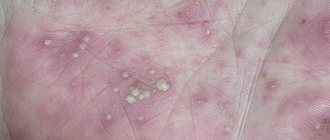
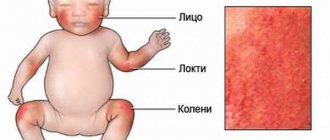
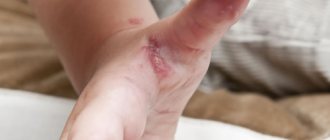
Such formations most often appear between the fingers or on the patient’s palms.
The disease mainly manifests itself due to prolonged stress and disturbances in the functioning of the body (immune and nervous system, gastrointestinal tract).
When treating dyshidrosis, a positive result can only be obtained during complex therapy and through the correct prescription of medications.
Medical history
Sometimes dyshidrosis is also called pompholyx, which translated from ancient Greek means “bad sweating.” Thus, we can conclude that this disease was known already in ancient times, and its cause was named then.
This opinion existed for a very long time - the main cause of dyshidrosis was considered to be blockage of the ducts of the sweat glands. Dyshidrosis was popularly called dropsy, which is explained by the appearance of bubbles with watery contents on the skin of the sick person.
Bubbles with watery contents (dross)
The first scientific description of the disease was given in 1873, but its etiology has not been fully elucidated to this day.
Most often it is considered as a disorder of a polyetiological nature, caused primarily by allergic reactions to food and medications.
However, such factors as a reaction to stress due to hereditary predisposition and exposure to negative environmental factors cannot be excluded.
Types of dyshidrosis and localization on the body
As already mentioned, dyshidrosis is localized on the human body in only two places - on the hands and on the feet, so there are only two types of this disease: dyshidrosis of the skin of the hands and dyshidrosis of the skin of the feet.
As a rule, it affects people with excessive sweating of the skin on the palms and soles, and the disease worsens in winter and becomes more pronounced.
However, in hot weather, especially in humid climates, similar rashes may appear on other parts of the body. In severe cases, a persistent form of the disease may appear, in which its external manifestations do not depend on the time of year and do not disappear even with adequate treatment.
Diet for dyshidrosis
In the diet, you should avoid increased consumption of carbohydrates, allergenic foods (strawberries, citrus fruits, raspberries, honey, salt, eggs, melon, coffee, tomatoes, smoked meats, milk, melons, fish, chocolate, spices), as well as alcoholic beverages.
The diet for dyshidrosis includes increasing the consumption of fermented milk products (yogurt, kefir, yoghurt, cottage cheese). Vegetable, lean soups, porridges, baked and boiled potatoes, fresh cucumbers, sunflower oil are useful.
How to cure dyshidrosis? Increase your walking and rest time. Try as much as possible not to overload the nervous system. Avoid contact with household chemicals and washing powder. Protect your hands from allergies to paint; wear cotton gloves, not rubber gloves, which cause your hands to sweat. It is recommended to wash your face and hands with mild, additive-free soaps, and use shampoo without fragrances or dyes.
Dyshidrosis is difficult to treat and people’s reviews often confirm this. In case of allergic reactions, cleansing of toxins from the body and treatment of the hands and feet of the sick person with folk remedies is prescribed.
Causes and symptoms of dyshidrosis
Tips from our readers
I got rid of dermatitis in 1.5 months! A simple remedy that I learned about from this article helped me...
Currently, a number of hypotheses have been put forward as to what causes dyshidrosis, but it cannot be said that its etiology has been completely clarified.
One of the main reasons is still considered to be blockage of the sweat ducts, but then why does dyshidrosis not appear in the armpits, where there are no fewer such ducts?
Therefore, you should pay attention to the following factors that can provoke the development of the disease:
- allergies to chemicals contained in household chemical products (detergents, insecticides, etc.),
- allergies to substances contained in perfumes, cosmetics and skin care products;
- allergies to food (strawberries, exotic fruits, mushrooms, etc.);
- allergies to medications (antibiotics, etc.);
- development of fungal infections on the skin;
- immunity disorders and endocrine system dysfunction;
- emotional stress, prolonged nervous tension, too much mental and/or physical stress;
- disturbances in the functioning of the vascular system;
- contact with nickel and cobalt in food or in the environment.
About 5% of people who have eczema on the skin of their hands suffer from dyshidrosis. It is also diagnosed in about a third of people prone to allergic reactions.
This applies mainly to people of adolescence, young and middle age, since after 50 years the symptoms of the disease manifest themselves less and less actively and disappear on their own in older age.
Why is dyshidrotic eczema dangerous?
This disease is not capable of leading to death, but it is quite capable of complicating a person’s life.
Even more interesting:
What are sores on the back of the throat?
Is eczema contagious or not?
One of the most common skin diseases is eczema.
It can occur on the skin of people of any age, most often on the hands, from children to adults. Symptoms: the skin peels, becomes dry, and spots appear on it. Most often it affects the skin of the hands, neck, and face. Symptoms intensify in the autumn-winter period. Many people are concerned about whether eczema is contagious. Some people mistakenly believe that the disease is similar in etiology to contagious scabies.
Causes
In order to accurately answer whether eczema is contagious, you need to understand the reasons why it occurs.
Factors influencing the appearance of eczema:
- Nervous tension, stress, frustration, depression.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and digestive system.
- Metabolic disorders.
- Various infections and inflammations.
- Skin injuries on the hands.
- Endocrine diseases, hormonal imbalances.
- Allergic reaction to foods/medicines.
- Chemical exposure.
- Using some cosmetics, wearing jewelry.
- Insect bites on hands.
- Exposure to household chemicals.
These reasons lead to the appearance of eczema if:
- The person has a weakened immune system.
- There is a hereditary predisposition to the disease.
Sometimes the disease appears in pregnant women, children with weakened immune systems, poor hygiene, and so on. The disease, although not contagious, is insidious.
Can you get eczema or not?
Eczema is not an infectious disease. The disease manifests itself when the body has problems with the immune system. It is impossible to become infected through contact with a sick person. Is eczema transmitted? No, eczema is not transmitted.
Microbial eczema is also not contagious. The fact is that it is not microbes that are to blame for its appearance, but a combination of different reasons.
If germs get on the skin, they are destroyed by the immune system. There is no skin inflammation at all. If the immune system cannot cope with germs, spots may appear on the skin. But they pass quickly. Microbial eczema is not contagious.
Can eczema be inherited?
Eczema itself, even microbial, is not inherited. However, a predisposition to this disease is inherited. A predisposition to atypical dermatitis, psoriasis, allergic rhinitis, and neurodermatitis is also transmitted. This happens often.
Most often, the disease occurs in those children whose parents both suffered from similar diseases. Then symptoms appear quickly.
In order to reduce the risk of developing skin eczema, the baby should be fed breast milk for as long as possible. Minimum – 6 months. At this time, the child develops a healthy and strong immune system. This simple action can preserve your health for many years.
Even if a person has skin eczema, he may not inherit a predisposition to it if he treats it and leads a healthy lifestyle.
Is seborrheic eczema contagious?
Symptoms of seborrheic eczema: the appearance of flaking on the scalp, dandruff, scales. This disease is not contagious. It may occur if:
- The person does not maintain hygiene.
- The person is not eating properly.
- The person is under constant nervous tension or has recently suffered severe stress.
The main cause of development is fungus. To prevent the fungus from passing from one person to another, you should always use only your personal comb, wash your hair more often, and dry with your personal towel.
Is mycotic eczema contagious?
Mycotic disease is a type of microbial eczema. The reason for its appearance is an allergy to a certain fungus. Most often it affects the skin of the arms, palms, feet, legs, feet. This disease, like microbial eczema, is not contagious and cannot be transmitted from person to another person. Symptoms: redness, rash, itching.
[smartcontrol__shortcode key=”contagious eczema” cnt=”3" col=”3" shls=”false”]
What to do to avoid getting infected with fungus?
In order to avoid becoming infected with fungus, you must:
- In a public swimming pool, sauna or bathhouse, wear shoes (your own or disposable ones).
- Use only your own towel/comb.
- Wear exclusively your personal items, especially hats/mittens.
Mechanism of development of eczema
Mechanism of development: interaction of microbes with skin cells, causing inflammation. The resulting pathology is more pronounced than with an allergic reaction.
Development of the disease external (symptoms):
- Reddish spots appear on the skin of the hands.
- Papules appear on the spots; they are brighter in color than the spots.
- Bubbles with liquid (pus) inside form.
- The bubbles burst.
- Crusts appear.
- Peeling begins.
The disease can be overcome. The main thing is to act immediately. Otherwise, it goes into a chronic stage, from which it is no longer possible to get rid of it.
One of the symptoms is itching.
Types of disease
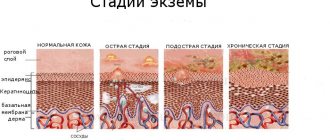
- Acute form, lasts no more than three months. Symptoms: bright spots, the patient experiences severe itching of the hands.
- Subacute form, lasts no more than six months. Symptoms: itching decreases, peeling appears.
- Chronic form. It can last indefinitely and definitely – more than 6 months. During periods of remission, eczema is practically invisible, but during inflammation it looks the same as in its acute form.
The disease happens:
- Nummular. Symptoms are the appearance of round spots, swelling, yellow crusts. The skin of the hands most often suffers from it.
- Post-traumatic. Formed during damage when the skin does not regenerate well.
- Varicose. Develops with varicose veins.
- Sycosiform. Occurs due to inflammation of the hair follicles. Symptoms - the spots have a bright color.
Dyshidrotic eczema
Dyshidrotic eczema occurs in a chronic form. Characterized by the appearance of swelling, spots, and small blisters.
Dyshidrotic disease develops against the background of disorders in the human endocrine system, human immunity, and metabolism. May occur due to the development of allergies.
Dyshidrotic eczema often manifests itself against the background of stress and nervous strain. Sometimes it appears after exposure to household chemicals on the skin.
Some doctors believe that dyshidrotic disease is associated with blockage of the sweat glands. However, this statement is refuted by many factors.
Dyshidrotic disease is not contagious. It can be treated.
Treatment
If left untreated, the disease becomes chronic. Treatment involves relieving inflammation, relieving symptoms, and treating the disease that caused the disease.
For example, if the disease is caused by an allergic reaction, then it is necessary first of all to get rid of the allergen. To do this, you can take tests to determine the allergen.
Often, for a complete cure, the patient has to completely change his lifestyle. The main thing is not to be nervous, eat right, and maintain hygiene.
As for local therapy, the following are used:
- compresses – antiseptics;
- ointments for drying the skin;
- ointments with corticosteroids.
Systemic therapy includes:
- taking antihistamines;
- taking immunomodulators;
- taking antibiotics.
So, is eczema contagious or not? This is not a contagious disease that can be treated if you deal with the disease in time. It cannot affect those around the patient.
Source: //allergolog.guru/zabolevaniya/ekzema-zaraznaya-ili-net.html
Prevention
Prevention of relapses of dyshidrosis is at the same time the basis of its treatment. To this end, it is necessary to avoid all factors that can provoke a relapse, first of all, to exclude contact interaction with household chemicals.
In modern life this is very problematic, so the use of protective gloves is strongly recommended.
True, some people are allergic to these rubber gloves themselves, so it is recommended to wear cotton gloves underneath them to protect them from contact with the skin. Soap used for washing hands should be soft and neutral.
It is worth consulting with your doctor about the perfumes, cosmetics and skin care products that you regularly use. They may contain substances that can cause an exacerbation of the disease.
A healthy lifestyle, physical activity, a balanced diet - all this is an integral part of the treatment of any disease, and dyshidrotic eczema is no exception, because strengthening the immune system will help, if not completely cure, then at least avoid acute relapses.
There will be a separate article about diet, but a metal such as nickel is worth special mention, since it is considered one of the provoking factors for dyshidrosis.
Try not to use nickel-plated cookware or other household items that contain nickel.
It can even be found in jewelry, not to mention kitchen utensils. Fortunately, beds with nickel-plated headboards are a thing of the distant past, and today they are hardly seen in our homes, so you are not in danger from this side.
If, despite all preventive measures, blisters begin to appear on the skin again, immediately begin treatment using all available methods - both official and traditional medicine.
Dyshidrosis folk treatment
Traditional treatment is effective, including baths with a decoction of string, celandine, chamomile, yarrow, and sage. To do this, pour up to ten spoons of the above herbs into a saucepan, then brew with one liter of boiling water, then bring to a boil and leave in a water bath for up to 30 minutes. After straining, pour the broth into a container for the bath, adding up to five liters of cooled water.
To prepare the next bath you will need oak bark. You should take up to five tablespoons of the herb and keep it on the fire, bringing to a boil for 20 minutes. Immerse your hands in this bath for 20 minutes.
By doing these procedures, you will reduce itching and swelling. However, be sure to consult your doctor before starting, as having a tendency to have plant allergies will make your health worse.
The information presented in this article is intended for informational purposes only and cannot replace professional advice and qualified medical care. If you have the slightest suspicion that you have this disease, be sure to consult your doctor!
You can overcome eczema and other dermatitis!
Redermis is an absolutely natural remedy for most dermatitis for children and adults!
- Helps get rid of all types of eczema, dyshidrosis and atopic dermatitis;
- Helps eliminate itching and blemishes on the skin;
- Dispensed without a doctor's prescription;
- Can be used at home;
- Cleanses the body of toxins in 1 course;
- Unlike hormonal ointments, the collection is absolutely safe;
- Suitable for adults and children.
This is a drug that allows you to forget about itching, pain, peeling in the shortest possible time, literally in one course, and cure even very complex cases within a couple of months.
The occurrence of skin diseases is extremely unpleasant, especially when they appear on open areas of the body in the form of rashes, redness, and peeling.
This causes discomfort to the sick person and others. One of these unpleasant diseases is dyshidrotic eczema.
Dyshidrosis is a chronic skin disease that affects the surface of the hands and feet. It is expressed in the appearance of swelling, redness, serous-purulent blisters.
If left untreated, dyshidrosis can develop into true eczema. In addition, it can affect the nail plates.
How to treat?
Medicinal methods of treating dyshidrosis include treating diseased areas of the skin, strengthening the immune system, and antibiotic therapy. At the initial stage of the disease, non-traditional treatment methods with folk remedies and homeopathic medicines are possible. Recipes from healers are suitable for getting rid of dyshidrosis and for boosting the body’s immune strength. The disease due to endocrine system disorders is treated with pharmaceuticals.
Treatment with drugs
Zinc ointment will help in the fight against rashes.
Effective drugs for localizing and neutralizing the rash are Advantan cream and zinc ointment. Iodine is suitable as a disinfectant. To eliminate the disease caused by an allergic reaction, Claritin tablets are prescribed. When the blisters do not go away for a long time, and the affected areas do not restore their former tone, laser treatment is prescribed. The procedure is performed on the face and neck, where the skin is especially delicate. Allergic foot hydrosis can be cured with synthomycin emulsion and compresses with lead water.
Removing dyshidrosis with folk remedies
Herbs will help treat the disease at home. The most widespread use of compresses soaked in herbal decoctions. To restore the skin, infusions of oak bark, chamomile, currants and sea buckthorn with the addition of lemon and horseradish are used. Healers advise applying compresses twice a day.
A pharmaceutical ointment or emulsion based on naphthalene and sulfur will quickly cure dyshidrosis of the palms and feet. To treat blisters and peeling of facial skin, lotions with soda and furatsilin are used. Drinking tea with echinacea and thyme will help boost your immunity. It is good to disinfect the skin with chamomile infusions and tea tree oil. To improve the epithelization process, use sea buckthorn oil or shea butter.
Therapeutic diet
The diet should be rational, healthy and tasty.
Since the disease is characterized by an imbalance in the water balance of the skin and problems with sweating, the diet for dyshidrosis includes the exclusion of foods that negatively affect these processes. It is recommended to reduce the amount of hot spices, salt, and fatty foods consumed, and to exclude strong alcohol from the diet. Porridge and pasta made from durum wheat, bran, yoghurt and low-fat kefir will be useful. The menu must include fresh vegetable salads, apples and low-calorie fruits. It is better to exclude citrus fruits, as well as foods that cause allergies.
Physiotherapy
The disease resolves after a course of magnetic therapy. A popular physiotherapy procedure for dyshidrosis is electrophoresis. A therapeutic course of 5-10 procedures is prescribed. Physiotherapy is recommended to be taken in combination with a therapeutic diet. A good remedy is to quartz the affected areas using a “Tube-quartz” device. The procedure disinfects the skin and promotes healing.
Other treatments for dyshidrosis
A popular way to treat the disease is ozone therapy and cryotherapy. The procedures are expensive, but they get rid of the disease quickly, guaranteeing a long-lasting treatment effect and no relapses. A popular method of eliminating the disease is laser therapy, which restores the appearance of the skin, removing formed microscars and peeling on the face and décolleté.
Where is it localized and how does it manifest?
There are different types of dyshidrotic eczema of the hands and feet. Most often, the disease affects the hands, much less often the feet. The main symptom of the pathology is the presence of small bubbles (vesicles) on the skin of the palms and soles.
The bubbles are filled with liquid and are located in the deep layers of the dermis. Also, there is hyperemia, which can intensify and gradually spread to adjacent healthy areas of the skin. The patient is bothered by unbearable itching.
After opening the vesicles, serous crusts and purulent erosions appear.
Over time, cracks and hyperpigmentation of the skin form in their place. The entry of pathogenic bacteria into the wound will provoke purulent inflammation, which will be accompanied by swelling, fever and weakness.
What is dyshidrosis?
Dyshidrosis is a pathological condition in which a rash appears on the skin in the form of blisters and cavitary elements. Very often, watery contents form inside the bubbles.
It is necessary to distinguish between true dyshidrosis and dyshidrotic eczema. This type of eczema is the formation of purulent blisters in the area of the feet and palms. Dyshidrotic eczema can affect the fingernails and toenails.
Previously, we discussed an article on weeping eczema.
Factors influencing the occurrence of the disease
The true causes of the pathology have not yet been studied. But there are factors that influence the appearance of vesicles on the legs and fingers:
- genetic predisposition to the pathological process;
problems with the functioning of the immune system;
- physical and psychological fatigue, stress;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- disorder of the endocrine system;
- allergic reactions to certain foods;
- skin reaction to the aggressive composition of detergents.
Dyshidrosis of different parts of the body: problem or normal?
What does it represent?
The disease manifests itself in the form of various types of rashes on the skin - from itchy red dots in certain places of the body to blisters. Dyshidrosis of the hands and face is common; the rash appears in the décolleté area, on the arms and legs. The disease is often observed in pregnant women who are prone to allergic reactions, and a rash can also appear in a child.
Causes
The basis of the disease is a disruption of the sweat glands of the skin, as a result of which the water balance of the epidermis changes and a rash appears. Malfunctions of the glands can be caused by a disease of the endocrine system and an allergy to an external irritant. Dyshidrosis during pregnancy is caused by hormonal changes in the body; the disease on the body in children is often of an allergic nature. A common cause of dyshidrosis is weakened immunity. Peaks of the disease occur in the spring and autumn periods, when the body is most vulnerable. The causes of the disease are:
- physical and psychological stress beyond measure, stress and neuroses;
- use of medications that can cause allergies;
- skin contact with caustic chemicals;
- bites of wasps, ants and other insects;
- viral, bacterial and fungal skin infections;
- food allergies.
Symptoms depending on location
Dyshidrosis, regardless of location, gender, age, leads to discomfort and restrictions.
The symptoms of the disease are similar to eczema and are expressed in the appearance of redness of the affected area of the skin, itching and the formation of blisters of different sizes and textures. Dyshidrosis is not contagious, but its primary symptoms can be confused with other skin diseases and dermatitis, so diagnosis should be performed in a clinic and not independently at home.
Facial lesion
On the face, skin dyshidrosis causes discomfort not only physiological, but also aesthetic. The affected areas of the epidermis are characterized by changes in skin texture - redness, microcracks and peeling, and small blisters form. A common cause of the rash is an allergic reaction to perfumed cosmetics or foods. In sore areas, the skin swells, itches, and there is a burning sensation and heat.
Hands and feet
Dyshidrosis appears on the hands in the form of redness of the skin, bubbles with liquid form gradually, changing the texture from small to dense pimples. The affected areas begin to itch, the skin becomes dry and peels, causing pain. The course of the disease may be accompanied by fever, loss of strength and loss of performance. The most common disease is on the fingers, but dyshidrosis of the feet can occur. To avoid confusion with fungal dermatitis, it is better to consult a doctor.
In the absence of timely treatment and infection with pathogens, the blisters can increase to the size of a large pea and fill with pus.
How is diagnosis carried out?
At present, no methodologies have been created that could be used to determine dyshidrotic eczema. The doctor will be able to make a diagnosis based on an analysis of the clinical picture and course of the disease.
The rashes are compared with signs of other skin diseases (fungal infections of the fingers, psoriasis) and unlikely options are excluded.
For a more accurate medical conclusion, additional studies are prescribed:
- scrapings for the presence of pathogenic fungi;
- seeding the contents of the vesicles for microorganisms.
What is the treatment based on?
It is not recommended to treat dyshidrosis on your own; only a dermatologist can select adequate therapy.
For a complete recovery, it is necessary to find out and eliminate all the causes of dyshidrotic eczema.
Drug therapy
The use of several pharmaceutical drugs at the same time is not allowed. This is due to the likelihood of allergic rashes (those with dyshidrosis are often allergic).
With a concomitant inflammatory process, antibiotics with a wide range of effects are prescribed.
It is permissible to use several groups of medications:
- Sedatives are used to reduce nervous excitability and relieve stress. Herbal medicines are suitable: Novo-passit, Persen, Valerian tincture, Corvalol.
- Antiallergic drugs can reduce dermatological rashes and reduce the resistance of the immune system. The following drugs are suitable: Citrine, Suprastin, Erius, Zyrtec.
- In severe cases, corticosteroids and diuretics are prescribed.
Local therapy
The use of antimicrobial creams and ointments (Fucidin, Levosin), wound-healing drugs with the active ingredient dexpanthenol (Panthenol, Bepanten) is allowed.
If there are non-healing erosions and fluid is released from the vesicles, the disease can be treated with compresses from a solution of Furacilin, Chlorhexidine, Miramistin, and boric acid.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
Physiotherapeutic treatment of dyshidrotic eczema is prescribed to strengthen the immune system.
After consultation with the doctor, a course of such procedures can be carried out:
- cryotherapy;
- ultrasound and laser treatment;
- magnetic therapy;
- mud therapy;
- baths with mineral salts.
After complex therapy, the appearance of the affected areas significantly improves. To consolidate the effect, it is recommended to improve your health in a sanatorium or at a seaside resort.
Vitamin therapy
Drugs are selected individually in each case. A visible result appears when riboflavin, vitamins A, E, group B and C are introduced into the daily diet. The consumption of a large number of foods that contain the recommended substances is approved.
Vitamin therapy is used in complex treatment with medications, as well as during the recovery period.
Psychological help
Patients suffering from dyshidrosis are very worried about the appearance of their hands and feet. People around you often ask questions about skin defects, which causes even greater feelings of embarrassment.
A stranger's gaze at the affected areas of the skin can put the patient into a stressful state. It turns out to be a vicious circle: a person is constantly depressed because of his illness, and nervous tension leads to an exacerbation of dyshidrosis.
You can break this ring with the help of psychologists.
Dyshidrotic eczema of the hands and feet: photos, symptoms, causes and treatment
Dyshidrotic eczema, or dyshidrosis, as an independent disease was first described at the end of the 19th century.
However, its etiology has not yet been fully elucidated, although the disease is one of the most common in dermatology.
A comprehensive treatment method for dyshidrotic eczema, which is persistently chronic, allows not only to reduce the frequency of relapses, but also to completely get rid of the unpleasant disease.
Description
Dyshidrosis is not contagious and is not transmitted from person to person, but it causes a lot of unpleasant sensations . The vast majority of symptoms of the disease appear on the palms and fingers, and only a fifth of cases occur on the feet.
Dyshidrotic eczema does not discriminate by gender: both men and women, aged from 20 to 50 years, are equally affected. There are frequent cases of the disease appearing in young children who have a hereditary predisposition to allergies or suffer from increased excitability of the nervous system.
The name “dyshidrotic” developed historically, since there was previously a version linking the disease with blockage of the sweat glands, which turned out to be untenable. Nevertheless, there has been a connection between the disease and hyperhidrosis - increased sweating, which most often manifests itself on the soles and palms.
Classification and forms
The main symptom of dyshidrosis is the appearance of small vesicles filled with serous exudate. The disease begins in an acute form, which becomes chronic with periodic relapses.
Depending on the degree of damage to the skin, the following types of disease are classified:
- True - the rashes are concentrated only on the palms and are localized in the deep layers of the skin. Bursting and then drying out, the bubbles provoke unbearable itching.
- Contact. Develops after contact with irritants - washing powders, detergents and other aggressive substances. At the same time, many new bubbles appear against the background of already drying vesicles.
- Microbial. At the site of scratching, areas with microcracks form, into which pathogenic microorganisms penetrate, causing secondary infections. The lesion becomes purulent.
In hot and dry climates, another form of dyshidrotic eczema, lamellar eczema, may appear. In this case, there are no blisters, and flaky, ring-shaped spots appear on the palms and soles.
Symptoms
This type of eczema appears on the palms and fingers and soles of the feet.
The vesicles that form at these sites resemble sago grains in appearance. Gradually they increase in size and fill with serous fluid. Then the vesicles burst, forming a weeping surface, after which the skin begins to peel and become cracked.
You can see what dyshidrosis looks like on the palms and fingers in the photo below.
The picture of the disease is supplemented by the following symptoms:
- painful itching
- erythema,
- swelling,
- painful sensations,
- burning.
If pathogenic microorganisms penetrate into cracks and abrasions, an inflammatory process may begin with suppuration and the formation of abscesses. In this case, there is a slight increase in temperature and a general deterioration in the patient’s condition.
Complications
The risk of developing complications is associated primarily with the addition of a secondary infection, the pathogens of which can penetrate the body. The inflammation that occurs in this case sometimes affects the lymphatic vessels and nodes, causing lymphadenitis and lymphangitis.
In addition, if treatment is not started in a timely manner and constant scratching of the affected areas increases the likelihood of the appearance of phlegmons and ulcers, as well as panaritium on the fingers. At the site of long-healing lesions, unsightly scars form, which can cause discomfort.
If you notice the first signs of dyshidrotic eczema, you should make an appointment with a dermatologist, who will make the correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment appropriate to the degree of damage.
Diagnostics
The symptoms of dishydrative eczema to some extent coincide with the symptoms of other skin diseases, in particular palmoplantar psoriasis.
The doctor must conduct a differential diagnosis in order to clearly distinguish one pathology from another.
And since the disease is often hereditary, the dermatologist will add to the history of the disease information about cases of allergies or eczema in several generations of immediate relatives.
In addition, laboratory and microbiological tests may be needed to confirm the diagnosis to reveal the nature of the disease. To determine the irritant that provoked dyshidrosis, a series of allergy tests is prescribed.
If the patient has concomitant chronic illnesses, consultation with other specialists - an endocrinologist, gastroenterologist, allergist - will be required. Pregnant women should coordinate the doctor’s appointments with a gynecologist, and if the patient is a small child, with a pediatrician.
Eczema often brings moral suffering to patients, disrupting their normal lifestyle, and causes insomnia, nervous breakdowns, and depression. For such patients, part of the treatment program will be observation by a neurologist or psychiatrist, who will help him cope with psychological disharmony.
Treatment with medications
First of all, the patient must be relieved of the most painful symptom - itching, so the doctor recommends starting with taking antihistamines: Cetrin, Claritin, Tavegil, Suprastin, Zyrtec.
To restore disturbed sleep and relieve neurotic symptoms, sedatives are prescribed: valerian tincture, peony tincture, Notta, Persen, Novopassit.
To relieve swelling, reduce erythema and disinfect affected areas of the skin, external agents are indicated - ointments and creams:
- D-Panthenol,
- Radevit,
- Losterine,
- Naftaderm,
- Beloderm,
- Celestoderm.
Some topical products contain corticosteroids. In addition to their beneficial properties, they have many contraindications and side effects, so only a doctor should prescribe them.
In the event of a secondary infection, antibacterial ointments are included in the treatment regimen: Lincomycin, Erythromycin, Bactroban or Fucidin. They must be applied to the hands of both hands, the soles of the feet and each affected finger to prevent the spread of the disease.
Vitamin therapy
Dermatologists say that many skin diseases, including dyshidrosis, are caused to some extent by a lack of vitamins and minerals in the body. You can fill this gap by taking complex preparations containing the necessary set of ingredients to maintain the health of the epidermis:
- Decamevit,
- Supradin,
- Aevit,
- Centrum,
- Pikovit.
In severe forms of the disease, injections of B vitamins are used to quickly regenerate the skin, improve its blood supply and heal wounds. The duration of the course and dosage are determined by the doctor on an individual basis.
Traditional methods
In the initial stage, traditional therapy medications will help cope with some of the symptoms of dyshidrotic eczema. Recipes for the most popular and effective remedies are given below.
- Peel raw potatoes and grate them. Place the pulp in cheesecloth. Apply to affected areas 2 times a day.
- Finely chop the cabbage leaf and mix with the egg white. Use as a compress 1-2 times a day until complete healing.
- Pour two tablespoons of oak bark into 1 liter of boiling water and leave for half an hour in a water bath. Cool, strain and use for hand or foot baths for 20 minutes before bedtime.
- Pour a tablespoon of celandine herb into 1 glass of water and bring to a boil. After cooling, make lotions from the infusion several times a day.
- Sophora officinalis tincture, as well as sea buckthorn oil, which can be purchased at the pharmacy, have a wound-healing effect. They are applied as a compress to the affected areas.
Since eczema is often a consequence of allergies, herbs should be used with caution so as not to worsen the disease. It would be best to coordinate traditional treatment methods with your doctor.
Diet
The main component of complex therapy for dyshydrative eczema is adherence to a certain diet, which does not allow the consumption of foods that cause allergic reactions. These include:
- smoked meats, marinades, canned food,
- brightly colored fruits and vegetables and juices from them,
- citrus fruits, bananas, pineapples,
- fatty meats,
- baked goods made from white flour, sweet pastries,
- chocolate, coffee, cocoa, tea.
The consumption of alcoholic drinks, energy drinks and sweet soda is unacceptable. People who smoke should quit this habit.
The list of permitted products includes the following products:
- low-fat fermented milk products,
- wholemeal bread, biscuits,
- light-colored vegetables and fruits, greens,
- lean meat and fish,
- porridge,
- vegetable broths.
The use of mineral water is recommended - Borjomi, Svalyava, Mirgorodskaya. Among other drinks, compotes and jelly made from dried fruits and light juices are recommended.
General recommendations
General recommendations for patients are:
- limit the consumption of alcohol, sweets, smoked and spicy foods;
- the inclusion of vegetables, fruits, and natural fermented milk products in the diet is approved;
if the disease affects the feet, it is necessary to change socks often;
- carefully adhere to the rules of personal hygiene for body care;
- wear rubber seals when doing housework;
- in acute forms of the disease, avoid direct contact with water and detergents;
- patients should not wear clothes made of wool and synthetic fabric;
- Dyshidrosis can be effectively treated only after complete recovery from existing chronic infectious diseases (sinusitis, caries, tonsillitis).
Using Losterin cream
Drugs from the “Losterin” series are prescribed for the complex treatment of many dermatological diseases. The main active ingredients included in “Losterin”: extracts of medicinal herbs, urea, natural oils, deresined naphthalan.
The balanced composition allows you to effectively act on the skin affected by dyshidrosis on the arms and legs.
Losterin cream has a pronounced antimicrobial effect, relieves inflammation, and reduces itching. The product restores damaged areas of the epidermis, reduces irritation, and improves the regenerative functions of the epidermis. The cream has proven itself in the treatment of eczema, atopic and contact dermatitis, lichen, ichthyosis, psoriasis and other skin diseases. Suitable for everyday use.
Advantages of Losterin cream:
- contains no dyes, fragrances, or hormonal substances;
- the skin does not get used to it;
- the drug "Losterin" is not limited in duration of use;
- Excellent absorption and leaves no stains.
Positive results in the treatment of dyshidrotic eczema will be visible after 7-10 days. Itching will significantly decrease, cracks in the skin will tighten, and damaged areas on the arms and legs will dry out. Improvement will be noticeable with continued use.
Tips for using Losterin cream: apply a thin layer to damaged skin 2-3 times a day. The duration of therapy is from 14 days to a month. The duration of treatment is determined by the severity of the disease.
Contraindications: intolerance to the components of Losterin cream.
Dyshidrosis is characterized by damage to the human skin; the disease is especially pronounced on the arms, palms and fingers, legs and soles of the feet.
Treatment of hand dyshidrosis
To eliminate dyshidrosis, it is necessary to identify the main cause of the disease and eliminate provoking factors. Otherwise, the treatment will be ineffective, and the disease will progress to the chronic stage. When the first signs appear, you should consult a dermatologist, endocrinologist, neurologist, or gastroenterologist.
The therapy uses an integrated approach, which includes medications for external and internal use, traditional methods, a special diet - all remedies are selected individually. Physiotherapy also helps well - electrophoresis, acupuncture, laser treatment, magnetic therapy, cryotherapy.
Drug treatment
To treat dyshidrosis, drugs are used that help eliminate unpleasant symptoms, reduce inflammation, and soften the skin.
Main groups of medicines:
- antihistamines – eliminate itching, burning, swelling (Cetrin, Claritin, Loratadine)
- anti-inflammatory drugs are necessary for infection of open wounds, their suppuration (Pipolfen, magnesium sulfate);
- sorbents for quick cleansing of the body - Polyphepan, Eneterosgel;
- diuretics to eliminate swelling (Furosemide, Fonurit);
- glucocorticosteroids for advanced forms of the disease (Belogent, Sherizolon).
Cetrin helps get rid of itching and burning of the skin
Additionally, it is necessary to take vitamin-mineral complexes and means to strengthen the immune system.
There are no exact specific methods for diagnosing dyshidrosis; the diagnosis is established on the basis of an external examination, anamnesis, and the frequency of the appearance of rashes is important.
Tablets and capsules
Oral medications eliminate the manifestations of dyshidrosis, help normalize the general condition of the body, and are used as maintenance therapy. The treatment regimen and duration are selected by the doctor.
Tablet drugs for the treatment of dyshidrosis:
- Belloid – improves sleep, helps get rid of irritability, fights vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- Panangin - the product contains magnesium and potassium, helps strengthen the heart muscle, improves blood circulation;
- Calcex and other calcium-based preparations;
- Furosemide, Hypothiazide – diuretics;
- Suprastin, Cetrin - antihistamines.
If dyshidrosis occurs due to problems with the gastrointestinal tract, liver disease, cholecystitis, then atropine sulfate is prescribed.
The drug Panangin improves blood circulation
Preparations for topical use
External medications are one of the main components of successful treatment of dyshidrosis. They help eliminate pain and reduce itching.
Local agents:
- lotions with Burov's solution, Resorcinol;
- Zinc ointment - dry the bubbles;
- Fukortsin is an antimicrobial, drying agent;
- Ethacridine is an antimicrobial ointment;
- Syntomycin and Tetracycline ointment, Levomekol, to eliminate suppuration.
Local remedies should be used 2-3 times a day until the unpleasant symptoms are completely eliminated.
Advantan is a drug from the group of glucocorticosteroids, produced in the form of regular and fatty ointments, creams, and emulsions. The product moisturizes the skin well, eliminates itching and rashes, it should be used once a day. The duration of therapy for adults is 10–12 weeks, for children over four months old – no more than 28 days, the emulsion should be used for 14 days. The medicine cannot be used for dermatological manifestations of syphilis and viral diseases in the affected area, skin tuberculosis.
Advantan ointment moisturizes the skin and relieves itching
Sinaflan is an inexpensive hormonal drug to combat itching and inflammatory processes, produced in the form of an ointment or gel. Cream, liniment. The product should be applied to clean, dry skin 1-2 times a day for 10 days; for children, the duration of therapy is 5 days. Contraindications – infectious skin lesions, open wounds, malignant tumors, pregnancy, lactation. Adverse reactions include allergies, pigmentation disorders, rarely diseases of the digestive tract, and an increase in blood pressure.
How to treat a disease with folk remedies?
Non-traditional methods help get rid of pain, itching, inflammation, moisturize the skin, but the main cause of the disease cannot be eliminated with their help, so they must be used in conjunction with traditional methods.
- Soda baths are one of the best remedies for the treatment of various dermatological diseases; they have antipruritic and anti-inflammatory effects. You need to dissolve 35–40 g of powder in 500 ml of warm water, immerse your palms in the bath and hold until it cools completely. Wipe thoroughly and apply medicinal ointment.
- Herbal baths help get rid of the main manifestations of dyshidrosis at home. Mix chamomile inflorescences, sage and string in equal parts, pour 30 g of the collection into 1 liter of boiling water, bring the mixture to a boil over low heat. Leave in a closed container for half an hour, strain, add 2 liters of warm water. The duration of the procedure is 20–25 minutes.
- Baths with oak bark quickly eliminate inflammatory processes - brew 1 liter of boiling water with 30 g of crushed raw materials, simmer over low heat for a quarter of an hour. Leave for half an hour, filter, keep your hands in the warm broth for 25–30 minutes.
Soda bath is an excellent remedy for treating dyshidrosis at home
Diet
Since dyshidrosis often develops against the background of food allergies, it is necessary to exclude all allergenic foods from the diet.
What not to eat if you have dyshidrosis:
- brightly colored vegetables and berries;
- citrus fruits;
- Exotic fruits;
- sweets with chocolate, cocoa, coffee;
- bee products;
- fish;
- nuts;
- sweet pastries;
- semolina porridge;
- eggs.
During treatment it is necessary to abstain from chocolate
During treatment, you should avoid fried, smoked, spicy, and salty foods. You cannot drink carbonated and alcoholic drinks, packaged juices. The basis of the menu should be products of plant origin, fermented milk products, cereals, pasta made from durum wheat, limited consumption of lean meat.
What it is
A person has sweat glands under the skin; their number is not the same in different parts of the body.
These glands produce a secretion - sweat, which comes out through the skin pores. This excretory organ is of great importance - it participates in thermoregulation of the body, moisturizes and protects the skin, and cleanses the body of waste products.
The disease dyshidrosis occurs when the sweat glands are blocked, when they become unable to perform their functions.
Externally, dyshidrosis is manifested by the formation of numerous blisters filled with serous fluid. Rashes bother a person - they become inflamed, itchy, painful.
Bursts of bubbles are accompanied by the pouring out of their contents. Later, ulcers and suppuration form at the site of the ruptures. After healing, no traces remain at the site of their formation.
Symptoms and course of pompholyx of the feet
Plantar dyshidrosis is a chronic disease, exacerbations of which can occur at any time, but are more common in the autumn and spring seasons.
The following sequentially developing symptoms are characteristic of foot dyshidrosis:
- Itchy small blisters form on the lateral surfaces of the toes, and sometimes on the skin of the soles, located under the keratinized layer of skin and filled with a light transparent liquid. The skin around the blisters is unchanged.
- Over time, the bubbles that arise spontaneously open with the formation of small ulcers and cracks, or undergo reverse development: the liquid disappears from them, they fall off, after which the caps of the bubbles begin to peel off;
- With the “dry” form of pompholyx, peeling can begin immediately, without the formation of blisters;
- The skin gradually recovers, sometimes it may remain rough.
The exacerbation lasts on average from ten to twenty days. If the skin around the blisters becomes red and swollen, thickening and tenderness of the inguinal lymph nodes are noted - we are more likely talking about dyshidrotic eczema, provoked by an infectious-allergic skin lesion.
↑ Return to contents
Causes
Skin dyshidrosis is caused by internal and external causes. Experts most often refer to the allergic or neurological nature of the disease.
This condition indicates serious disorders occurring in the body, affecting its most important organs and systems.
What can cause dyshidrosis of the limbs:
- weakened immunity, state of immunodeficiency;
- chronic diseases;
- tendency to an allergic reaction;
- metabolic disease;
- changes in hormonal levels;
- severe psycho-emotional shock;
- mental and physical fatigue.
Reasons for the appearance of herpes on the body. Types of strains
When specific small blisters appear on the human body, accompanied by itching and various unpleasant sensations, dermatologists, virologists and infectious disease specialists diagnose herpes.
Signs of infection by the virus are found in different parts of the body - face, back, chest, genitals and mucous membranes. The danger of the common man virus is that it invades the genes of cells and destroys them from the inside.
Doctors cannot remove HSV from the body once and for all. The goal of herpes treatment is to eliminate symptoms and prevent relapses.
Why do herpes blisters appear on the body?
Strains of herpes penetrate the human body already in the first year of life, if he has had contact with infected people. The pathogen is localized in the nervous system, so it is impossible to get rid of it.
In a healthy body, HSV lies dormant and is passive. The latent period can be quite long until favorable circumstances arise for infection.
Experts see the reasons for the appearance of herpes blisters on the body in different conditions:
- Frequent stress.
- Immunodeficiency.
- Infectious pathologies.
- Exacerbation of chronic diseases.
- Diabetes mellitus and its consequences.
- Treatment with certain medications (glucocorticoids).
- Strong temperature changes for the body (overheating, hypothermia).
Since herpes on the body is of viral origin, it is important to know whether this pathogen is contagious or not to others. The answer from experts is: yes, HSV infects a healthy body. The strain penetrates into a new environment in several ways - sexually (unprotected intimate relationships in any form), airborne droplets (with saliva), and household contact (through shared objects).
The herpes virus tolerates different environmental conditions well. When frozen at temperatures down to -70°C, the pathogen dies within a few days. In hot conditions with temperatures above +55°C, the strain dies faster.
Herpes on the body: common types of strains
Experts have studied 8 types of the virus that causes herpes. The most common are HSV-1 and HSV-2. These types of herpes on the body affect the lips (people call blisters a cold) and genitals. Type 2 herpes is called genital.
Type 3 herpes is familiar to doctors and patients from diseases such as chicken pox and shingles. In childhood, the body becomes covered with elements of chickenpox, but the symptoms of the pathology are easily relieved. Secondary infection gives a specific rash on the body. Shingles should be treated comprehensively using external antiviral agents and oral medications (antihistamines, painkillers, vitamins).
Doctors rarely encounter type 4 herpes infection. The Epstein-Barr virus affects the lymphatic and nervous systems, causing lymphogranulomatosis and mononucleosis.
Type 5 herpes is caused by the disease “cytomegalovirus”. Venereologists consider it a sexually transmitted infection, since the strain is transmitted through unprotected contact. But it also spreads through the air and through blood transfusions between a person infected and healthy with herpes.
Types 6, 7 and 8 of herpes have been little studied by doctors. But doctors know that these strains appear as sudden rashes and affect the nervous system. As a result, neurological abnormalities develop, including chronic fatigue syndrome.
Herpes simplex blisters appear not only on the skin. In some cases, the pathogen is localized under the nails or on the cuticle. A similar disease is called “herpetic panaritium”.
How does herpes appear on the body?
A person experiences significant discomfort with herpes zoster. The disease is not limited to the spoiled aesthetics of the body, it causes malaise and pain.
The patient has a slight chill, he experiences general weakness and registers an increase in temperature. Increased sensitivity and soreness of the skin as symptoms of herpes on the body are explained by the spread of the virus along the nerve located in a specific anatomical area. In case of mechanical damage to the rash, the pain lasts from 2 to 4 weeks until the wounds heal.
Herpetic rashes form on the body in large quantities. The lesions resemble a cluster of tight, watery blisters ready to burst. Individual elements can merge into a single blister and occupy large areas of the body. The skin in the affected area changes color to pink or reddish.
Elements of herpes open on their own within 3–4 days from the moment of appearance. They burst, and after the infectious fluid flows out, these places become ulcerated and overgrown with crusts. Healed crusts leave light spots on the skin.
The photo below shows what herpes looks like on the human body. Look closely at the images and avoid being close to people who have blistering rashes.
Occasionally, damage to the body by the herpes virus is manifested by such symptoms as:
- Chills.
- Fainting.
- Hyperthermia.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Migraine and dizziness.
- Weakness of the muscles in the area of the rash.
- Distorted sense of smell and perception of taste.
Additional symptoms indicate a complicated course of herpes disease and require immediate contact with the clinic. They are especially dangerous for children's bodies.
Video:
Symptoms and treatment
Dyshidrosis is classified into symptomatic and true . Similar symptoms occur when affected by a fungal or bacterial infection, eczema, dermatitis, toxicoderma.
True dyshidrosis is characterized by impaired functioning of the eccrine sweat glands.
Increased sweating leads to blockage of the excretory ducts, the top layer of skin loosens, and blisters form. Small rashes can merge into plaques, the affected area increases.
Symptoms of dyshidrosis:
- formation of bubbles on the surface of the skin with a dense surface and serous contents;
- the places where the vesicles are localized hurt, itch, itch, local hyperemia and swelling occur;
- Over time, the skin in the affected areas becomes rough, peels off, deep cracks may appear on it, and ulcers appear.
Treatment of dyshidrosis of the hands and feet is carried out comprehensively, combining medications, external agents, and physiotherapeutic measures. A prerequisite for recovery is general strengthening therapy, regular prevention, and special nutrition.
Dyshidrosis of the hands
Most often, dyshidrosis appears on the hands - between the fingers, on the outer and back of the hand. The disease is accompanied by thickening of the skin, swelling, redness, inflammation, and in severe cases, bleeding.
Numerous blisters itch very much; after they open, the skin becomes rough, cracks appear that are difficult to heal. The state of discomfort can last for quite a long time.
How to treat skin dyshidrosis:
- at the very beginning of treatment, you can use traditional medicine methods - baths with string or chamomile, sea buckthorn oil, soda or saline solution for disinfection;
- if the disease progresses, then you should consult a dermatologist and start taking medications - painkillers and antihistamines, sorbents, sedatives, and immunity boosters;
- local therapy is an essential component of successful treatment; these can be ointments with a regenerating effect based on zinc, silver, lead, panthenol, products with hormones or antibiotics;
- To increase the effectiveness of medicinal and external agents, physiotherapy is used - electrophoresis, magnets, laser, ozone therapy, electrosonotherapy.
Dyshidrosis of the feet
Foot dyshidrosis is an unpleasant and painful phenomenon that can be noticed on the feet of children or adults. In this case, watery blisters cover the lateral and plantar parts of the foot, appearing on and between the toes.
During the acute period, the feet swell, become red, the skin is very itchy and painful.
Over time, the itchy rashes open up, forming flaky crusts. This attracts attention and interferes with normal life activities.
Treatment is aimed at eliminating inflammation, speedy restoration of the skin, and preventing the formation of new blisters.
A complication is the addition of a fungal or bacterial infection, then the disease can become chronic and often recur.
Is eczema contagious or not: ways of transmitting the disease, risk of heredity
Eczema is a non-infectious skin lesion that manifests itself as specific rashes with a weeping surface. Seeing the unpleasant appearance of the rash, you involuntarily wonder whether eczema is contagious or not? The disease has similar symptoms to scabies. To determine the danger of eczematous lesions, it is necessary to understand in detail the etiology and pathogenesis of the disease.
The mechanism of eczema
The disease occurs under the influence of provoking factors: hereditary predisposition, bad habits, reduced immunity, hormonal disorders, allergic reactions.
These factors lead to hyposensitization of the body. Foreign agents interact with cells of the immune system. The latter begins to perceive its own cells as foreign. Inflammatory changes in the epidermis appear. At the same time, the functioning of the nervous and vascular systems is disrupted.
External and internal environmental factors irritate the endocrine glands. An increased sensitivity of the body is created, which is favorable for the development of dermatitis.
//www.youtube.com/watch?v=5fr4vPy7hXQ
Symptomatically, the disease manifests itself as inflammatory foci with peeling and cracks. Eczema is characterized by specific rashes - transparent blisters that burst.
They leave behind an erosive surface with droplets of liquid (in the form of dew). The patient complains of severe pain, itching, burning.
Typical localization of the disease is the palms, feet, fingers and toes, outer ear, head.
Is eczema contagious?
When they see a patient with symptoms of pathology, people around them try to distance themselves from the unfortunate person. Most believe that it is easy to become infected with the disease through close contact. The disease resembles scabies, and the association with the sight of the patient is unpleasant. Dermatologists from all over the world deny the fact about the contact and household route of transmission.
The clinical picture of the two diseases is similar. Scabies is an infectious disease. Caused by ticks. Infection occurs in crowded places. The infection is transmitted through bedding and bath accessories. Attacks sexual partners.
Eczema is not an infectious disease. Pathology occurs against the background of reduced immunity.
Weak children suffer from illness. When they come into contact with allergens, they develop a specific rash. The pathology is localized mainly on the hands.
Such children are not allowed to enter the playground! Most mothers will not let their kids play with the neighbor's sick child. The pathogenesis of the disease is based on allergies.
Eczema is never transmitted to another person by airborne droplets, household contact, or fecal-oral routes.
Conditionally infectious types
There are several types of disease: dyshidrotic, varicose, seborrheic, microbial, mycotic, idiopathic, occupational, and childhood.
Among the presented forms, only microbial types are classified as conditionally infectious. It is a secondary disease that occurs in areas of bacterial, fungal infection of the skin of the face and limbs.
Inflammatory signs of pathology are layered on existing symptoms.
The microbial form appears in the area of postoperative scars, wounds, trophic ulcers, and cracks. Abscesses appear around the primary focus. They burst and can merge with each other. Over time, they become covered with dry crusts. Patients complain of intense itching and burning in the affected area.
Microbial eczema is not contagious. Infection occurs when bacteria or fungi come into contact with the skin of a healthy person.
The risk of infection is 10-15%. It occurs during prolonged close contact with the patient. Transmission of infection does not occur through a handshake.
Patients should lubricate eczematous blisters with antiseptic drugs. These measures reduce the risk of infection to zero.
Is eczema inherited?
The disease is not a hereditary pathology. Only a genetic predisposition is passed on to the younger generation from the older generation.
A decent percentage of people do not seek medical help when signs of eczematous lesions appear. They are trying to overcome the pathology on their own.
Due to improper treatment, the pathology becomes chronic. Over time, parents begin to think about the health of their offspring. After all, many diseases and syndromes are inherited.
If the mother or father is sick, the child has a 30% chance of developing the disease.
Don't panic right away! The risk of developing the disease is not critical. Hereditary predisposition is the readiness of an organism to inherit a certain property, quality, function from its relative.
The disease can appear in children for various reasons. Periodic vitamin therapy, hardening, and the absence of bad habits prevent the occurrence of pathology in offspring.
Ill parents may not pass on the predisposition to their future children. To do this, you need to promptly seek medical help, properly treat the disease, and follow medical recommendations.
In what cases can it be transmitted?
The disease is dangerous in the following cases:
- the eczematous process may be complicated by the addition of a bacterial infection. Microorganisms penetrate the skin and cause inflammatory changes in the epidermis. Pathology can be suppressed at its initial manifestations. Short courses of antibacterial therapy will help cure the disease in 3-4 days. If the immune system of a healthy person works without interruption, it can independently eliminate germs and viruses;
- During pregnancy, a decrease in immunity is observed. Any infection is dangerous for a pregnant woman. Its transmission occurs through prolonged contact with the patient. Expectant mothers are advised to monitor their own health. During pregnancy, it is recommended to avoid contact with possible carriers of the infection.
How to prevent the disease
Eczema is not a contagious disease. It poses a serious danger if complications develop. Incorrect treatment and diagnosis lead to chronicity of the pathological process. The chronic form occurs with long periods of remission and exacerbation. Unbearable itching disrupts the normal rhythm of a person’s life. The patient develops psychological problems.
Simple preventive measures will help prevent the development of pathology and complications:
- At the first symptoms, you should seek medical advice. Timely treatment will help quickly get rid of the pathology;
- Doctors recommend annual medical examinations and treatment of chronic diseases. The latter disrupt the functioning of the body's immune system. Becomes an easy target for infectious and non-infectious agents;
- Proper nutrition replenishes the body's energy reserves and enriches it with vitamins and minerals. High-quality low-fat food prevents the development of chronic diseases and increases the body's defenses. Some people are prone to food allergies. It acts as a predisposing factor for the occurrence of pathology. It is advisable to exclude citrus fruits and chocolate from the diet;
- Daily physical exercise, swimming, walking in the fresh air, work and rest schedule strengthen the body. Easily gets rid of foreign agents from the internal and external environment;
- compliance with personal hygiene rules and daily skin care prevent the development of dermatitis;
- injuries, ulcerative defects, cracks are entry points for bacteria and fungi. Timely treatment of injuries with antiseptics prevents microorganisms from coming into contact with the skin;
- People prone to dermatitis need to take courses of vitamin preparations every six months. Medicines improve the functioning of all internal organs and systems.
The article has been verified by the editors
Source: //CoriumMed.ru/ekzema/zaraznaya-ili-net.html
Prevention of dyshidrosis
Preventive measures help to significantly prolong remission and eliminate the risk of the disease itself and its recurrent conditions.
What you need to do to prevent dyshidrosis:
- Lead a healthy lifestyle, give up bad habits - alcohol, smoking.
- Eat right, eliminate from your diet foods that contain preservatives, flavor enhancers, and trans fats.
- Being physically active and sport helps strengthen the immune system, which means the body will be better able to resist infections that attack from the outside.
- Comply with hygiene standards and requirements. Skin rashes are often a sign of poor hygiene.
- Strengthen and maintain immunity. These can be hardening procedures, sun and air baths, traditional medicine recipes.
- Avoid contact with potential allergens, especially if a person is prone to seasonal allergies.
- Train stress resistance, because constant anxiety and excitement significantly weaken the body’s natural defenses.
- Contact your doctor promptly and follow his instructions. Very often, self-medication leads to a significant deterioration of the condition and provokes complications.
Skin dyshidrosis requires long-term treatment under medical supervision. You should seek help from a specialist at the first signs of illness, only then will the patient have every chance of a successful recovery.
Medical approaches to the treatment of plantar dyshidrosis
Unfortunately, the treatment of dyshidrosis is quite a big problem, since it is not possible to directly influence the causes of the disease and the mechanisms of its development. Treatment is rather symptomatic in nature and is aimed at eliminating local manifestations and improving the general condition of the body.
Local treatment
Depending on the stage of the disease, the patient is prescribed the following types of local treatment:
- treatment of affected skin areas with fucarcin;
- baths with a weak solution of potassium permanganate;
- lead water or lead oil - special compounds containing lead molecules;
- lotions with rivanol or a quarter percent solution of silver nitrate;
- if there are signs of infection, use antibiotic ointments: synthomycin, levomycolic, etc.;
- Glucocorticoid ointments (if an allergic origin of the disease is suspected): hydrocortisone, fluorocortisone, etc.;
- When the process subsides - wound healing ointments and pastes with silver, panthenol, vitamins (if there are no allergies).
↑ Return to contents
General treatment
In addition to the drugs prescribed by related specialists, the following drugs are prescribed:
- Antihistamines (second-third generation, without sedative effect);
- Drying agents (atropine or belladonna preparations);
- Diuretics (short - up to three days - course and in small doses);
- Intravenous injections of calcium chloride, 10 ml for a course of 5-10 days, or taking a solution of calcium chloride by mouth, one tablespoon four times a day;
- Calming (sedative) drugs, primarily of plant origin (valerian, motherwort, tincture of peony and Rhodiola rosea). If such drugs are not effective enough, a psychotherapist may prescribe daytime tranquilizers: adaptol, afobazole, noofen.
- Sleeping pills are prescribed only in short courses, up to 10 days, strictly according to indications.
Physiotherapeutic methods of treatment can also be used:
- Ultraphonophoresis of various medications on the affected areas of the skin;
- Laser irradiation of blood;
- Ozone therapy;
- Indirect diathermy on the lumbar sympathetic nodules.
There is evidence that even persistently recurrent forms of dyshidrosis tend to spontaneously cease over time.