.
Most people associate the word “shellfish” only with seafood, and the disease of the same name is known only in medical circles. Despite the beauty of the name, this disease can cause a lot of discomfort. There is no need to be particularly afraid; molluscum contagiosum is a simple disease for an experienced dermatologist.
Molluscum contagiosum is an unpleasant disease
Drug treatment
After the appearance of a separate nodule, rapid spread of the disease is possible.
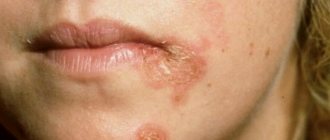
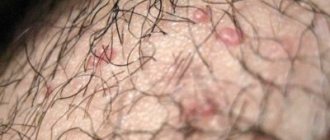
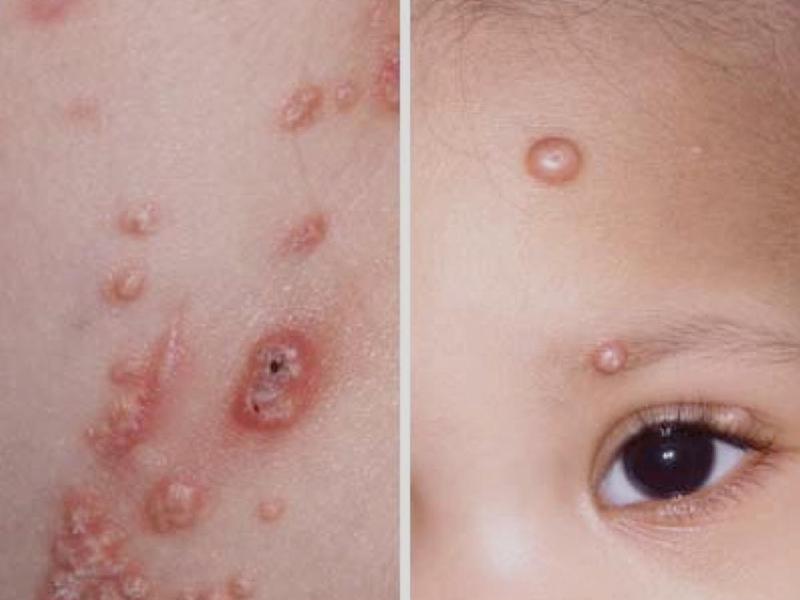
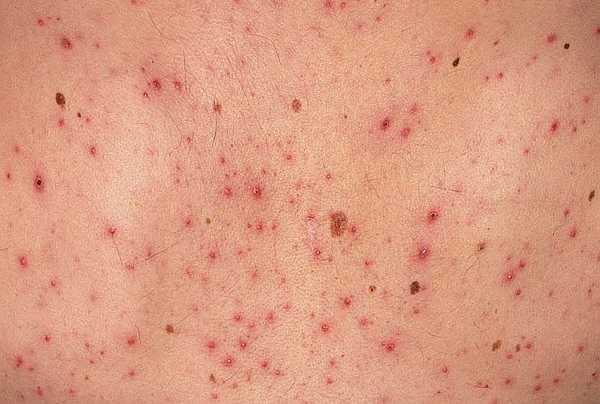
The lesion itself appears in the form of a small white or pink semicircular papule (nodule), up to 5 – 6 mm. In the center of each node there is a small depression resembling a navel. The disease is easily confused with rubella, chickenpox, measles, but there is one symptom that is a sign of this particular viral dermatitis - when you press on the tubercle, white contents appear from it, similar to a mushy granular mass, where the mollusks themselves are located.
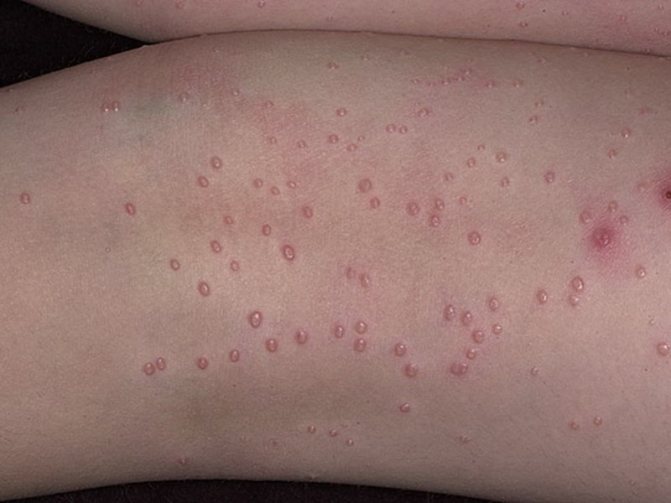
The blisters appear as individual papules or entire rashes on the abdomen, head, thighs, neck, and limbs. Sometimes molluscum contagiosum forms entire clearings on a child’s face. Very rarely, nodules are observed on the palms and soles.
- weakened immune system
- hot humid climate
The disease does not cause severe itching, pain or discomfort in the child. After a virus attack, the disease usually develops within 2 to 8 weeks. Final recovery occurs between 12 and 18 weeks.
In extremely rare cases, the disease lasts from a year to 4 years. In children, when fully mature, the mollusks look like convex pimples with a diameter of up to 8 mm. When drained, they form rashes and plaques.
- multiple rashes
- individual nodes up to 10 mm in diameter, sitting “on a leg”
- very large plaques in the form of growths that are formed by the fusion of small ones
Parents are always interested in how to get rid of molluscum contagiosum in children faster, but it is more important to control that children do not scratch the nodules and cause infection.
Treatment of molluscum contagiosum in children has its own specifics and a direct connection with the immune system. It is believed that immunity to this disease develops very slowly in the child’s body, but gradually it will cope with the infection on its own within 2 months. For this reason, specialized treatment for molluscum contagiosum in children is not considered so necessary.
Therefore, if the child has been confirmed with this diagnosis after all the tests, doctors insist that they just need to wait until the disease inevitably goes away on its own without any treatment. It is also believed that antiviral drugs, suppositories, ointments and procedures do not speed up the recovery process.
But some doctors still insist that treatment is still necessary if the child’s immunity is reduced due to constantly occurring colds in children’s institutions, and that it will not cause harm, and the likelihood of a shorter recovery period increases. The result depends on the immune system, the age of the child and the area of the lesion.
Specialists are faced with the task of how to cure molluscum contagiosum in a child in the most gentle and at the same time effective ways.
- prevents infection of healthy tissues
- prevents the mollusk from entering a healthy cell
- disrupts the RNA of the virus itself in the blood
The causative agent of the disease is orthopoxvirus, a relative of the viruses that cause chickenpox and smallpox. Today, four varieties have been identified and studied. Subspecies MCV-1, MCV-2 are to blame for the appearance of nodules on the face. They are transmitted through contact. Scientists have found that close contact does not always lead to infection. Strong immunity prevents viruses from multiplying, suppresses them and destroys them, preventing them from entering the active phase.
The disease spreads through contact and household contact, when the contents of the nodules, due to friction on clothing or scratching, fall on household items.
If we talk about children, we should especially be wary of infection:
- children who do not yet go to school;
- for allergy sufferers;
- those who are forced to take hormonal medications;
- non-compliance with hygiene rules;
- living in unhealthy environmental conditions;
- exposed to stress and overwork.
Primary signs in the form of a rash appear no less than 2 weeks later. after contact with a virus carrier. In some cases, the hidden period can last up to six months. Since the contents of the papules are infectious, the virus quickly spreads to new areas.
The disease develops as a result of the entry into the body of a pathogenic microorganism - orthopoxvirus from the family Poxviridae of the genus Molluscipoxvirus. The virus can affect people of any gender and age. In the countries of the former USSR, the disease is most often caused by viruses of types 1 and 2.
- Type 1 (MCV-1) – most often affects children, as it is transmitted indirectly and by contact.
- Type 2 (MCV-2) - transmitted through sexual contact, so molluscum contagiosum in adults usually provokes this type of virus.
Accordingly, the disease in children is provoked by a type 1 virus and can be transmitted in the following ways:
- contact-household (in contact with the skin of an infected person);
- indirect (through touching common things at home, in kindergarten, etc.);
- water (you can get infected in public swimming pools, water parks, etc.).
Molluscum contagiosum manifests itself in the same way in all cases. Children are most susceptible to the disease:
- with reduced immunity;
- living in hot climates with poor sanitary and hygienic conditions;
- those suffering from eczema or atopic dermatitis;
- taking glucocorticoid hormones.
In 80% of cases, children under 15 years of age (most often 2-6 years) become infected with this disease.
The cause of molluscum contagiosum is a virus from the smallpox group, from the poxvirus family. In the international taxonomy of viruses it is called Molluscum contagiosum virus: link.
- Only a person is sick. Animals don't get sick!
- Scientists have discovered several types of molluscum contagiosum virus.
- The source of the virus is the patient’s skin lesions.
- The virus is stable in the external environment.
- The virus is transmitted by contact from a sick person (which is often in children's groups). Infection can also occur when using hygiene items or clothing of a sick person, in a pool, in a bathhouse, on the beach, etc.
- The incubation period (the period from infection to the appearance of symptoms on the skin) is from 2 weeks to 6 months.
- Predisposing factor to the disease: decreased general and/or local immunity in the skin. In HIV patients, molluscum contagiosum occurs very often (up to 15% of patients with HIV infection).
- Through microtraumas of the skin and scratching, the virus penetrates the surface cells of the skin epithelium (epidermal cells), integrates into them and begins to multiply. At the same time, the activity of immune cells in human skin is suppressed for a certain time, which also leads to the rapid development of the virus.
- Mostly children and adolescents are affected.
- In adults, when a mollusk appears on the body, one should look for the cause of a decrease in local or general immunity. This could be diabetes mellitus or atopic dermatitis. This could be chemotherapy for blood cancer (leukemia) or HIV infection. This may include aggressive antibiotic therapy or the use of corticosteroid ointments.
- After treatment, the virus is no longer in the human body. Immunity to it is unstable. Therefore, after a few years a person can become infected again.
We suggest you read: What causes warts on the face Because under a microscope, the contents squeezed out of the skin formation look like a mollusk. And “contagious” means contagious.
As for laser treatment, this method is considered the most acceptable, since it allows you to remove all formations without a trace. There will be no scars or other marks left on the child’s thin skin, and a final cure will occur.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the map of acne on the face: what do they mean? Location of acne on the face and diseases
Cryodestruction is the most effective and painless method of treating molluscum contagiosum. This manipulation takes several minutes. Using this procedure, even the most voluminous formations are removed. The method of diathermocoagulation or electrolysis is based on splitting the body of a mollusk with a high-frequency current.
These techniques do not cause any pain and last a very short time. In this case, complications such as open hemorrhage are not observed.
Removal of papules with a laser beam is carried out in a clinic, is an absolutely painless method and is easily tolerated by patients. In this case, anesthesia is not required, and the result is quite stable.
After molluscum contagiosum in children has been treated, all clothing must be sanitized.
It is advisable to wash pillows, as well as blankets and other bedding, soft toys and towels. Be sure to wash all items that have been used by the patient.
Molluscum contagiosum in adults can take on a genital form. The reason for this form of the disease lies in non-compliance with the rules of intimate hygiene and sexual contact with an infected partner. They get rid of the mollusk mechanically - the nodular formations are scraped out, after which antiseptics are used.
To eliminate papules from the genitals, laser, cryotherapy and electrolysis are used. These methods are the least traumatic. If molluscum contagiosum occurs with multiple rashes, then the patient is prescribed antiviral and antibacterial therapy.
Causes and symptoms of the disease
The pathology is viral in nature. Until today, the luminaries of science have not been able to create a medicine that can completely cure this disease. This is due to the fact that DNA molecules are present in the structure of the virus. And treatment in this case is aimed at strengthening the patient’s immunity, which would increase the intervals of relapses.
With a diagnosis such as molluscum contagiosum in men, the main symptom of the disease is rashes that have the shape of a hemisphere. As a rule, the rash is similar in color to the skin tone and in rare cases has a pinkish tint.
A similar manifestation of the disease can be seen after the incubation period has expired, which lasts approximately 20 days. A skin rash during the development of the virus can be either single or group. In the male half of the world's population, rashes may appear:
- on the penis;
- in the pubic area, thighs;
- in the lower abdomen.
At the same time, the formation of a rash can also be observed on the scrotum.
As for the fair half of humanity, the manifestation of a viral infection such as molluscum contagiosum in women can be seen in:
- hips;
- labia majora and labia minora.
In some cases, symptoms of the virus are observed in the pubis and vagina.
It should be noted that the size of the nodules that appear on the skin can vary from 1 mm to 1 cm in diameter. If you press on the edge of such a nodule, a plug with a cheesy consistency emerges from it. This feature is one of the main evidence that the developed disease is precisely molluscum contagiosum.
Rashes that appear on human skin do not cause pain and, as a rule, do not require treatment. Without therapeutic measures, rashes in the groin disappear without a trace after 2-3 months.
The area of the rash will directly depend on how the infection occurred. It is precisely because infection occurs through sexual intercourse that the rash becomes localized on the inner thighs. The rash appears in the pubic area, on the external genitalia. If the level of immune defense decreases, the rash on the body will reappear.
Epidemiology
Molluscum contagiosum is widespread everywhere and only among people. Both children and adults get sick. The incubation period ranges from 2 weeks to 6 months.
Children and young people (usually men) are most often affected. Shaving contributes to the spread of infection on the face.
In the Russian Federation, about 5% of children suffer from molluscum contagiosum. Basically, these are children from 1 year old. At a younger age, the disease is not registered, which is due to the presence of immunity transmitted from the mother or a long incubation period of the infection.
Risk factors:
- Poor living conditions, overcrowding and failure to comply with basic personal hygiene rules.
- Long-term use of corticosteroids and cytostatics by patients, which significantly reduces the functioning of the immune system.
- The disease often occurs in HIV-infected patients, as well as people suffering from skin diseases such as atopic dermatitis and eczema.
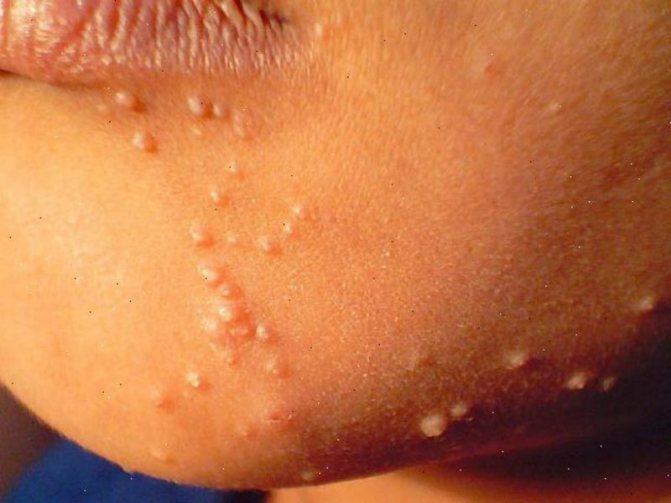
Rice. 4. Molluscum contagiosum on the neck and chin area.
Rice. 5. Molluscum contagiosum on the face and behind the ear.
The disease is transmitted by contact, mainly in everyday life. Factors of transmission of infection are the patient’s personal belongings (washcloth, towel, etc.). The infection is also transmitted through direct contact with affected skin, which occurs during sexual intercourse. When scratching or touching the lesions, viruses spread to other areas of the skin.
In the Russian Federation, about 5% of children suffer from molluscum contagiosum. Basically, these are children from 1 year old. At a younger age, the disease is not registered, which is due to the presence of immunity transmitted from the mother or a long incubation period of the infection. Infection occurs in families and organized groups, where children become infected from each other. Even epidemic outbreaks of the disease are possible.
Causes of complications
Molluscum contagiosum rarely causes complications. The disease is not dangerous to human health and does not cause a deterioration in general well-being. In rare cases, a secondary bacterial infection may occur. At the same time, the papules begin to become inflamed, and suppuration intensifies. After healing, scarring is possible.
A complication of molluscum contagiosum is the spread of rashes over large areas of the skin and an increase in their size. Such signs indicate a strong decrease in the body's defenses and require the use of immunomodulatory drugs, as well as identifying the cause of low resistance to infections.
With the exception of a cosmetic defect, there are no complications. You can stop the process by:
- You can’t touch the formations again.
- Under no circumstances should you comb them.
- You need to wash your hands more often.
- It is necessary to use emollient creams and ointments.
Molluscum contagiosum is not a dangerous, although unpleasant, disease. The main characteristic of the pathology is the occurrence of a cosmetic defect. The dermatologist decides whether to treat the molluscum or not, based on the prevalence of the process and the degree of discomfort experienced by the patient.
The causative agent is the orthopoxvirus Poxviridae, a molluscum contagiosum, which is also called infectious because of its virulence. Both children and adults suffer. Externally, the disease may resemble smallpox or chickenpox, but not with such pronounced blistering rashes, without death and even without painful symptoms.
It goes away on its own, but it can last for a very long time, from 6 months to 2 years. It does not pose a danger to life, but it causes a feeling of discomfort and causes cosmetic defects to the skin, especially in the acute stage, so those who are sick strive to recover from the contagious mollusk by taking advantage of medical help. It worsens in the warm season.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Fungus on the penis in men: what it looks like (PHOTOS) and how to treat fungus on the genitals
Infection is possible through contact and sexual contact, through the interaction of unprotected mucous membranes and the presence of microwounds and microcracks on their surface, as well as through contaminated household items or through the use of other people's hygiene items. Molluscum contagiosum only affects humans, but pets can serve as carriers of the virus.
Pathogenesis
It is believed that disruption of epidermal growth factor plays a decisive role in the development of molluscum contagiosum. The virus, having penetrated into the keratocytes of the basal layer of the epidermis, begins to rapidly divide. Viral DNA actively accumulates in the stratum spinosum, resulting in the formation of a nodule in the epidermis. In the center of the nodule, destruction occurs - the destruction of epidermal cells.
In the cytoplasm of the cells of the stratum corneum and granular layer, rounded formations are formed - mollusc bodies. They are large, 25 - 35 microns in diameter, round in shape, and contain numerous virions.
The inflammatory component is often absent or minimally expressed. With a long course of the disease, the lesions are represented by a granulomatous infiltrate.
Rice. 6. In the thickness of the horny and granular layers, round cytoplasmic inclusions are formed in cells during the disease - mollusc bodies (photo on the left). Herniation of hyperplastic epidermis into the dermis. Mollusc bodies with keratinous masses fill the crate-shaped depression (photo on the right).
Molluscum contagiosum in adults on the face, photo
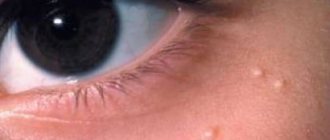
As a rule, the formations are not numerous and do not differ in large size, but even single small papules spoil the aesthetics of the face and cause some complexes in the patient.
Papules on the face
The formation of molluscum contagiosum papules on the face occurs more often in children than in adults. If this does happen, then this indicates suppression of the immune system and the need to strengthen the immune system, as well as conduct examinations for various immune diseases.
Particularly often, nodules appear on the eyelids. They have a classic appearance: papules, similar to pearls with a depression in the center, filled with horny masses, painless. The nodules contain many mollusc bodies with numerous virions.
When the formations are located on the edge of the eyelid, chronic follicular conjunctivitis of mild or significant severity, often recurrent, superficial keratitis or micropanus often develops. Corneal erosions often occur in the upper areas, sometimes over the entire surface. They are small, often combined with punctate epithelial keratopathy.
Molluscum contagiosum on the face should be distinguished from epidermal cyst, syringoma and keratoacanthoma.
In an uncomplicated course, it is better not to touch the lesions, since in most cases the disease goes away on its own within 1.5 - 3 months. If necessary, electrocoagulation, cryodestruction or laser therapy are used. The nodules dry out and fall off on their own, leaving no scars.
The prognosis for molluscum contagiosum on the face in individuals with a normal immune system is favorable. Avoid spreading the infection to other parts of the body.
Rice. 8. Molluscum contagiosum on the face. Nodules on the upper and lower eyelids.
Rice. 9. Molluscum contagiosum on the face Multiple nodules on the upper eyelid.
Rice. 10. Molluscum contagiosum on the face Multiple nodules on the lower eyelid.
Molluscum contagiosum in HIV patients
Molluscum contagiosum in HIV-infected patients is registered in 5 - 18% of cases. The disease is more severe than in persons with normal or slightly reduced functioning of the immune system.
Characteristic rashes in the form of dome-shaped nodules with an umbilical depression in the center are often recorded on the skin of the face and genitals. They are numerous (hundreds of elements), fast-growing, and significantly disfigure the patient’s face.
Often the disease exhibits resistance to traditional therapy. In some cases, progression of the infectious process is observed during treatment.
The disease must be differentiated from deep mycoses, for which a morphological study should be carried out.
Treatment of molluscum contagiosum in HIV patients should be carried out against the background of antiretroviral therapy.
Rice. 11. Molluscum contagiosum on the face in HIV-infected patients.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with cuperosis on the face: causes and treatment of capillary mesh
Characteristic rashes in the form of dome-shaped nodules with an umbilical depression in the center are often recorded on the skin of the face and genitals. They are numerous (hundreds of elements), fast-growing, and significantly disfigure the patient’s face. There is a tendency to cluster and form giant conglomerates. In 5% of patients, a rash appears on the eyelids.
For HIV-infected patients, concomitant superficial keratitis and follicular conjunctivitis are not typical.
Symptoms of molluscum contagiosum in adults
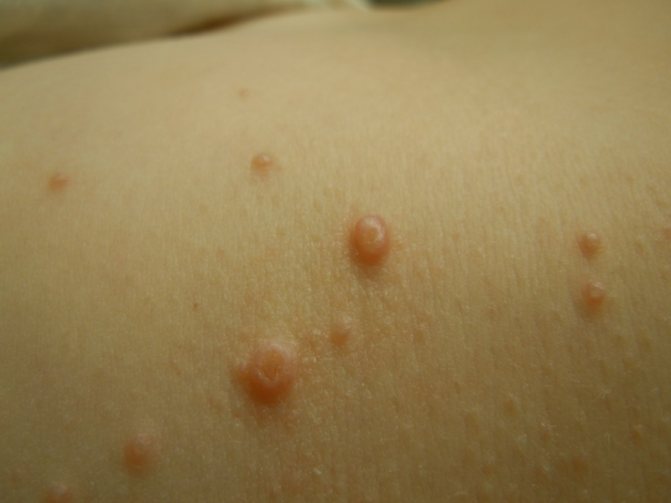
of a sick person and is a source of danger and spread of the virus, and transmission can occur in two main ways:
- in direct contact with a carrier of molluscum contagiosum (during sexual intercourse, kissing, shaking hands)
- at the household level through the personal belongings of a person infected with the virus (towel, personal hygiene items, and even through water in the pool that had contact with the patient)
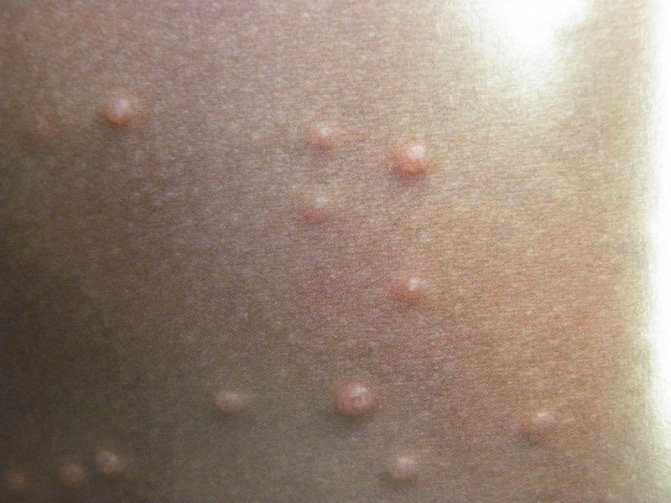
The first manifestations of the disease are expressed in the appearance of single nodules that have different localizations:
- on the face (usually in children)
- in the groin area
- on the genitals
- on the hips
- on the stomach
There is a small depression in the center of the formation, and the internal contents look like a white cheesy mass. Soon the size of the nodules begins to increase to 5 mm, and along with this the number increases.
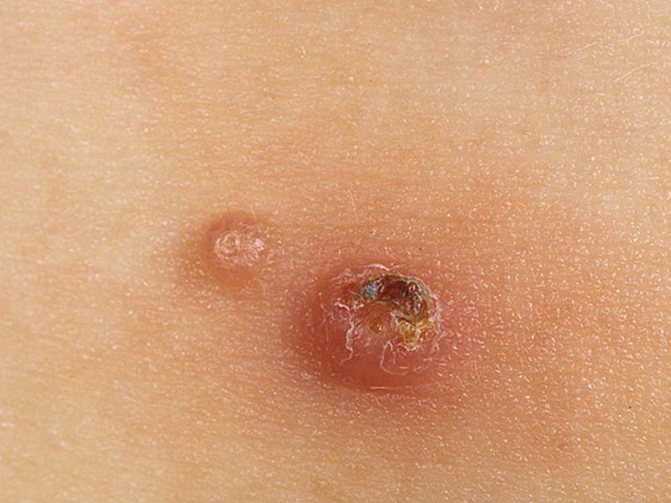
Purulent process in a damaged papule
The number of papules in most cases ranges from a few to ten. In medicine, there are also known cases of the formation of several dozen elements, combined with each other or arising separately. The most common reason for such a massive occurrence of formations caused by this virus is the scratching of papules and the transfer of infectious internal contents along the skin.
As a rule, the number of elements of molluscum contagiosum on the skin depends on the patient’s immunity. If the immune system functions well and produces a sufficient amount of antibodies, then the formations will be rare.
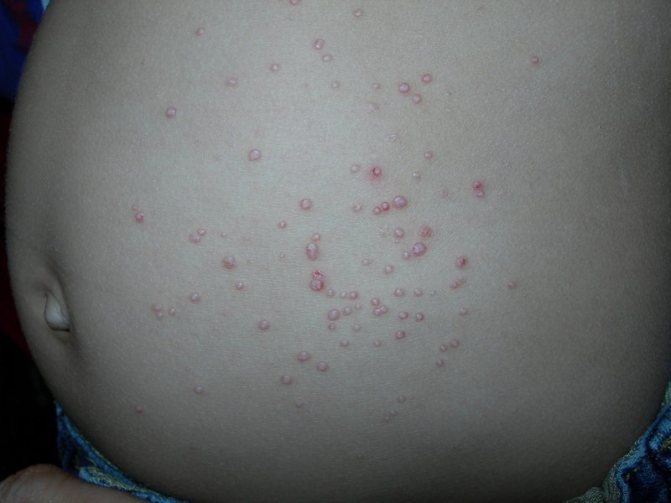
Multiple formations due to infection with molluscum contagiosum virus
In more advanced cases of the disease, itching may occur, and in rare cases, pain in the areas where the rash occurs. With constant scratching of the papules, inflammation, redness around the node and the onset of a purulent process may occur.
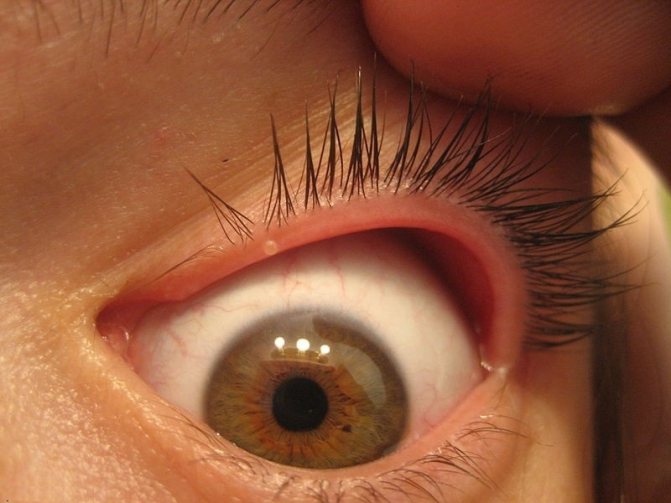
The danger of molluscum contagiosum papules being located on the eyelid is that close proximity to the eye can lead to the contents of the nodule entering the conjunctival cavity. This can provoke concomitant diseases such as conjunctivitis, blepharitis or keratitis. These eye diseases are treated traditionally.
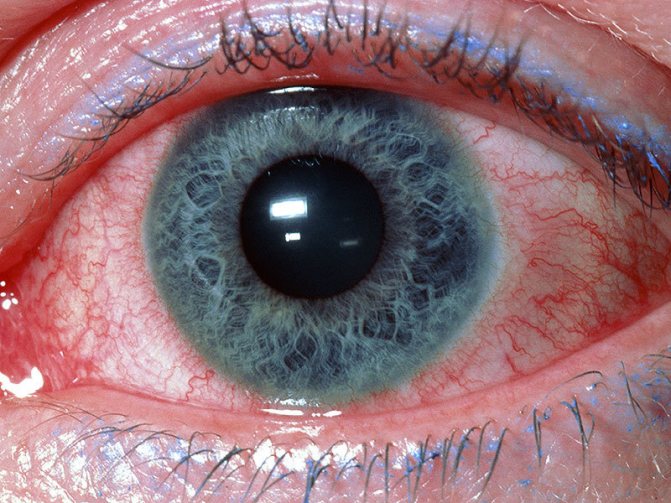
Discharge from a papule can cause conjunctivitis
Nodules in this area of the body are no different from formations in other places. The papules have a spherical shape, from which a curdled mass is released. Molluscum contagiosum on the genitals can have many elements of varying sizes.
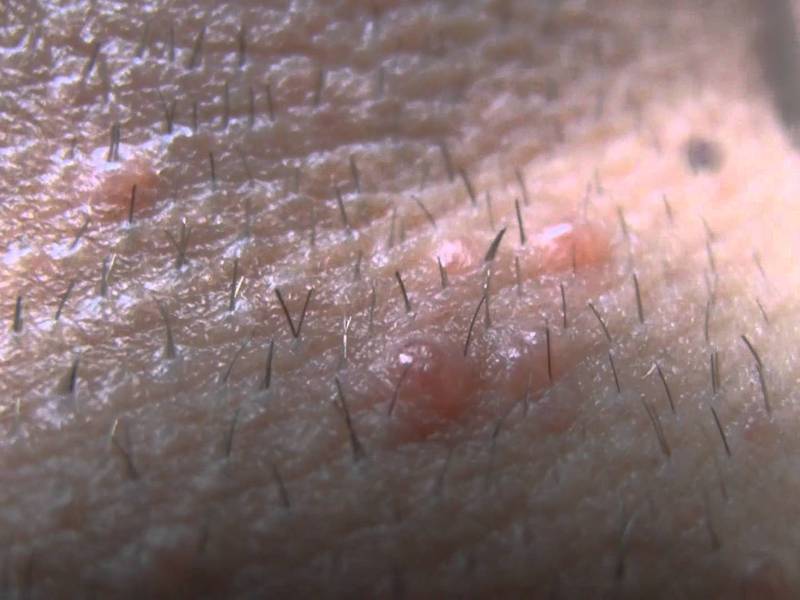
Papules in the pubic area
Molluscum contagiosum papules are treated with the following substances:
- iodine
- fukortsin
- celandine
- hydrogen peroxide
- some acids

In case of painful sensations, the papules are treated with lidocaine. To enhance the immune response, the doctor prescribes various immunomodulators in the form of suppositories (Viferon, Laferabion), tablets and drops. It also makes sense to use some antiviral drugs.
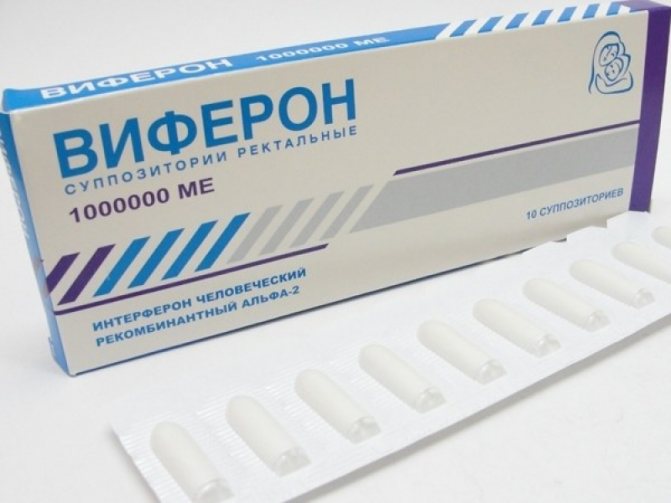
Viferon suppositories activate the immune system
It is also important to prevent the patient from coming into contact with contaminated hygiene items and clothing, otherwise the fight against the disease will be unsuccessful - there is a high risk of relapse.

Therefore, it is very important to seek qualified help. The doctor will prescribe medication and choose the most appropriate method for removing papules on the body of a patient with molluscum contagiosum.
In case of infection through sexual contact, it is necessary to examine the sexual partner and prescribe the necessary treatment. After removing the tumor, a crust remains on the skin, which then falls off. The healing process is very fast.
To prevent the spread of infection, you should:
- Do not comb knots;
- Do not leave areas with a rash open (try to bandage them);
- Do not let anyone use your hygiene products;
- If nodules appear on the face of an adult man, then you should refrain from shaving;
- Avoid sexual intercourse if the rash is localized in the genitals;
Doctors strongly do not recommend squeezing out nodules on your own. When the nodule is damaged, an active substance is released, which can spread the rash to other areas and infect another person.
During illness, you should limit yourself to water procedures and completely avoid bathing in the bathroom. You can only take a fairly cool shower for a short time, giving up washcloths. After the washing procedure, do not dry the body with a towel, but lightly blot it.
You can introduce an infection through the wound, which will provoke a more complex course of the disease and worsen the condition of the skin.
If the diagnosis is made correctly and all the doctor’s instructions are followed, you can soon get rid of the mollusk safely. The treatment will be successful, the rash will leave no scars or any marks on the skin. Molluscum contagiosum is not a terrible disease.
2) It is imperative to find out the predisposing factor to its appearance in adults. Why did he appear?
3) In adults, the most common location of molluscum contagiosum is the genitals and groin area. In women: on the pubis and labia. In men - on the penis and pubis. In this case, it has similarities both with the initial stage of genital warts and with pustular diseases in the genital area. This arrangement is due to sexual transmission.
4) In treatment, it is necessary to correct the general disease, which led to a decrease in immunity and activation of the virus:
- treatment of diabetes mellitus,
- correction of dysbacteriosis,
- correction of drugs that suppress the immune system (cytostatics, corticosteroids, including locally in the form of ointments) treatment of HIV infection.
5) It is quite possible that a child caught a mollusk in kindergarten, and then the adults got sick. All family members must be examined at once.
6) Treatment of pregnant women with molluscum contagiosum differs from other women: you should stop using antiviral and immune drugs, and do not use cauterizing agents such as supercelandine. The only treatment method for pregnant women is removal of molluscum papules.
In children and most adults, without treatment, the symptoms of molluscum contagiosum go away on their own as soon as antiviral immunity is formed. Term – in 4-6 months, sometimes 1-2 years.
We invite you to read: Antisorbent can be used to cover a wound oncology
Molluscs on the body can only be treated for medical reasons: trauma, inflammation. Cosmetic indications are solely at the request of the patient.
1) Removal of formations
2) Local treatment
3) General treatment
4) Treatment of complications (inflammation, allergies, skin ulcerations)
1) Removal with tweezers or a surgical spoon (curette)
- First, the doctor performs local anesthesia of the skin with Emla cream or another surface anesthetic.
- The doctor squeezes the jaws of the tweezers and squeezes out the contents of the papule (as in the video below). If necessary, the resulting small cavity can also be scraped out with tweezers or peeled out with a curette (a sharp Volkmann spoon). If the papules are small, then no curettage will be needed.
- After this, the doctor carefully removes the curdled masses and cauterizes the resulting wound with 3% hydrogen peroxide and tincture of iodine.
- Some patients at home perform an independent opening of the molluscum papules with a needle, as in this video. We remind you: it is not recommended to do this yourself. By wiping the skin with a napkin, thereby spreading and rubbing viruses into neighboring areas of the skin, you only spread the infection even further.
- After removing the mollusk, the wound should be treated with iodine or brilliant green once a day for another 3 days.
- With proper removal of the elements of molluscum contagiosum, no scars remain on the skin.
We suggest you read How to remove a mole quickly at home
2)Electrocoagulation
The doctor cauterizes the papule with an electrocoagulator (electric knife). Subsequently, after such treatment, scars may remain.
- The rash in adults is localized on the skin of the torso, face (often on the eyelids), neck, armpits, and sometimes in places of trauma. When the infection spreads through sexual contact, a rash appears on the skin of the pubis, abdomen, genitals, inner thighs and around the anus. The appearance of nodules on the scalp, tongue, lips and buccal mucosa has been recorded. The appearance of a rash on the soles and feet is an atypical localization. In children, nodules are localized on the face and torso.
- The number of rash elements varies - from single to multiple (in people with immunodeficiency). In HIV-infected patients, the rash is profuse (hundreds of nodules).
- The nodules are located separately, randomly, rarely merge into large conglomerates, which is called “giant molluscum contagiosum.”
- The color of the papules is pink, pink-orange, yellow, pearly white or the color of normal skin. They are shiny and translucent. They have a round, hemispherical shape with a depression in the center in the form of a navel, filled with horny masses.
- Most of the nodules have a depression in the center filled with horny masses, which is clearly visible when magnified using a manual lens, dermatoscope or otoscope.
- When pressed from the sides, a dense, cheesy-looking keratin mass emerges from the nodule, containing Lipschütz’s mollusc bodies, with a huge number of virions. In atypical or advanced cases, this sign is absent.
At the beginning of the disease, tiny papules (1 - 2 mm) appear. Over time, they increase and reach 2 - 4 mm, in some cases - 5 - 10 mm. The nodules reach their maximum size within 1 to 3 months.
- Agminant. When papules merge, giant conglomerates (“giant molluscum contagiosum”) are formed, reaching a diameter of 2 cm.
- Horny. There is keratinization of the rash elements.
- Generalized. It is noted when the rash disseminates.
The use of folk remedies in the fight against the virus
Compliance with hygiene rules with daily treatment of the genitals with soap and water and changing underwear helps prevent the spread of infection. After a pool or sauna, it is important to take water treatments.
People infected with molluscum contagiosum should not be in a group during an exacerbation. During this period, it is not recommended to visit a massage therapist, baths, or swimming pools. To prevent infection, it is important to use personal belongings and hygiene items.
Molluscum contagiosum rarely develops in people with strong immune systems. Proper nutrition, exercise, and walking help increase the body's resistance to infections. Preventive measures include regular cleaning of the room from dust, which may contain the virus.
The appearance of molluscum contagiosum on the genitals causes severe discomfort to patients. The disease becomes the cause of psychological complexes. Injury to papules can cause re-infection and inflammation. Formations on the genitals of a viral nature require mandatory treatment. If signs of molluscum contagiosum appear, you should contact an infectious disease specialist.
If experts recommend abandoning attempts to treat the virus, explaining that the disease will go away on its own, but you still want to speed up the healing process, then you can resort to the help of traditional medicine. There are several recipes to cope with the manifestations of the disease:
- Using garlic, 1 head of which should be thoroughly chopped and 1 tsp added to it. butter. The resulting composition must be stirred and lubricated with it on the nodules three times a day.
- In addition to garlic, you can take advantage of the healing properties of the string. For this you need 2-3 tbsp. l. crushed medicinal plant, pour 1 cup of boiling water, bring the solution to a boil, then leave to brew for 1 hour. The resulting tincture can be used to wipe the rashes 3 times a day for 1 week.
- Bird cherry leaves can also be crushed, squeezed out the juice, and then rub the resulting juice onto the affected areas of the body.
The main measure of disease prevention should be considered the rules of personal hygiene. Therefore, it is very important to shower every day. You should also change bed linen at least once a week, and change underwear daily.
For people who are sexually active, the rule for life should be the absence of casual sexual contact. And, most importantly, do not forget to strengthen the immune system, since weak immunity greatly increases the likelihood of infection.
Thus, molluscum contagiosum, which manifests itself in intimate parts of the body, of course, does not cause any significant discomfort. However, this does not mean that the disease does not need to be treated.
Molluscum contagiosum on the genitals is a contagious (contagious) disease of smallpox nature. According to statistics, the inguinal localization of the pathological process is observed most often. The main category of patients are children under 5 years of age. Pubertal patients, and especially adult patients, are much less common. It is important to note that adult patients suffer exclusively from the genital form of the described pathology.
Very little is known about the causes of the development of molluscum contagiosum, as well as about the pathogenesis. It is known for certain that the causative agent of the disease is transmitted both through unprotected sexual contact and through interaction with infected objects (domestic route). What is it recommended for patients to know?
This disease is viral in nature, its causative agent is a filterable virus related to the smallpox virus. The pathogen has nothing to do with shellfish. The mollusk (syl) received its name for its distant resemblance to a snail shell.
- It appears only on the skin, without affecting the internal organs, mucous membranes and skin of the feet and palms of a person.
- Most often, the mollusk is diagnosed in children aged one to ten years, although it can infect other age categories.
- The incubation period of the disease is two weeks. In some cases, the latent period takes a long period of time - up to several months.
- The appearance of active rashes coincides with a temporary decrease in the patient’s immunity or with simultaneously occurring acute or chronic diseases.
We suggest you read How and where moles are checked for cancer: reviews
Removal of molluscum contagiosum with nitrogen
A quick and effective way to combat molluscum contagiosum is to remove it using a laser. This procedure is carried out quickly and is absolutely painless, as it is performed under local anesthesia.
The advantage of the method is also that the removal is carried out under sterile conditions, which prevents the contents of the papules from getting onto other areas of the skin and the formation of new formations. If a specialist completely removes all nodules, then the patient is absolutely healthy and no new papules will be formed.
An alternative to laser removal of molluscum contagiosum is cauterization with nitrogen. The advantage of the method is an excellent aesthetic effect, since there are no visible scars or cicatrices.
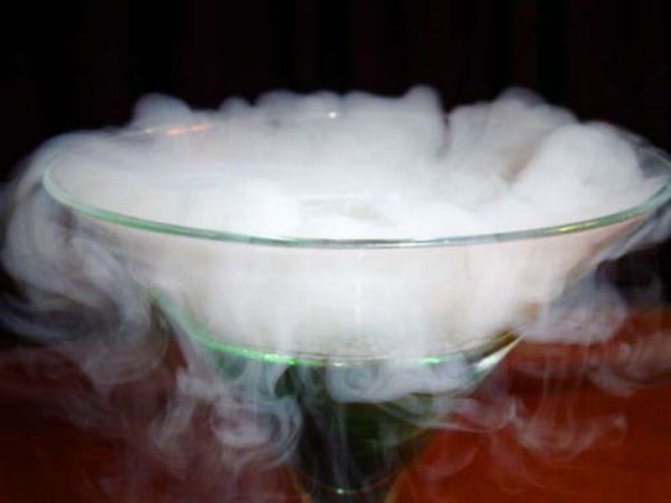

After this, the papule turns white, which indicates the death of the mollusk’s body and its destruction. The disadvantage of the technique is that in some cases these manipulations must be repeated, with a break of a week. This may not be very convenient for a patient who wants to get rid of the disease as quickly as possible.
Where to go with a problem
When the first signs of molluscum contagiosum appear, the patient should contact a dermatologist or infectious disease specialist. An initial examination can be done by a general practitioner.
If symptoms of the disease are detected, the patient is prescribed treatment. If an infection occurs in the bikini area, labia in women, penis and scrotum in men, removal of papules is recommended. Getting rid of rashes is necessary due to their constant trauma, which causes the rapid spread of the virus to healthy areas of the skin.
Use of ointments
For people who, for some reason, cannot carry out radical removal of molluscum contagiosum, there are more accessible and simpler ways to get rid of the disease. In particular, you can heal with the help of various ointments.

Antiviral drug "Acyclovir"
The range of pharmacies offers the following remedies for this viral disease:
- Viferon is an ointment whose main active ingredient is interferon, a protein responsible for the body’s immune forces. By rubbing the product into the affected areas, the body's immune resistance to the virus increases. Also, being integrated into cells, interferon does not allow the virus to penetrate the membranes, which prevents the growth of formations
- Acyclovir is an antiviral ointment that, with regular use, will help get rid of molluscum contagiosum. The product is also widely used for smallpox, herpes and other formations of viral etiology
- Cycloferon is an ointment that has a complex effect. The product is an immunomodulator, but at the same time it has an antiviral effect and relieves inflammation. Its application has its own nuances, so it is necessary to consult a specialist.
- Imiquad is a cream that stimulates the production of interferon, which can fight viruses and resist their effects. The product must be applied to the affected area of the skin for a long time - at least 9 hours, then its effect will have a result.
Immunomodulator ointment "Cycloferon"
It is easy to prepare products for external use yourself. There are several ways to treat molluscum contagiosum.
The ointment can be made from garlic and butter. The mixture should be applied to the affected skin three times a day. If garlic juice is well tolerated in its pure form, you can treat papules only with it. The easiest way is to peel a clove of garlic, make a few cuts and lubricate the knots.
The herbal infusion also helps get rid of molluscum contagiosum. To prepare, you need to take 1 tablespoon each of eucalyptus, yarrow, juniper and calendula. The mixture must be infused in a glass of boiling water for at least an hour. The medicinal drink should be drunk twice a day, 120 ml. Course - 14 days. This method is contraindicated if there is intolerance to any component.
To get rid of molluscum contagiosum, you can use a decoction of pine needles. It has a powerful antiseptic property and promotes rapid healing of the skin.
ethnoscience
Traditional methods of treating molluscum contagiosum allow you to fight the disease without the use of mechanical procedures or the use of medications. Medicines and remedies prepared at home can not only fight the infection, but also restore the immune system, which plays a key role in preventing relapses.
- One of the most effective methods of treating and preventing the disease is the use of garlic, which has well-known powerful antiviral properties. The cloves are ground into a paste and a small amount of oil is added, which in turn is applied to the diseased areas of the skin. Apply this compress three times a day, then rinse thoroughly.
- Another effective method is to use a decoction of celandine, as well as freshly squeezed juice from it. The scheme of use of this product is similar to garlic gruel. You can also use decoctions of bird cherry leaves and juice from these leaves, the use of which allows you to get rid of skin sores in a short time. In general, traditional medicine offers a wide range of natural remedies that have a beneficial effect on the skin. We should not forget about the need for preliminary consultation with specialists, thanks to which complications and the development of the disease can be avoided.
It is important to remember that the appearance of molluscum contagiosum is only a symptom that indicates the presence of a virus in the body. Therefore, treatment of the disease must be comprehensive and include several, often diametrically opposed, manipulations that will completely get rid of the infection and the consequences to which it led. Only a qualified specialist can make a correct diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment, who, thanks to examination and laboratory tests, is able to determine the cause of the disease and prevent it from reoccurring. Don’t neglect your own health even if you discover the slightest pathology - contact a specialist who will be able to prescribe effective treatment for you.
Sometimes a person encounters a disease such as molluscum contagiosum in intimate places. This pathological condition is a viral skin disease.

Doctors note that molluscum contagiosum on the genitals can be observed in men, women and children. However, the disease is often diagnosed in adolescence. As for children and adolescents, the disease manifests itself on the skin of the face, eyelids and nose. In adults, the appearance of rashes can be observed in the groin area. The virus is transmitted through contact and household contact and during intimate intimacy.
Carrying out prevention
In order to protect yourself from this pathology, you must follow the recommendations below:
- It is very important to constantly follow basic rules of personal hygiene by keeping your home clean.
- You also need to constantly strengthen your immune system.
- Contact with sick people should be completely avoided. This is especially important because the disease being described is viral in nature.
- You should practice exclusively protected sex. Promiscuous sexual activity can cause not only molluscs, but also other even more dangerous diseases.
- If you want to protect yourself from this skin disease, you need to regularly carry out preventive examinations with appropriate specialists.
Influencing the virus with drugs
Drug therapy consists of taking medications, treating with ointments and solutions that can destroy the structure of unaesthetic nodules. For this purpose, products based on cantharidin, tretinoin and trichloroacetic acid are used. Drugs in the form of Chlorophyllipt, Fluorouracil or benzoyl peroxide may also be suitable. Treatment with medications compared to surgical tactics is considered less traumatic and quite effective.
But it’s worth remembering once again that doctors are against helping the body fight this virus. In situations where a generalized type is detected, antiviral treatment is carried out in conjunction with local therapy. Patients are prescribed Viferon along with Acyclovir or Isoprinosine. Treatment with immunomodulators is also considered appropriate.
How to remove molluscum on the face?