What it is?
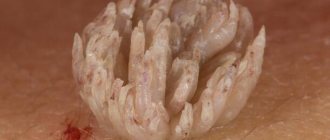
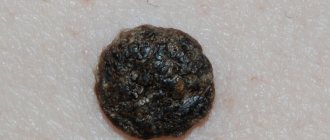
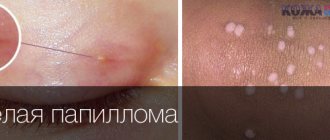
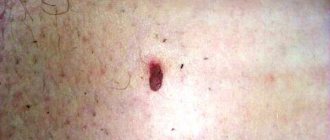
Basal cell papilloma is a growth on the skin that forms from the basal cells of the epidermis or hair follicles. A flat formation with clearly defined edges protrudes slightly above the skin. It develops very slowly, and the size of the papule varies from 1 mm to 5 cm.
The growth does not cause pain or discomfort. Minor discomfort is possible when rubbing against clothing or jewelry - it all depends on the location.
Papilloma appears on open areas of the skin and is more common in older people. Both men and women are equally susceptible to it. Diagnosing a growth in children is extremely rare.
The formation is single in nature, never metastasizes, and therefore is considered benign. However, various unfavorable factors can provoke the development of basal cell carcinoma.
Classification
Depending on the external signs, several types of basal cell papilloma are distinguished:
- pigmented - a new formation of various colors,
- superficial - a growth located exclusively on the skin, does not affect the layers of the mucous membrane,
- ulcerated – there are small ulcers on the papule,
- scleroderma-like - the most common and most non-standard type,
- nodular - similar to a nodule, often multiple, but does not cause discomfort.
The growth also differs in morphological form:
- may have a leg
- sometimes occupies a large area of the body.
On the skin around the papilloma, regardless of its classification, dilated capillaries are visible. They nourish the tissues of formation.
The shade depends on the amount of pigment in the body and can range from light yellow to dark brown. The growth on the mucous membrane becomes pink.
Drug treatment of growth
Drug treatment is the most common method of eliminating diseases. It includes taking medications and applying them externally. This method must be carried out strictly according to the prescription of a medical specialist. Under strict control of treatment effectiveness. The most effective remedies for eliminating warts are:
- Podophyllin is a cauterizing drug with cytostatic and necrotizing effects. Its use directly depends on the location of the warts. If the oral cavity is damaged, the neoplasm should be removed, and the damaged area should be generously lubricated with podophyllin once a day for 2-10 days. For papillomatosis of the bladder, the solution is injected into the internal cavity once a day for 3 days. The duration of treatment can be increased by the doctor to 3 weeks. This drug is contraindicated for women during pregnancy and breastfeeding, as well as for children under 12 years of age.
- Feresol is a cauterizing drug that coagulates skin proteins. Using a special spatula located under the lid of the drug, the medicine is applied to the growth 2 times with an interval of 5 minutes. The duration of treatment is 4 days, with constant breaks of 7 days. Contraindications for use are children under 7 years of age and people with pigmented nevi.
- Immunomax is an immunostimulating drug. For adults, this drug must be administered intramuscularly at a dose of 100 units over 6 days, following the following regimen: 3 days of injections, 4 days of rest, 3 days of injections. This drug is contraindicated in children under 12 years of age and in the presence of allergic reactions to the components of the drug.
Important! If drug treatment does not bring positive results after 3-4 days, you should immediately consult a doctor to change medications!
Causes
The tumor appears when HPV is present in the body. Virus infection occurs in the following cases:
- during blood transfusion,
- during intimate relations without contraception,
- through open injuries and damage to the skin,
- during childbirth (from mother to child).
The incubation period lasts one month. After this time, the symptoms of the disease either appear in various formations or subside for an indefinite period. Much depends on the human immune system.
Activation of the virus occurs with a sharp decrease in the body’s defenses, therefore the following factors influence the appearance of papilloma:
- diseases of an infectious or inflammatory nature in acute or chronic form,
- pathologies of the endocrine system,
- unbalanced diet,
- great physical activity,
- lack of vitamins,
- hormonal disbalance,
- gout,
- stress and frustration,
- pregnancy.
The cause of papilloma under the arms is excess moisture in the skin folds, which is an ideal place for microbial flora.
Diagnostics of education
If a growth is detected, you should visit a dermatologist. Diagnosis of papilloma is carried out by visual examination.
To clarify the type of formation, the doctor prescribes a series of studies.
- PCR method - determines the presence and quantitative content of the virus. Clarifies the classification of papilloma, as well as the nature of the disease.
- Biopsy - a piece of growth is removed for examination.
- Cytology – checks the probable malignancy and level of tumorigenicity.
Attention! These procedures are mandatory for any type of growth, since it is important to exclude the appearance of seborrheic keratosis. The disease is similar to basal cell papilloma, but the form is formed due to age-related changes on the surface of the skin, and not due to HPV.
If the diagnosis reveals the degeneration of HPV into basal cell carcinoma, the dermatologist redirects the patient to an oncologist. The doctor will conduct additional research and prescribe more effective treatment.
Varieties
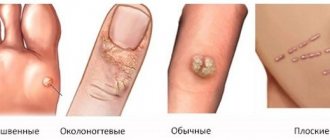
The most common types of papillomas:
- basal cell papilloma (a flat or slightly convex formation that appears mainly in old age);
- single (appears unnoticed and does not cause discomfort);
- vulgar papilloma (pineal-shaped formation, located on the hand or knee);
- plantar (localized on the feet);
- squamous (the surface of this type of tumor is smooth, they have a spherical or polygonal shape);
- thread-like (has an elongated shape, the color of papillomas of this type is yellowish).
We suggest you read: Pain in the scrotum: causes, aching pain under the scrotum and what to do if there is pain in the scrotum in a boy.
Diagnosis of HPV involves a fairly extensive list of measures aimed at determining the possibility of the formation of cancer cells. By its structure, any wart is a benign neoplasm that occurs as a result of activation of the virus. Today, there are several dozen strains and categories of HPV that can cause the formation of various seals on the skin and mucous membranes.
Diagnosis of HPV begins with a visual examination of manifestations and their classification. An experienced specialist can easily identify genital papillomas and condylomas from other neoplasms on the surface of the skin or mucous membranes. However, the initial examination only confirms the presence of the virus, but does not in any way answer the question about the nature of its origin, which requires further more detailed testing necessary to determine the possible consequences of the development of HPV.
There are several methods to obtain the necessary information, but only a biopsy is one of the most effective and high-quality methods that makes it possible to most accurately study the virus. It involves taking a small section of tissue that forms the papilloma and further studying it. Today, there are several variations of biopsy, differing in the principle of taking material. They look like this:
- incisional involves taking part of the growth;
- excision involves removing the entire tumor using a surgical method;
- puncture - material is collected by puncturing the papilloma with a needle.
The choice of sampling technique is determined directly after the initial examination by the attending physician and based on its results. At the same time, sometimes the collection of material requires colposcopy, which is prescribed in cases where there is a risk of developing oncology or in order to completely eliminate it. As a rule, such studies are prescribed for damage to the mucous membranes and involve their detailed study.
Therapeutic measures
It is useless to fight papilloma with medications, since the growth cannot be treated with medication. Typically, such formations are removed using hardware methods.
Types of excisions
- Radio wave removal - exposure to radio waves. The procedure does not leave swelling or redness. All residual traces disappear over time.
- Cryodestruction is the removal of a tumor with liquid nitrogen. Under the influence of low temperatures, papilloma cells freeze and gradually die. For large lesions, multiple procedures may be required.
- Electrocoagulation – burning out the growth with an electric current of a given frequency. With this method, the virus stops spreading, and the likelihood of relapse is reduced to zero. Sometimes minor marks remain.
- Laser therapy – evaporation of papilloma cells with a laser beam. After the procedure, a dry crust appears. After a couple of days it disappears and does not leave a scar.
Modern methods help to quickly and painlessly remove a benign tumor. It is important to consult a doctor in time to prevent the development of oncological degeneration.
What to do after the procedure
After removing the growth, recommendations are given regarding further care of the resulting wound:
- do not touch with your fingers, do not pick,
- avoid contact with water,
- prevent dirt from entering.
Additionally, you need to treat with an antiseptic solution. If you follow simple rules, the wound will quickly heal, leaving no reminder of papilloma.
People's Councils
Many people prefer to get rid of growths using traditional medicine.
- Daily treatment with celandine juice. After the procedure, the papilloma must be covered with a plaster. Apply until it disappears completely.
- Two parts of baby cream are mixed with one part of chopped garlic. The mixture is applied to the neoplasm and covered with a film for three hours. Use daily for at least two weeks.
- Use of aloe. A fresh leaf is cut in half and fixed on the papilloma for 12 hours. Apply until it disappears.
Attention! The effectiveness of folk recipes is not confirmed by anything. Before using any product, you need to get your doctor’s approval and find out about possible contraindications.
Prognosis and prevention
Basal cell papilloma can be easily eliminated the first time. In rare cases, relapses occur. If it reappears, immediate contact with a dermatologist is required. Only an experienced doctor will be able to conduct additional diagnostics and prescribe a new regimen for getting rid of the formation.
It is impossible to completely get rid of the human papillomavirus. However, you can adhere to preventive measures that will maintain the state of the immune system at the proper level and prevent the appearance of growths:
- get rid of bad habits,
- treat emerging diseases in a timely manner,
- be sexually active with one partner,
- avoid stress and nervous tension,
- eat a balanced diet,
- exercise,
- have a good rest,
- take seasonal vitamin complexes.
In case of periodic failures of the body's protective functions, it is better to consult an immunologist. The doctor will prescribe appropriate treatment and restore immunity.
Any new growths on the skin (pins, condylomas, warts) can develop and change. And basal cell papilloma is no exception. If growths are detected, immediate diagnosis and treatment are required. Even harmless papules can become malignant over time and cause serious complications.
Is basal cell papilloma dangerous?
Papilloma is a neoplasm that does not develop into cancer in children. Adults, if growths are detected on the body, should immediately seek help from a doctor. The fact is that often, seborrheic keratosis is found in the structure of the growth, which occurs due to age-related changes. In many cases, this is the main reason for the degeneration of the growth into a malignant tumor.
It is important to know that keratotic papilloma does not go away on its own! It requires high-quality and long-term treatment!
For women, basal cell keratosis papilloma is dangerous for causing cancer of the rectum, uterus and cervix. There is also a high probability of developing cervical erosion. Women who are addicted to alcohol and addicted to smoking are especially at risk of complications. That is why, if growths or their modifications are detected on the body, you need to immediately give up bad habits.