of the mole;
- the nevus is divided into lobules;
- change in color of the nevus;
- skin depigmentation;
- the mole causes pain;
- nevus bleeding.
Sending tissues for histological examination is a mandatory procedure. It is prescribed in WHO protocols for the management of patients with suspicious nevi and papillomas, except for those removed by laser or radio wave. Patient consent for the study is not required.
Methodology
Histological analysis takes place in several stages. This includes the preparation of sections, the use of microscopy methods, and quantitative and qualitative analysis of the results obtained.
Finished samples can be studied after the material has been collected, but the best results are obtained from pre-processed materials. Fabrics are treated with fixatives to prevent their decomposition. They can be treated thermally and dehydrated in carbon dioxide.
To prepare sections, specialized equipment is used - ultramicrotomes for examination in electron microscopes or microtomes for studying the sample in light equipment.
Additionally, the fabrics are dyed to improve image contrast. When using an electron microscope, ultrasections are fixed in specialized grids. To improve image contrast, fabrics are treated with compounds of uranium and other metals.
Methods of histological analysis:
- Light – classical microscopes with varying degrees of magnification.
- Ultraviolet - using rays from the ultraviolet part of the spectrum. Cell and cut defects invisible under normal lighting become visible.
- Fluorescent - the study is carried out using mercury, xenon lamps.
- Phase contrast – used when other methods of studying samples are ineffective. Fabrics are pre-dyed.
- Electronic - the sample is irradiated with a stream of electrons. The advantage of this method is multiple magnification and high resolution of the equipment.
Is it possible to remove a mole without histology?
The requirement for mandatory histological examination of any neoplasm is prescribed in the WHO diagnostic and treatment protocols. Oncologists and dermatologists use similar instructions, regardless of the legal status and form of ownership of the clinic.
Skin cancers are classified as aggressive tumors. They are not recognized by the cells of the body and quickly penetrate into the deep layers of the dermis, large lymph nodes and other organs and systems. Melanoma already at the initial stage gives rise to secondary tumors.
Five-year survival statistics for stage 3 skin cancer range from 50 to 78%, depending on the rate of metastasis, the presence of secondary foci and the body’s response to treatment. At stage 4, only 10–15% of patients survive. In the initial stages of cancer, 70 to 97% of patients can be saved.
In the vast majority of cases, relapses occur 2–2.5 years after tumor removal. Massive neoplasms are more dangerous; recurrence of the disease is observed in 50% of patients in the first year after surgical treatment. For a thin tumor with a diameter of less than 3 mm, the risk of relapse is only 10%.
The sooner the doctor removes the suspicious formation and conducts a histological examination, the higher the likelihood of a favorable treatment outcome. Qualitative analysis should not be abandoned.
If a nevus is removed for cosmetic or prophylactic purposes, its tissue will be sent for further examination to rule out the malignant nature of the cells.
If the oncologist is confident that the birthmark is benign and does not prescribe histology, the patient has the right to request an analysis of the removed tissue.
An exception is papillomas evaporated using a laser beam due to the lack of biomaterial. Keep in mind that every nevus can be dangerous.
How long does it take to perform histology?
The duration of processing of tissue samples should be checked with your doctor. There are 2 types of analysis:
- Emergency - the cut is examined during the operation. This allows, if necessary, to expand the scope of surgical measures and remove more tissue. And immediately after removal of the tumor, begin drug treatment. Used in controversial cases, when new circumstances are identified during surgery.
- Planned - used when the diagnosis is beyond doubt, and an emergency study confirmed the doctor’s assumption. The processing time for results is up to 7 days.
The timing of the study is influenced by the following factors:
- legal status of the laboratory or clinic - private or public;
- analysis methods and equipment used in a particular medical center;
- laboratory workload;
- force majeure circumstances.
What to do if the histology is bad
Poor histology of moles after removal is not a final diagnosis or verdict. The correct diagnosis will be made by an oncologist based on the following factors:
- age, gender;
- visual inspection results;
- tissue histopathology;
- individual, family history of the patient;
- history of skin cancer;
- data from other examination methods.
During a histological examination, the presence of a malignant process, the type of carcinoma, and its degree are determined. Based on these data, the doctor chooses patient management tactics and develops a treatment plan.
Interpretation of analyzes
The results of the study are interpreted by an oncologist. Often the information on the form is presented in Latin using specialized notations.
The breakdown of the histology results of the mole is as follows:
- Personal data – full name, address, type of material for research, place of tissue collection, full name of the attending physician.
- Method, method of analyzing samples - urgent, ordinary. The substances with which the tissues were treated are indicated.
- Main conclusion.
This paragraph indicates the nature of the neoplasm - malignant or benign. The doctor will indicate the microstages of the tumor process according to Clark (1967 protocol) and Breslow, stages according to the TNM system, and the size of the tumor.
A separate point - the stages of metastasis, the number of affected lymphatic collectors, the size of the secondary tumor - is determined microscopically or visible to the naked eye, the types of metastases, the presence of distant lesions.
Additional information – primary disease or relapse. If the nevus tissue is normal, this will be indicated on the analysis form.
Many patients are interested in the possibility of error. Unfortunately, it is practically excluded. The histological examination data is accurate; the main indicators are checked using several methods.
The research is objective - the results can be deciphered by doctors from any country, regardless of what language they speak there. For this purpose, a sample of the removed tissue is sufficient.
Histological analyzes are recorded on glass slides and stored for a certain time.
Oncological diseases of any organ are extremely dangerous for the health of adults and children. Melanomas are characterized by rapid growth and active penetration into healthy tissue.
If a mole changes, during this period it is not recommended to turn to traditional healers and use untested treatment methods. Consult a doctor and have the tumor removed. And histological analysis will solve all the questions! Leave the decoding to your oncologist!
The article was approved by the editors
Source: https://ProMelanin.ru/rodinki/gistologiya.html
Bad results
If histology results are positive and the presence of cancer cells is confirmed, treatment tactics depend on the size of the detected tumor:
- Tumors that are in the first stage of development are an indication for surgical resection of the mole with the inclusion of healthy surrounding tissue. Next, the patient will undergo targeted drug therapy.
- Neoplasms at the second stage of development require a biopsy of the lymph nodes located near the tumor. They may need to be removed. Of course, resection of the problematic mole is performed. Anti-cancer treatment is being carried out.
- The third stage of oncology most often involves the elimination of all affected nevi and lymph nodes. Anti-cancer treatment is being carried out.
- The fourth stage of the disease with slightly changed moles is diagnosed extremely rarely. With this type of cancer, the patient has little chance of recovery; treatment is selected on an individual basis.
Timely examination of moles and monitoring their condition can reduce the risk of developing cancer. You should not refuse histology and removal of nevi if there are indications for this.
Price
Patients are interested in the question of how much removal costs.
Let's consider the cost of this procedure using the example of the city of Moscow.
| Service | Price, rub) |
| Specialist consultation | 1000 |
| Laser nevus removal | 1500-4500 |
| Surgical removal of neoplasms of the 1st complexity | 3000-4500 |