Causes and symptoms of throat burns
The most common causes of a laryngeal burn include:
- Drinking boiling water or too hot liquids, tea or coffee.
- Uncooked food.
- Chemical substances. A throat burn occurs if you inhale or swallow toxic fumes, various acids, iodine, or alcohol.
When an injury occurs, a person is tormented by acute and painful signs that are accompanied by certain symptoms. These include:
- Pain when trying to swallow.
- Burning in the throat.
- Profuse salivation.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Increase in temperature.
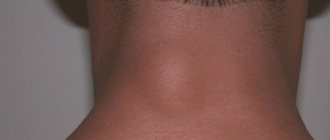
- Lymph nodes increase in size.
- If the burn is severe, a person may go into shock.
An injured person's voice changes and a cough appears. Its condition depends entirely on the causes of the mucosal burn and the extent of its spread.
Types of burns
A chemical burn to the throat is a very serious problem, the main cause of which in everyday life is alcoholic beverages or certain medications.
Interestingly, simply gargling with iodine solution or various alcohol tinctures can cause a chemical burn to the throat mucosa.
Our favorite iodine is an aggressive chemical that can cause severe tissue burns . “Yox”, “Lugol” are medications developed on the basis of iodine.
In the presence of severe tonsillitis or pharyngitis, the use of these drugs can lead to a burn of the mucous membrane.
Specific substances that cause chemical burns are: citric acid, ammonia, soda, vinegar, acetone, alkalis and acids, ethyl alcohol.
A burn to the throat by gastric juice during gastritis can be accompanied by pain and burning.
Acids can cause coagulation of muscle proteins, as well as the formation of a dry scab, which is a barrier to further penetration of the aggressive substance.
Alkalis have a much more aggressive effect on the laryngeal mucosa; they also dissolve proteins. Along with this, wet necrosis develops, which facilitates the internal penetration of chemicals.
Thermal burn of the throat occurs when drinking boiling water and hot food, or when inhaling too hot air, as happens during fires . In this case, due to a burn to the throat with boiling water, a large number of burn blisters may appear on the oral mucosa.
The victim may develop vision problems, deteriorate general health, and disrupt the functioning of some internal organs.
However, this is a milder form of throat burn compared to the effects of chemicals on the laryngeal mucosa. This is due to the short-term effect of hot substances, as well as their rapid neutralization with cool water.
Description and reasons
According to the type of origin, a burn of the larynx can be chemical or thermal in nature:
- The chemical is formed when swallowing concentrated acid-base or alcohol-containing compounds - iodine, acids (citric, acetic, hydrochloric), alkali (caustic soda), ammonia. Tissue damage continues until the aggressive substance is neutralized.
- Thermal burn occurs from too hot drink or food, steam during inhalation. Characterized by injury to the mucous membrane of the throat. Blisters appear in the mouth, and the victim’s health worsens. Cool water helps stop further tissue destruction.
Manifestations of a burn to the pharynx are distinguished by severity:
- First. Only the outer layer of the mucosa is affected, redness with slight swelling is observed.
- Second. A more serious lesion, accompanied by the appearance of blisters, a grayish film, and severe swelling.
- Third. Deep layers are involved, necrotic changes in the mucous membrane and nearby tissues are possible.
In everyday life, 1st degree burns most often occur, which do not pose a threat to life.
Causes
Thermal burn affects the throat when ingesting hot food or drink, and chemical burn when the throat is exposed to medications, alcohol, acids or chemicals.
The main causes of this type of damage are negligence and carelessness when interacting with hot liquids, food, as well as chemicals, alcohol-containing liquids and medications of a certain group.
Alcohol and alcohol . The risk group primarily includes socially vulnerable citizens suffering from addiction, who consume alcohol-containing liquids and low-quality alcoholic beverages for other purposes.
Damage from alcohol-containing liquids occurs if the alcohol concentration in them is more than 70 percent. This is the easiest type of lesion, since a membrane forms on the mucous membrane that does not allow alcohol to penetrate deep into the surface layer of the epithelium. If alcohol penetrates into the esophagus, a white coating of dead tissue cells appears on its internal surfaces.
The injury is accompanied by the following manifestations: pain in the chest and cervical region, weakness appears in the stomach, and the sensitivity of taste buds is dulled.
Hospitalization, if the esophagus is not damaged, is not required and after some time the tissue cells will recover on their own.
Hot food and liquid . Most often, the throat is burned by hot tea or food, as well as by inhalation of hot steam. Thermal burn of the throat occurs in most cases and does not pose a great danger if it does not penetrate into the deep layers of the mucous membrane. But it all depends on the temperature of the food, steam or drink ingested and on the time of action of the hot agent.
Children are most susceptible to these types of injuries. Therefore, to prevent a child from getting a burn on the palate from hot food, you should always check the temperature of the food served on the table.
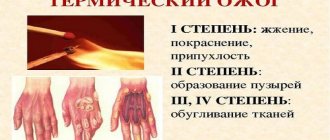
There are three degrees of burn injury:
- First degree. Acute pain, the mucous membrane turns red.
- Second degree. The appearance of a gray-white plaque with liquid blisters.
- Third degree. Tissue death is observed.
The first and second degrees of severity are the most common and with proper treatment, regeneration of damaged areas occurs quickly. Grade 3 is very rare, it is the most difficult and can only be treated in a hospital.
Causes and symptoms of throat burns
There are several factors that damage the mucous membrane of the throat. Among the most common reasons are the following:
- carelessness when using toxic substances, alkalis, alcohol solutions and vinegar;
- drinking excessive amounts of strong alcoholic drinks with high alcohol content;
- inhalation of smoke from smoking cigarettes, hookahs or during a fire;
- violation of safety rules when staying at industrial facilities where toxic fumes are present;
- incorrect use of alcohol settings in self-therapy of tonsillitis, pharyngitis and other diseases;
- damage during quartzing.
Also, the larynx can be damaged due to the internal influence of gastric juice. This phenomenon often occurs in patients suffering from high stomach acidity.
Alcohol and alcohol
The risk of alcohol burn occurs when drinking medical alcohol with a strength above 70 degrees and vodka-based drinks. In case of a burn from these drinks, a person loses his sense of taste, feels a general decrease in immunity and pain in the stomach and neck. Due to a burn from vodka or other alcoholic drinks, a pronounced white coating of dead tissue forms inside the ENT organ.
Alcohol burns are considered the most harmless of the chemical category, except in cases where the walls of the esophagus are damaged. In most situations, serious tissue damage does not occur due to the formation of a film on the surface of the larynx, which blocks the penetration of alcohol into deep tissues.
If the throat is injured by alcoholic drinks, there is no need to carry out specialized procedures - the mucosal tissues regenerate on their own over time. If your injury is serious, you may need to go to the hospital. As a result of a medical examination, it is checked whether the walls of the internal organs are affected and what treatment is necessary to restore the tissue.
Thermal burns of the inner walls of the larynx are often caused by eating hot food or exposure to boiling water on the pharynx. There are several degrees of burn that this factor can provoke:
- with a 1st degree burn, the mucous membrane of the throat turns red and begins to swell;
- the onset of the 2nd degree is characterized by the appearance of a grayish coating with blisters;
- the most severe degree 3 leads to tissue death.
Due to carelessness while eating hot food, in addition to pain, there is a risk of developing an inflammatory process in the nasopharynx.
Gastric juice
Damage to throat tissue by gastric juice occurs due to a disease that provokes the injection of bile into the mucous membrane. With the constant release of bile, cancer of the digestive organs and ulcers may develop. This type of burn is a chemical injury, and treatment requires professional consultation with a gastroenterologist.
A burn to the pharynx by gastric juice can occur for various reasons. The most common causes of injury are:
- oxidative process due to consumption of excessively fatty or sugary foods;
- opening of the sphincter as a result of alcohol entering the stomach or during sleep;
- stomach overloaded with food.
The peculiarity of chemical burns is that because of them, cellular structures are destroyed to the point of complete necrosis. Chemical damage can be caused by the penetration of caustic substances into the body. Acids lead to the coagulation of muscle proteins, and alkalis dissolve proteins and act on deep tissues.
Often people get a chemical burn when trying to self-treat at home. When treating the respiratory tract, injury can be caused by the incorrect dosage of medications such as Lugol, Yox, hydrogen peroxide and alcohol tinctures. Signs
It is possible to determine the presence of a burn of the larynx by a number of symptoms observed in the victim. Signs include:
- burning sensation in the palate;
- intense secretion of saliva;
- pain in the larynx (sometimes there is a sharp and painful pain when swallowing);
- swelling of the lymph nodes and a feeling of lack of oxygen;
- attacks of coughing, nausea and vomiting.
In severe situations, there is a risk of developing a state of shock. Even a minor burn can cause improper respiratory function and lead to suffocation. This problem is especially relevant for children and the elderly. If primary symptoms characteristic of this type of injury are detected, first aid should be provided, and then go to the hospital for further treatment.
Throat is the general name for the nasopharynx, pharynx and larynx. The nasopharynx passes into the pharynx, which gradually narrows and ends with the larynx. The larynx connects to the esophagus. A burn to the throat disrupts the coordinated functioning of this system.
Severe pain appears, especially when swallowing. The nasopharynx area feels dry and burning. Profuse salivation begins in the oral cavity. If the larynx is damaged, the voice changes, and hoarse notes appear in it. Possible vomiting.
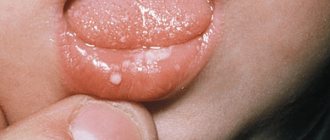
The appearance of the mucous membrane of the throat changes. A mild first-degree burn is indicated by the formation of white spots on the mucous membrane. After 2-3 days, the spots begin to disappear. When blisters appear on the mucous membrane, a second-degree burn is diagnosed. These blisters take longer to heal, ranging from two to four weeks.
The most dangerous are third-degree injuries, which are characterized by copious discharge of pus. Pus indicates the death of body tissue. The tissues are not completely restored, scars remain.
A burn to the larynx also causes disruptions in the functioning of the entire body:
- the temperature rises;
- digestion is disturbed (constipation, disorders, feeling of heaviness in the stomach, increased gas formation in the intestines);
- lymph nodes enlarge;
- pulse increases, blood pressure rises;
- the victim has difficulty breathing;
- an allergic reaction is possible.
Mucous membranes are the most delicate and sensitive tissues in the human body. This makes them easily susceptible to injury and damage, which may be accompanied by the following general symptoms:
- enlarged lymph nodes, swelling of the soft tissues of the mouth;
- a persistent burning sensation with profuse salivation;
- difficulty swallowing due to severe pain;
- fever up to 38-39 °C, chills;
- nausea, vomiting.
| Aggressive substance | Characteristic signs of injury |
| Iodine solution, Lugol | Brown or blue-gray vomit. |
| Alkali | The vomit is oily and contains elements of the mucous membrane. Wet necrosis. |
| Acid | Specific odor from vomit and mouth. Dry scab. |
| Alcohol | A whitish coating of dead tissue forms on the walls of the mouth and tongue, and taste sensations disappear. |
| GERD | Stomach juice backs up into the esophagus, causing heartburn, belching and sore throat. |
The consequences of grade 2-3 damage are often toxic shock and suffocation. When the respiratory tract is damaged, the following appears:
- cough;
- suffocation;
- chest pain;
- hoarseness of voice.
Further treatment
At the first stage, the ambulance team inserts a tube into the victim and performs a gastric lavage with 10 liters of water, before which they are offered to drink 100 ml of painkiller for pain relief. After probing the esophagus, analgesics are also administered to relieve pain shock.
The department of the clinic provides complex treatment, which consists of administering medications to stimulate cardiac activity, as well as the functioning of the kidneys, lungs, hormonal drugs, and painkillers.
In the first few days, the victim will have to be treated by drinking 100 ml of a 5% solution of novocaine. You can also take a small amount of vegetable oil diluted with an antibiotic.
In a hospital setting
If damage to the pharyngeal mucosa is treated at home under the supervision of a doctor, then 2nd and 3rd degree burns can only be treated in an inpatient setting.
| Drugs | Titles |
| Painkillers |
|
| Detoxification (intravenous) |
|
| Antibiotics |
|
| Antiseptics (rinses) |
|
| Sedatives |
|
| Antihistamines |
|
| Wound healing (acceleration of regeneration and epithelization) |
|
In extreme cases, surgical methods are used. Indications for surgery: deformations, scars, ulcers that led to dysfunction of the pharynx and esophagus.
At home
When treating mild burns at home, folk remedies and basic physiotherapy give good results:
- herbal gargles (gargle with decoctions of chamomile, calendula);
- chilled neck compresses;
- douching of the oral cavity and larynx with rosehip and peach oils;
- inhalation;
- lubricating the throat with sea buckthorn oil.
An effective diet for quickly restoring the mucous membrane is eating only pureed cool foods.
Signs of a burn at different stages
1st degree:
- the surface layer of the epithelium is damaged,
- a person experiences swelling and redness in the mouth and mucous membranes,
- you may feel a sensation of pain and burning in the throat,
- The patient's condition is not deteriorating, but is in a stable condition.
2nd degree:
- a person develops specific blisters that contain gray films,
- 2 weeks after receiving a burn, plaque begins to separate,
- wounds begin to heal and heal, forming scars at the burn sites,
- the person feels slight weakness for 2 weeks after the injury,
- It is allowed to increase body temperature to 38 degrees.
3rd degree:
- it is characterized by signs of intoxication,
- burned areas die off
- scabs appear
- ulcers form
- the functions of the pharynx, larynx, and esophagus are impaired.
Causes
Burn injuries in most cases occur in workers at enterprises due to non-compliance with safety precautions. They also occur in everyday life due to negligence or in people under the influence of alcohol. Thus, it is possible to develop a burn to the throat if you mistakenly take a substance that is not intended for internal use (acetic essence, technical alcohol, etc.).
There are two types of burns – chemical and thermal.
Chemical
With this type of burn, the damaging substance gets inside, causing a traumatic effect not only on the throat, but also on the oral cavity.
A burn can be either isolated or combined.
The latter often occurs when:
- Ingestion of a large amount of a concentrated chemical substance, which results in concomitant damage to the esophagus and stomach.
- Inhalation of toxic fumes, which additionally damages the mucous membrane of the larynx, trachea and bronchi.
First aid
Help must be provided immediately - the prognosis and speed of recovery depend on this.
First of all, the source of the lesion and the extent of the injury are established. If the burn was caused by boiling water, the victim should be given:
- cool water, which stops the spread of lesions inside the esophagus;
- crushed ice for slow resorption;
- Novocaine or Lidocaine to suppress pain.
In case of a burn of chemical origin, you need to select a neutralizing reagent:
- for acids - soda solution (teaspoon per 1 liter of water);
- for alkalis - a weak solution of citric or acetic acid;
- for alcohol-containing substances - as much clean water as possible (drink in small sips);
- if the nature of the aggressor is unknown, washing the stomach with milk will help.
With 2-3 degree burns, severe pathologies develop, so a mandatory examination of the victim by a specialist is required. Wrong actions can cause disability and even death of a person.
Treatment of a chemical burn
When treating a laryngeal burn or nasopharyngeal burn caused by chemicals, it is important to neutralize the source of the problem. If scabs appear at the site of the lesion, then the substance is an acid. Then apply a soda solution (1 teaspoon per 250 ml of water). If jelly-like discharge forms there, then the source of the damage is alkali. It can be neutralized with a weak solution of 9% vinegar (1 teaspoon per 500 ml of water) or 0.1% solution of citric acid (6.4 g per 1 liter of water). When a small amount of a harmful substance enters the stomach through the larynx and esophagus, it is neutralized using fermented milk products.
A burn to the pharynx may be accompanied by severe swelling that interferes with breathing. Then antiallergic drugs such as Diazolin and Suprastin are indicated. They are taken in combination with painkillers, sedatives and antibiotics.
In case of first degree injury, healing of the damaged mucosa is carried out under the supervision of an otolaryngologist.
The following tools are used for this:
- decoctions of anti-inflammatory herbs (chamomile, sage);
- mild essential oils (lavender, peach).
In case of more serious injury, patients are hospitalized in the general surgical department and are prescribed complex treatment. Seriously ill patients are sent to the burn department of the regional hospital. If a large area of the throat mucosa becomes covered with scars or bleeding ulcers, surgical intervention is necessary. It is performed by a surgeon, otolaryngologist and combustiologist.
First aid
A favorable outcome in treatment will depend on the speed of assistance, the nature and degree of mucosal burn. Initially, it is established what could have caused the injury. To do this, a visual examination of the room is carried out, the presence of a specific odor of the substance that caused the burn is taken into account.
If this does not give any result, then you need to examine the wound and the patient’s mucous membrane, carefully examine the vomit and the type of scab.
If the burn was caused by interaction with alkali, then the vomit will contain pieces of mucous tissue. When injured by iodine, they turn blue or brown. After a burn, a scab appears, the color of which can tell a lot:
- with acid burns it is yellow, that is, the injury occurred due to nitric or hydrochloric acid,
- for black - sulfuric acid, for white - hydrogen peroxide.
Once the agent that caused the burn has been accurately determined, measures can begin to eliminate the effect of this chemical. There are rules that should be remembered and followed immediately after a throat injury.
When injury occurs from various acids, it is necessary to give a lime mixture.
For alkaline burns - diluted citric acid.
The person must be provided with antiseptics and given a flow of fresh air.
If the burn is quite serious, it is necessary not to waste time, but to take the victim to the hospital, where doctors can quickly provide qualified medical care.
Precautionary measures
Given the seriousness of the problem, every measure must be taken to prevent it.
Here are simple tips to help avoid burns to the throat mucosa:
- learn and comply with safety requirements at work;
- use personal protective equipment when working with chemicals;
- Carefully check the temperature of food and drinks before taking a sip;
- never use a repeatedly increased dose of the drug to improve the effect;
- do not self-medicate according to the principle “the longer the better”;
- Check the contents of vials and bottles, especially dark glass, for color and odor before use.
Following these tips protects a person from severe pain and disruption of the respiratory and digestive systems.
A throat burn has clear signs and is easy to identify. It is important to find out how to treat a throat burn and act as soon as possible. Then it will be possible to provide effective assistance to the victim.
Treatment methods
All further measures aimed at a speedy recovery will depend on how badly the throat is damaged. If doctors have diagnosed severity levels 2 or 3, then the patient must be treated in a hospital where qualified care will be provided. With severity level 1, restoration of the mucous membrane can occur at home; the main thing is to observe the following measures:
- Mandatory pain relief. You can take tablets or special solutions.
- Use valerian and bromine as sedatives.
- Treatment with antibiotics to minimize the spread of infection or infection.
- In order for the wound to heal faster and all functions to be restored, you need to infuse oil-based preparations with a special syringe.
- To reduce the level of intoxication, it is necessary to administer a solution of glucose, hemodez, rheopolyglucin.
- Gargle with antiseptic agents to prevent the development of further throat infections.
For the most severe and complex injuries, surgery may be prescribed. Most often, surgical intervention is needed in cases where scars or ulcers begin to form. Usually they begin to greatly interfere with the normal functioning of the body. Therefore, operations are performed on the trachea, larynx, and esophagus.
Treatment of thermal burns
Treatment involves cooling the affected area of the throat.
To do this, drink cold (but not ice) water in small sips. You should try to hold the water near the sore spot until it warms up, then swallow. To reduce pain, painkillers are used, for example, analgin, lidocaine and novocaine. Analgin is given intramuscularly, and lidocaine or novocaine is administered to the throat. In the first degree, gargling with weakly concentrated aqueous tinctures of chamomile, calendula, and eucalyptus helps a lot. These herbs relieve inflammation. For burns to the lower larynx, treatment includes cold compresses on the neck. You should definitely consult an ENT doctor. Hospitalization is usually not required.
Throat burn: types and causes, manifestations, first aid, how to treat
A throat burn is a serious injury that can be either chemical or thermal in nature. What symptoms are observed in the victim and how to treat the burn?
A laryngeal burn is damage to the mucous membranes that occurs as a result of exposure to high temperatures or aggressive chemicals. This injury is quite widespread in everyday life, because a burn to the pharynx can be caused by consuming hot food and drinks. Damage from alcohol or acetic acid, Lugol, iodine, caustic alkalis, and concentrated steam is often found.
Experts consider a chemical burn to the throat to be the most difficult in terms of treatment and further recovery. Even a visit to the dentist can provoke injury, for example, if arsenic or other potent drugs come into contact with the mucous membranes of the larynx.
Young children are also susceptible to this type of damage and, due to their curiosity, may well try household chemicals. According to the international classification, burn injuries to the throat are divided by specialists into 3 degrees:
- The first degree is characterized by redness of the larynx and swelling of the mucous membranes.
- The second degree - manifests itself with specific blisters and the formation of gray films on a red and swollen throat.
- Third degree - manifested by necrosis of the affected tissues. Muscle tissue, ligaments and cartilage tissue are affected.
Lesions of the larynx of the second and third degrees require competent and timely assistance to the victim. Otherwise, extremely serious consequences are possible in the form of an attack of suffocation, poisoning, scarring and even the death of the patient!
How does it manifest?
Doctors identify the following clinical symptoms that appear in a victim with a throat burn:
- Sharp pain in the throat, with a tendency to intensify when trying to swallow;
- Intense salivation;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Cough syndrome;
- Pain localized in the chest area;
- Voice changes;
- Feeling of lack of air;
- Swelling of the cervical lymph nodes;
- A strong burning sensation in the palate;
- Hiccups.
In severe cases, a state of shock may develop. Even minor injuries can cause respiratory problems and cause suffocation, especially when it comes to a child or an elderly person.
Therefore, having identified the first symptoms characteristic of this injury, you should urgently provide first aid to the victim, then take him to a medical facility and transfer him to the hands of professionals.
Causes of defeat
The causes of throat burns are varied:
- Carelessness, inattention. Caustic alcohols, acids, and vinegar are indistinguishable from water in appearance; they are mistaken for a safe liquid and drunk.
- Alcohol or alcohol damage.
- Parental neglect. A child under 3-4 years old, unattended, tastes everything he can reach.
- Burns caused by smoke when inhaling a hookah.
- Failure to comply with safety regulations at work. We are talking about industrial burns of the nasopharynx and esophagus caused by inhalation of toxic fumes.
- Damage by quartz during the quartzing procedure.
- As a result of self-medication.
- Intentionally consuming dangerous liquids or substances in an attempt to commit suicide.
Depending on the influencing factor, burns, according to the International Classification of Diseases, are divided into two groups:
- thermal (ICD code T28.1);
- chemical (ICD code T28.6).
In the first case, people can injure their mouth, palate, throat, trachea, esophagus (sometimes nasopharynx) with too hot food, spicy foods and seasonings (hot peppers), boiling water or very heated steam.
In the second, the list of chemical agents that can cause burns is much wider:
- alcohol containing poisonous corrosive alcohols;
- ethanol;
- ammonia;
- ammonia;
- iodine;
- acetone;
- sulfuric, hydrochloric acids, their vapors;
- lemon acid;
- vinegar;
- bleach, chlorine vapor;
- caustic soda.
According to statistics, most often people get alcohol and alcohol burns to the throat.
Alcohol and alcohol
Alcohol burn occurs when swallowing medical alcohol 70-96% and vodka-based tinctures. The victim loses his sense of taste, experiences weakness, pain in the chest, neck, and stomach. A white fibrin coating of dead tissue forms on the walls of the esophagus, resembling the white of a boiled egg.
Treatment of children
For children, a throat burn has quite serious consequences, since they have a very narrow lumen of the larynx and pharynx. Therefore, as a result of even the most minor injury, swelling appears, which interferes with or even complicates the swallowing process. One of the most serious consequences is difficulty breathing.
At this moment, the child begins to grab his throat and actively gasp for air. He may lose consciousness. Therefore, parents or other adults should urgently call an ambulance, which will quickly provide qualified assistance.
For a baby, the healing process lasts much longer, since most often the burns are deep and serious, making it impossible to carry out some treatment methods. In addition, the child must visit a psychologist.
Features of treatment
A burn of the mucous membrane of the throat of the first degree and sometimes the second is treated at home; in more severe cases, the victim is hospitalized. Successful treatment and recovery requires compliance with the following medical recommendations:
- Silence. The patient should talk as little as possible and avoid raising his voice.
- Rinse with chamomile decoction and antiseptic solutions.
- Abstinence from spicy, sour, hard salty foods.
- Following a diet with a predominance of liquid and puree foods. The patient's menu should include broth, sour cream, cheese, eggs.
For burn lesions of the throat, treatment involves mandatory drug therapy. A qualified specialist will advise you individually on how to treat a lesion in a particular case. Patients are usually prescribed analgesic and antibacterial drugs, and glucocorticosteroids are used to reduce swelling.
The mucous membranes of the larynx in the affected area are regularly treated with antiseptic and oil products - such procedures give a very good therapeutic effect! The surface of the larynx can also be lubricated with Vaseline, beaten chicken egg, using a sterile cotton swab.
Among the most common traditional medicines used to combat this disease are the use of peach, olive, sea buckthorn and rosehip oils. These products can be used for oil inhalations and external treatment of burned areas. Home treatment for thermal burns may include oil inhalations, sucking ice cubes, applying cold neck compresses, rinsing with sage and chamomile infusions.
Proper recovery also requires certain diet therapy. Products such as egg whites, vegetable and butter, cool drinks, and cream contribute to the speedy rehabilitation of the patient. For medicinal purposes, the oil is consumed in its pure form, 4 times a day.
Nutrition and lifestyle during treatment and rehabilitation
A person should begin to follow a special diet so as not to aggravate the condition of a sore throat. A special diet will depend on the severity.
Sometimes the doctor may prescribe to eat food only in liquid form, rubbing it through a special grater or mixing it in a blender. Do not eat hot, spicy, sour or hard foods.
A person with a burnt throat should definitely eat oil about 4 times a day (vegetable or butter). To alleviate the condition, you can apply cold compresses to the damaged area. In this case, you should not strain your throat and maintain absolute silence for some time.
Therapy
Burns can be treated both at home and in the hospital. Doctors' intervention is necessary when injuries to internal organs are detected.
In any case, after the incident you need to contact a specialist who will determine the condition of the victim and prescribe appropriate therapy.
Use of medications
If a burn of 2-3 severity is detected in the throat area, treatment is carried out in a hospital setting using the following medications:
- Analgesics - Lidocaine, Analgin, Promedol. Aimed at combating pain syndrome.
- Drugs with a sedative effect - Persen, Novopassit.
- Detoxification therapy. Performed in case of serious injury. Special solutions are administered intravenously.
- Antibiotics. The latest generation drugs are prescribed with minimal side effects.
- Glucocorticosteroids. Designed to relieve shock and eliminate swelling.
- Antiseptics - Miramistin. Used to disinfect the throat throughout the entire treatment period.
- Anti-allergy medications - Suprastin, Tavegil. Eliminate swelling, fight itching and inflammation.
In case of deep damage to the mucous membranes, surgical intervention is performed to remove dead tissue and eliminate the consequences of the burn..
Home methods
For minor burn injuries, various folk remedies can be used for treatment:
- Sea buckthorn oil. With its help, burned mucous membranes are treated several times a day, which promotes their rapid regeneration.
- Infusions of chamomile, calendula. A large spoonful of plant material is poured with 200-250 ml of boiling water. After 25 minutes, the liquid is filtered and used for rinsing. Infusions relieve inflammation and swelling, disinfect and accelerate the process of tissue regeneration.
- Sour cream or cream. Use chilled. They need to be absorbed, which produces a cooling and soothing effect.
Diet
After a throat burn, you need to follow a special diet for some time. Until the mucous membrane is restored, it is forbidden to eat hot or hard foods, which can further injure the tissue.
It is necessary to avoid spicy, salty and sour foods so as not to irritate the damaged throat. All food should have a soft consistency and be served slightly warm.
Urgent Care
The prognosis of the disease depends on the quality and speed of emergency care. First, it is necessary to establish the damage factor by inspecting the scene of the incident and interviewing witnesses. Then they move on to inspecting the affected area. With acid burns, there is a dry scab on the mucous membrane, and with alkaline burns, there is a wet, jelly-like scab.
- First aid for thermal burns involves drinking cool water, crushed ice, or gargling with anesthetic solutions . Cold water will stop the burn from spreading into the tissue. You need to drink it in small sips, holding the water longer near the damaged area. Pieces of ice must be dissolved in the mouth. To reduce pain, you can take a solution of novocaine or lidocaine.
- In case of a chemical burn, first aid is aimed at neutralizing acids and alkalis that have entered the body. For acid burns, use a solution of soda, and for alkaline burns, use a solution of citric or acetic acid. The patient should rinse the stomach, give a glass of milk and a little vegetable oil, and then call an ambulance.
To alleviate the patient’s condition, it is necessary to provide an influx of fresh air, maintain a silent regime, and exclude from the diet foods that irritate the affected mucous membrane and interfere with regeneration.
Complaints
If the pharyngeal mucosa is burned, the patient is concerned about:
- pain that intensifies when trying to swallow, radiating to the ears;
- difficulty eating food - even liquid consistency (dysphagia);
- drooling (hypersalivation);
- violation of taste sensitivity;
- difficulty breathing;
- fever.
The clinical characteristics of symptoms can be presented in the table:
A burn to the mucous membrane of the throat affects the entire body as a whole, which is reflected in the development of intoxication.
| Severity of damage | Symptom | ||||||
| Pain | Salivation | Dysphagia | Taste disturbance | Fever | Breathing problems, cough | Vomit | |
| Grade I | It has a burning or stabbing nature and is localized in the upper part of the neck. Stores for 5-7 days. | It is observed for 3-4 days, the patient secretes an average of up to 300 ml of saliva in 24 hours. | The patient finds it difficult to swallow only solid food; the main discomfort comes from increased pain. | Lasts about a week or longer, recovery time depends on the area of the burn. | As a rule, it is not observed. | It is explained by reflex laryngospasm immediately after injury and an increase in tissue edema subsequently; The location of the damage site is also important. If you burn the lower part of the pharynx or larynx, there is a risk of asphyxia (suffocation). | Not visible. |
| Grade II | The pain is sharp, burning; with a combined burn, it is felt not only in the pharynx, but also in the esophagus and epigastric region. It can last up to 35 days or even longer. | It can be stored for up to a week, sometimes up to 10 days. Saliva production per day is from 1 to 1.5 liters. | It is impossible to swallow solid food, and it is difficult to swallow liquid food, which is accompanied by very intense pain. | Lasts about a month, recovers very slowly. | Develops within 2-4 days, indicators can reach subfebrile (37.1-37.9 °C), less often febrile (38-38.9 °C) values. | Repeated, occurs with a combined burn (damage to the esophagus, stomach), vomit may contain an admixture of blood and have the color of “coffee grounds”. It is explained both by direct damage to the mucous membrane and by irritation of the vagus nerve. | |
| Grade III | Inability to eat food of any consistency. | Taste sensitivity is absent for longer than 40-50 days and is not restored in all patients. | It develops immediately (rarely) or within 2 days, characterized by an increase to pyretic (39-40 ° C) and even hyperpyretic indicators. |
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the installation of veneers in 4 stages.
The chemical agent acts not only on the burned area of the throat, it can be absorbed and enter the blood; Burn reaction products released during tissue destruction are also capable of spreading throughout the body. Systemic damage is common in severe, widespread burns. The smell of a chemical agent that comes from the patient is felt during a burn with vinegar essence, ammonia, and also household detergents.
Prevention
It is known that burn diseases of the larynx are usually the result of simple carelessness. To prevent this, you need to pay a lot of attention to preventive measures, be vigilant and extremely attentive.
- Small children should not be left unattended. Before giving your baby a bottle of formula, try it. Do not leave hot drinks, household chemicals and other chemicals within reach.
- Hazardous substances should be stored in specially designated areas out of the reach of children.
- People who are interested in alternative medicine can use prescriptions only after consultation with a specialist.
- It is necessary to follow safety precautions and know the rules of first aid.
Depending on the type of damaging agent, a throat burn can be thermal or chemical.
Thermal injuries include:
- burn of the throat with boiling water (in case of accidental swallowing of hot liquid);
- hot steam (in case of violation of the rules of inhalation, during an industrial accident);
- hot air (in case of fire).
Chemical burns to the throat are caused by exposure to:
- alcohol;
- pharmacological agents (iodine, hydrogen peroxide);
- acids, alkalis and other aggressive chemicals (acetone, saturated solutions of ammonia, soda, citric and acetic acid).
Alcohol burns to the throat are caused by the consumption of ethyl alcohol (70 or 96%). Such injuries are diagnosed mainly in people suffering from chronic alcoholism, who instead of high-quality alcohol drink medical or industrial alcohol or tinctures based on it.
Of the pharmacological drugs, iodine often provokes injury. One of the well-known methods of treating pharyngitis and tonsillitis is gargling with iodine solution or preparations based on it (Yoks, Lugol). But if you gargle with an overly concentrated solution or use the drugs more often than the manufacturer recommends in the instructions, it is easy to get a throat burn from iodine.
A burn from chemical reagents develops as a result of accidental or special (during a suicide attempt) ingestion of acid, alkali, or inhalation of fumes from their solutions. When exposed to acid, dehydration and destruction of cells occurs, as a result of which the burned tissues become covered with a dry crust (scab). This crust prevents the penetration of aggressive substances deep into the tissue. And when exposed to alkali, protein structures are destroyed, forming a gelatinous mass (wet scab), through which the aggressive reagent easily penetrates into the underlying tissue, destroying them, causing massive necrosis. This is why burns from alkalis are more dangerous than burns from acid.
Acid damage also includes a burn of the larynx from gastric juice. The stomach produces hydrochloric acid, which is necessary for normal digestion. With esophageal reflux disease, stomach contents reflux into the esophagus. The result is damage to the esophagus and adjacent walls of the larynx by hydrochloric acid.
Health care
Serious chemical burns are usually treated in a clinical setting, under the supervision of specialists.
Often victims are completely unable to eat, so nutrient solutions are administered to them using droppers. The therapeutic course includes the use of strong painkillers, sedatives and antihistamines. In order to prevent the development of infectious complications, a course of antibiotic therapy is expected. In particularly severe clinical cases, patients are administered intravenously Hemodez, glucose solutions, which eliminate signs of general intoxication of the body and alleviate the condition of the victim.
If scars form and laryngeal stenosis occurs, the patient requires surgical intervention.
A throat burn is an injury that requires careful attention and mandatory referral to specialists. Treatment includes taking medications, diet therapy, rinsing, inhalation, and external treatment of the affected areas.
Timely first aid and competent, comprehensive therapy will help avoid the development of adverse consequences and achieve full recovery. Depending on the severity of the burn, the rehabilitation process takes from 2 weeks to six months.
source