Causes of white plaque
There are several groups of factors influencing the appearance of discharge. Some of them are the body’s natural reaction to hormonal changes. These are harmless causes that go away on their own. Another group is associated with female diseases or diseases that are sexually transmitted.
Common natural causes include the following:
- Pregnancy - in the first time (especially in the 1st trimester), the volume of discharge in women significantly increases. This directly depends on hormonal changes, with a large release of progesterone. The body weakens the immune system so as not to reject the fetus. The unborn child is a foreign object in the uterine cavity, so it must be protected.
- Adolescence – during puberty, a girl’s body undergoes restructuring. This occurs from 11 to 18 years of age. At this time, the microflora of the vagina is disrupted, often a white coating forms between the labia and on them. After hormonal changes, the microflora becomes normal and the amount of whitish discharge returns to normal.
- Changes in microflora after sexual activity - when a girl begins sexual relations, at first the body undergoes changes. The fact is that the female microflora of the external organs comes into contact with foreign microflora. This leads to the appearance of a white coating. This condition goes away on its own, so there is no need to worry about it.
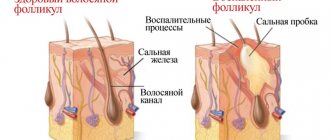
- The most common natural cause is the accumulation of smegma. This term refers to a mixture of secretion secreted by the sebaceous glands of the labia, dead epithelial cells of the mucous membrane and lubricant (it is necessary to moisturize the vagina). If smegma accumulates in large quantities, this indicates insufficient personal hygiene. With infrequent washing, the discharge may appear.
Smegma is a normal phenomenon; a white coating can be noticed even in girls of preschool age. In order to get rid of it, it is enough to wash your baby regularly. Twice a day will be enough.
Discharge in a newborn baby is a natural reaction of the body. The child adapts to unusual conditions. Discharge on the labia can be not only white, but also pink-brown. This symptom will subside 2 to 3 weeks after birth. The baby needs to be bathed 1-2 times a day, but you should not remove all the smegma from the child. It protects the genitals by preparing them for the environment.
White plaque on the labia may appear due to vitamin deficiency. With a lack of vitamins A, PP and E in women, the microflora in the vagina changes.
Salon treatments
Many women are concerned about very dark labia. If this problem occurs regardless of inflammatory diseases, then it generally does not bring any unpleasant sensations. But many girls believe that dark labia and the area on the inner thigh look extremely unaesthetic, and therefore are ready to take any measures to solve this problem.
In modern beauty salons, special procedures can be performed to whiten the skin, but they are not performed on the labia minora and mucous membranes. Several laser correction procedures can completely restore skin color and give it a more well-groomed appearance.
No matter how you try to lighten your skin, use a nourishing cream afterwards.
Don't worry too much about the color of your intimate areas. In these places, a woman's skin may actually have a darker shade. This is not a pathology, this is how nature intended it. So if it doesn't cause you physical discomfort, don't worry about it and continue enjoying life. After all, even the most harmless procedures can cause harm to the body.
When plaque speaks of disease
In some cases, white discharge indicates diseases of the reproductive system. In these situations, a whitish coating is only an indirect sign of pathology; in addition to it, women will experience a number of other unpleasant and painful symptoms.
Among them: burning, severe itching of the genitals, pain when emptying the bladder or sex, and clitoris, redness and dryness of the mucous membrane.
Photos of reasons
Women need to seek help from a gynecologist. The doctor will examine the vaginal mucosa, collect anamnesis, and give directions for the necessary tests. After receiving the results, doctors will make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
The most common diseases of the reproductive system that cause white plaque on the inner lips include: thrush, genital herpes and vulvovaginitis.
Thrush
If leucorrhoea on the labia minora is accompanied by a sour smell, and the discharge itself is similar in consistency to cottage cheese, then we are talking about thrush or vaginal candidiasis. This disease is caused by Candida fungi. They are found in the microflora of every person, but with weakened immunity, fungi begin to multiply.
Other symptoms include:
- swelling of the genitals;
- severe itching;
- redness of the vulva;
- pain when urinating;
- severe pain during sexual intercourse.
Typically, vaginal candidiasis appears in women during pregnancy, after taking antibiotics or hormonal drugs; as a result of long-term chronic diseases that have weakened the immune system.
White plaque due to herpes
Genital herpes is one of the most common causes of plaque on the labia. Once in the body, the virus constantly circulates in the human blood. Treatment only alleviates the patient’s condition, the relapse rate is over 98%.
Herpes is transmitted through unprotected sex (and the type of sexual relationship is unimportant). Bubbles filled with transparent or appear on the genitals. Tingling and itching appears. The ulcers burst, and in their place cracks appear, which are covered with a white coating. Soon the wounds tighten and heal.
Usually herpes is mild, but sometimes the virus can affect the cervical canal, urethra, and anus.
Vulvovaginitis
This is a disease in which the vaginal mucosa and external genitalia become inflamed. The pathology is caused by staphylococci, streptococci, gonococci and other microorganisms. Representatives of the fair sex develop a white coating.
Leucorrhoea is foamy, with air bubbles and an unpleasant smell of rotten fish. Ladies experience pain when urinating or having sex. The disease is also accompanied by itching and hyperemia of the genital organs.
Usually the disease occurs against the background of sexually transmitted diseases (chlamydia, trichomoniasis). It also appears after taking antibiotics, after damage to the vaginal mucosa, as a result of disruption of the endocrine gland.
White dots: what types of pathology can we talk about?
The list of diseases that cause rashes in the genital area is quite diverse.
Regardless of whether there are additional symptoms, you should see a gynecologist.
After examining and taking smears, the doctor will be able to determine what caused the rash.
- If white pimples appear on the skin, then most likely their formation is caused by a bacterial or fungal infection. In this case, therapy will be carried out with drugs whose action is aimed at suppressing the pathogen.
- In the case of a viral infection, treatment tactics will depend on the type of pathogen that has infected the genitals. It is possible that therapy will be aimed at removing formations using systemic drugs.
- In the presence of malignant forms, chemotherapy, surgery and radiation therapy are performed.
Allergic reaction
The appearance of small white dots in the genital area, including the labia, is often a sign of an allergy.
The rash can be single or multiple, the elements can merge with each other.
The patient complains of irritation and itching of the affected area.
When examining the skin and mucous membranes, hyperemia of the affected area is noted.
An allergic reaction can be triggered by:
- depilation of the intimate area using creams and other products necessary for the procedure;
- use of tampons and pads;
- wearing underwear made of synthetic fabrics;
- intimate hygiene products;
- local use of drugs;
- excessive hygiene of the genital area;
- using a latex condom;
- sexual partner's sperm.
Papillomas
When the body is infected with papillomavirus (HPV), neoplasms (condylomas) may appear on the skin and mucous membranes of the genitals.
Favorite places for the formation of white spots: the mucous membrane of the labia minora and majora and under them - in the perineum, the mucous membrane of the vagina, cervix and urethra.
The disease is transmitted by contact.
Symptoms of human papillomavirus infection:
- the presence of burning and itching in the area of the growth;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- swelling and hyperemia of the affected tissue;
- if condylomas are localized in the urethra, then discomfort occurs when urinating;
- the growths are colored from white to pink;
- possible enlargement of the inguinal lymph nodes;
- if the growths bleed, then there is a high probability of degeneration into a malignant form.
The development of HPV can be provoked by a decrease in the activity of the immune system and the presence of vitamin deficiency.
Diagnosis is based on the result of a PCR smear analysis.
Fat cysts (Fordyce granules)
They are hormonal in nature.
Formed during the process of blockage of the sebaceous gland.
The pathology is a cosmetic problem and is not contagious.
The defect does not pose a danger to its owner.
In appearance, hormonal nodules look like a scattering of white grains filled with yellowish contents (lipids and cells of dead epidermis).
The size of the dots is about 1-2 mm.
Cysts do not manifest themselves in any way and do not affect the quality of a woman’s sexual life.
Occasionally, ladies may complain of periodic itching.
Cystic formations can be removed at the woman’s request by electrocoagulation, laser or cryodestruction.
Surgical excision is not used as it may leave scars on the skin.
"Retin-A" is a remedy that can have a positive effect in the fight against fatty cysts.
Leukoplakia
The development of pathology occurs against the background of hormonal imbalance.
The causes of the pathology have not been sufficiently studied.
It appears as whitish dots on the mucous membrane of the labia.
Symptoms at the beginning of the disease are accompanied by the appearance of dryness, slight tingling and burning, which appear more often at night.
If you do not consult a specialist in time, then over time the symptoms become more pronounced.
This pathology refers to precancerous diseases.
In the absence of timely treatment, cancer may develop.
Genital herpes virus
The onset of a viral infection begins suddenly.
A small watery rash forms in the intimate area, at the site of which there is acute pain and a burning sensation.
In some cases, there is a rise in temperature.
After some time, the watery dots open and dry out.
In their place, crusts form.
During the opening of the papules, a secondary infection may occur.
There are no scars left in place of the crusts.
The viral infection is chronic, so periods of remission alternate with periods of exacerbation.
The route of infection with the genital herpes virus is sexual.
Molluscum contagiosum
The pathology is of viral origin.
The disease is transmitted through sexual contact.
The duration of the incubation period can reach 2 months.
Localization of white spots during infection with molluscum contagiosum: pubic area, labia, perineum.
The size of the formations ranges from 1 to 1.5 mm.
There is a depression in the center of the formation.
When the element is squeezed out, a white substance is released.
If a secondary infection occurs, itching may occur.
An examination is enough for the doctor to make a correct diagnosis.
Treatment of white plaque
If the discharge is caused by natural causes, then no therapy is required; the leucorrhoea goes away on its own. But it is necessary to maintain personal hygiene, wash twice a day. You should not use ordinary soap, it dries out the mucous membrane. Stores sell special intimate hygiene products.
Antiviral drugs (Acyclovir, Zovirax) are used to treat genital herpes. At the same time, you should take a course of immunomodulators and vitamins.
Treatment of vulvovaginitis depends on the pathogen. Antibiotics from the tetracycline class and douching with zinc or copper sulfate are usually prescribed.
Conclusion
When leucorrhoea, itching and other symptoms occur, many women begin to panic. They don’t know why the labia itch and a white coating appears on them. The causes of discharge can be natural, which do not require medical intervention. In the second case, the signs indicate the presence of gynecological diseases.
White plaque on the labia often indicates the presence of a pathological process. It all depends on the accompanying symptoms of the disease. Moreover, a whitish coating can be observed at any age and even in newborn girls. This condition is dangerous during pregnancy, as it often indicates the presence of a disease. A white coating between the labia that does not cause an unpleasant odor, itching or burning will be considered normal.
Lichen planus
With such a defect, representatives of the fair half of humanity develop red spots on the labia minora or majora. In this case, it will visually seem that the middle of the formation is slightly depressed in the center.
This particular type of pathology can be determined by the following criteria. During the recovery stage, the red spot turns into an ulcer, which then heals completely, provided that the therapy is carried out correctly.
With this skin pathology, characteristic reddish elements with a depressed center appear on the labia. During the healing process, they turn into ulcers.
White plaque on the labia - causes
White plaque on the labia often appears as a result of the presence of genital candidiasis or thrush, as it is colloquially called. This is a fungal infection that causes a cheesy coating on a woman's genitals.
The main reasons for the development of this disease can be the following circumstances:
- Sexual contact with a sick person.
- Hormonal imbalance, often associated with age-related changes in teenage girls.
- Disturbance of the microflora of the external genitalia in connection with the onset of sexual relations.
Lipschutz-Chapin disease
This disease is caused by Doderline's vaginal stick. It is characterized by the appearance of small festering ulcers surrounded by a purulent rim. The eruptive elements have a soft structure and affect the deep dermal layers. In the advanced stage, patients suffer from severe pain.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with Exercise to enlarge the penis
Ulcers and wounds can also be caused by some diseases and pathologies not associated with sexual transmission. It is these pathologies that cause ulceration in girls before puberty. The following diseases can be distinguished:
- Vulvar dysplasia. It is a precancerous condition. The pathology is accompanied by the appearance of whitish, reddish or brown spots on the labia with severe itching. Melanoma exhibits a similar symptom.
- Allergic dermatitis of chronic type (neurodermatitis). It appears when exposed to an allergen with a genetic predisposition of the body. A clear seasonality of exacerbation is revealed, and, as a rule, in the winter season. The manifestation is characterized by intense itching. In adult women, the pathology is rare, but in girls under 11-13 years of age it is found quite often.
- Contact dermatitis or contact eczema. They develop in the form of an allergic reaction, but when exposed to an intensifying factor: ultraviolet radiation, highly aggressive detergents, extreme temperatures, etc.
- Vulvovaginitis, or an inflammatory reaction in the vagina and external genitalia. The most common pathogens: pyogenic and E. coli, helminths. Provoking reasons are non-compliance with hygiene rules, intoxication of the body, external influences. In addition to skin manifestations, the following symptoms are found: vaginal discharge mixed with pus, itching, pinpoint bleeding.
Where does plaque come from between the labia?
As mentioned above, a white formation on the labia can appear as a result of the physiology of the female body or as a result of illness.
Physiological reasons
Vaginal microflora can react to internal or external changes. During the period of hormonal changes in the body, girls aged 12 to 14 years may develop plaque on the genitals. Similar cases can be recorded during the period of bearing a child.
The beginning of a sexual relationship can also affect the condition of a woman’s genital organs. For example, in some cases, in this way, a woman’s organs are protected from foreign microflora of the sexual partner.
Other non-pathological factors can also cause white formations:
- lack of vitamins;
- tight underwear;
- errors in nutrition;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- Low quality body cosmetics.
If such factors are eliminated, the plaque will disappear on its own, without additional treatment. Such a plaque in infants is called a sexual crisis and is considered normal. Because this is how the body cleanses itself after childbirth. After 7-9 days, this condition usually goes away.
Plaque caused by natural causes should not be eliminated. It protects the normal microflora of the vagina and also fights pathogenic microorganisms. Smegma (the so-called white formations between the labia) is associated with the functioning of the sebaceous glands. Remove it with a cotton swab and vegetable oil. You can also moisten it with water. But you should not use various aromatic soaps and gels, so as not to irritate the delicate skin of the labia.
Pathogenic factors
If, along with plaque, additional signs appear - burning, itching, redness, pain, etc., then this may indicate the onset of a disease.
These include the following pathologies:
- infections associated with human genitalia;
- sexual diseases;
- fungus.
Among these pathologies, the following diseases are the most common:
- Thrush (candidiasis) and other fungal infections.
- Vulvovaginitis and vaginitis.
- Genital herpes.
- STDs such as syphilis, gonorrhea, etc.
There is no need to guess where the plaque on the genitals came from; it is better to immediately visit a gynecologist. Through examination and additional tests, he himself will understand the causes of this condition. To avoid catching candidiasis, you should use a condom if you are not sure about your sexual partner.
The appearance of a white coating on the labia is not uncommon, but whether it means that a woman has any disease or is a variant of the norm needs to be investigated. During the menstrual cycle, the color, consistency, smell and structure of vaginal discharge in the fair sex changes.
They may become more abundant, slimy, or creamy. The main thing is that the discharge does not have an unpleasant odor and does not cause discomfort in the form of burning and itching. The slightly sour smell of discharge from the genital tract may be the result of the work of conditional bacteria that normally live in an intimate place.
If, in addition to white plaque on the labia, you are bothered by pain in the lower abdomen, redness of the mucous membrane, pain after urination, as well as itching of the genitals and bad smell of discharge, immediately visit a gynecologist for examination and treatment.
Causes
There are many reasons for the appearance of ulcers on the genital organs in women. In this case, all provoking factors can be divided into the following categories:
- sexually transmitted diseases;
- inflammations that form in the vagina and genitourinary system, caused by infection of fungi, bacteria and other atypical microorganisms;
- skin diseases;
- allergic reaction.
There are other factors that provoke the formation of wounds in the vagina. However, they occur in isolated cases.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-oCu8MVf_Rc
As practice shows, 85% of the appearance of ulcers on the genitals is directly related to sexually transmitted diseases. Such phenomena pose a threat to the reproductive organ, and therefore require urgent contact with a venereologist or other highly specialized specialist.
If the cause of the appearance of wounds on the genital lips is due to sexually transmitted pathologies, the symptoms will be distinctive. Therefore, it is worth taking a closer look at each of the most common types of defects of sexually transmitted origin.
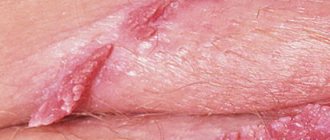
Ulcers are deep violations of the integrity of the mucous membrane, which arise as a result of the negative impact of physical, chemical, and infectious factors. Such sores on the labia are a consequence of impaired innervation and blood supply to the tissues. Their appearance is accompanied by discomfort, burning, itching; wounds do not heal for a long time.
Among the most common reasons are:
- mechanical injuries (for example, received during depilation);
- infectious diseases;
- genital pathologies (syphilis, pyoderma, candidiasis, etc.).
Oncological diseases mainly develop in women over 50 years of age during menopause. At this age, estrogen production decreases, the skin and mucous membranes of the labia become thinner and dry. Against this background, dense white elements appear, rising above the surface of the skin. Then they transform into ulcerative defects and erosions, growing in breadth and depth.
With candidiasis (thrush), ulcers with a white head appear. Beneath them is a pinkish, inflamed mucous membrane.
The white color of the rash also indicates the progression of genital herpes. In such a case, you should get tested and accurately determine the presence of infection.
When such rashes appear, women often present other complaints. These include:
- pain and discomfort in the pelvic and genital areas;
- feeling of itching;
- burning during urination;
- enlargement of regional lymph nodes;
- change in the amount and color of vaginal discharge;
- decreased libido;
- disruptions of the menstrual cycle;
- discomfort during sexual intercourse.
In 85% of cases, ulcers on a woman’s external genitalia are caused by such unpleasant pathologies as sexually transmitted diseases. This is a whole group of specific infections that require prompt consultation with a dermatologist or venereologist.
Wounds on the labia and vagina caused by sexually transmitted bacteria always have a distinctive feature and their own clinical type, namely:
- Chancroid. It is characterized by rashes on the labia that look like red spots. They form 10-15 days after infection. This type of rash can be presented in the form of multiple or single formations. After 8-10 days from the moment of their appearance, the soft chancre begins to degenerate into an ulcer of a rich pink hue. The wound formation gets wet, hurts and itches at the same time. Some ulcers heal and leave behind marks in the form of scars, while others appear on healthy areas of the skin of the labia. An advanced form of chancroid affects the inguinal lymph nodes like bubonic plague. The disease can cause significant harm to a woman’s lymphatic system. The disease is caused by the Ducray bacterium.
- Genital herpes. The most common cause of the formation of wounds and sores on the labia. The disease is caused by herpes infection genotype 2. First a red rash appears. The pimples then fill with pale red fluid, burst and turn into open sores. They itch very much, they secrete ichor, which, as it dries, forms a crust of a dense structure.
- Donovanosis. In dermatology, the disease has another name - granuloma venereum. A very dangerous and insidious disease, which is characterized by a particularly latent course. First, small pimples appear on the surface of the genitals. They may not change their appearance for 20-30 days from the moment of formation. Then each such pimple goes into the ulcerative stage, accompanied by severe pain. The danger of this type of wound formation on the labia lies in the fact that the ulcers are constantly growing, both in diameter and in depth. In the absence of adequate treatment, wounds on the labia can acquire the scale of an extensive inflamed wound with a deepening down to the bone tissue of the small pelvis. Stopping the growth of the infectious agent and the process of soft tissue resolution can only be done with the help of potent bacterial drugs. Otherwise, this will lead to loss of the reproductive organ, childbearing function and further disability.
- Syphilis. This is one of the most severe sexually transmitted diseases, which, before its development begins, forms a dense formation on the female labia called a chancre. As it matures, the skin in this part of the organ collapses, forming a round wound. After this, multiple ulcers and a red rash begin to form over the entire surface of the woman’s intimate area. A feature of the disease is that itching and pain are completely absent. Syphilis requires immediate treatment, as it can affect all organs and systems of the human body, right down to the cerebral cortex.
- Gonorrhea. One of the most common diseases of the external labia, which is caused by an infectious pathogen called Neiser's gonococcus. In addition to the characteristic rash on the skin, there is also internal damage to the vagina, rectum and urinary canal. This disease is characterized by the discharge of purulent contents from skin wounds and the vagina.
All these pathologies are dangerous for women’s health in their own way; they develop differently and make their presence known. Their distinctive feature is that they are all united by one feature. This is the appearance of wounds and rashes on the labia before the onset of the acute phase of the disease.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with the home treatment plan for prostatitis
Treatment
Depending on the identified disease, therapy is selected. It involves the use of external and internal products (vaginal tablets, ointments, creams, suppositories). The most popular medicines:
White plaque on the labia, not accompanied by other unpleasant symptoms (itching, burning, vaginal discharge), is not a sign of a dangerous disease. In other cases, you should immediately contact a gynecologist and undergo the necessary tests to identify the disease and subsequent therapy.
Gonorrhea
This venereal disease is caused by Neisser's gonococcus. It provokes the appearance of red ulcers on the labia, producing purulent discharge. The skin and mucous membranes turn red and thicken, and a yellowish-white coating forms on them.
Associated symptoms include severe pain during urination. If gonorrhea is not treated, it can result in infertility.
Gonorrhea is the most common sexually transmitted defect. The following symptoms are typical for this disease:
- first the rash spreads to the labia;
- then pimples appear on the bladder and rectum;
- then, a rash of purulent contents bursts and turns into ulcers.
The formation of acne is accompanied by itching and pronounced discomfort.