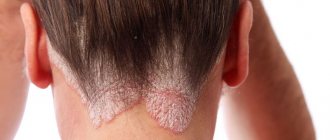
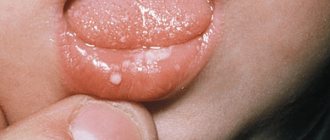
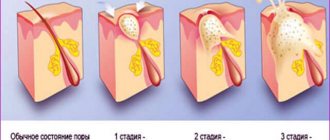
Recently, the number of cases of children's nails being affected by a fungal disease has increased significantly. This happens because the immune system in the first year of a baby’s life is very weakened, which provokes the rapid spread of infections, especially lesions of the skin and nails. Onychomycosis is a common fungal infection on the legs and arms that can occur in both children and adults. This lesion has a pathological form and leads to deformation of the nail plate. It is important to determine how to treat nail fungus in a child.
Main symptoms of damage
Fungal infections of the skin and nails often occur in children aged one to 14 years. In 80% of all cases, a child becomes infected with a fungus from his parents. Scales form on his skin and nails, on which there are a large number of fungal spores. After some time, the scales fall off and remain on the floor, carpet, bed and spread to other family members.

In order to promptly begin treatment of a fungal infection, parents should regularly examine the nails, skin of the baby’s feet and hands. It is important to pay special attention to even minimal changes in the appearance of a child’s nails. Fungus on the feet of children is dangerous because at the initial stage of development it does not provoke clear symptoms, so it is possible to determine the lesion only at a later stage. Parents should pay special attention to the following symptoms:
- splitting and severe brittleness of nails;
- thinning or thickening of the edges of the nail plate;
- the appearance of pronounced furrows;
- an unpleasant white coating;
- change in nail color;
- keratinization of the skin on the child’s foot;
- the appearance of pronounced cracks between the toes;
- severe swelling on the fingertips, changes in their shape.
Systemic drugs
If a fungus is found on the feet of children, and in an advanced state, the doctor prescribes medications with systemic action. The following drugs are best suited:
Nizoral
These tablets are prescribed against dermatophytes and yeasts. This medicine is also called Ketoconazole. To prevent fungus in children and stop its development, you need to give the drug to your baby only once. The dosage is 1 tablet. Repeated use of the medication is determined by the doctor depending on the symptoms.
Fluconazole
Its analogues are Flucostat, Diflucan and Mikoflucan. The product is not suitable for infants, but older children are already allowed to use it. Fights yeast-type fungi. The active components penetrate the plasma of these organisms within 30 minutes after the child takes the drug. The tablets must be taken every week. Already in the second week of taking the drug, the spread of fungal infection in the baby is blocked. Be sure to monitor the dosage.
Forkan
An analogue of this medication is Fluconazole. It will save the child from mycoses that are caused by saprophytes, including the yeast class. It should also be used once a week. Typically, therapy lasts 1.5 months, but according to the decision of the attending physician, the duration of treatment may be reduced or increased.
Lamisil
This is a medication that is used only in extreme cases. This rarely occurs in infants and older children. But if this happens, the doctor may prescribe such a potent medication. It should be taken once a day. Therapy usually lasts no more than a couple of months.
Orungal
This medicine has a wide spectrum of effects. Its analogues are Irunin, Itrazol, Kanditral, Rumikoz. It is used only as pulse therapy, that is, it is necessary to give the baby 1 capsule twice a week. After this, you need to take a break for 3 weeks and repeat the course again.
In total you need to complete 3 courses. In more severe cases, 6 doses are allowed at the same intervals.
Flucostat
If foot fungus is detected, then a triazole-type medicine is also suitable. Quickly affects yeast-like fungi and other pathogens of mycosis. This drug is considered the most powerful in action, but it acts selectively. This medicine should only be given to a child in extreme cases.
Microflucan
This is also a medicinal drug against yeast, microsporia and other fungal pathogens. You need to take this remedy until the symptoms completely disappear.
All these medicinal medications are effective and potent. But they are prescribed, as a rule, in the most severe cases, when other means no longer help. For example, when a child’s body is completely weakened and cannot cope with any infection. Then it is necessary to strengthen the immune system and suppress the fungus from the outside, and not use ointments and various applications.
Causes of fungus
Toenail fungus in children can appear for the following reasons:

Children who have the following lesions are most at risk:
How to treat foot fungus in a child at home?
A common case that parents encounter with their children is foot fungus.
This pathology affects not only children, but also adolescents and adults. An infectious disease includes a rash on the skin, “wetness” of the affected areas, and so on. The fungus does not go away on its own; you need to know what drugs and folk remedies should be used to treat this disease at home.
It is important to note that children should never be treated on their own. It is recommended to take your child to a doctor and get advice on the problem. The sooner this is done, the more effective and faster the baby’s recovery course will be. At the same time, many do not even know how to treat fungus on a child’s feet at home.
Types of disease
There are mainly four types:
- Interdigital fungus. This is the most common variety. Location: between the toes. Various cracks or eczema appear on the interdigital folds. Sometimes peeling of the affected area occurs.
- Hyperkeratic appearance. You may notice a change in the color of the nail plate and its structure, itching of the foot appears, the formation of the stratum corneum of the skin, and peeling.
- Erased form. This is a mixed type of interdigital and hyperkeratic form of the disease.
- Vesicular form. The rarest type of disease. A huge layer of peeling and large blisters appear on the skin. After opening them, erosion traditionally appears on the body, leading to serious consequences for the human body.
Causes
Before considering how to treat fungus on the legs of a child at 4 years old and at other ages, it is necessary to determine the causes, since often their elimination contributes to a rapid recovery.
In case of infection, the entire body weakens, thereby parents can see the child’s immune system is exhausted. It is considered normal if the baby has a fungus on his body. But don't rejoice.
Due to the impact of negative factors on the condition of a child or teenager, the infection “sets in”, that is, it begins to spread throughout the body, leaving behind not very pleasant consequences.
Therefore, there are reasons such as:
- Lack of personal hygiene. You should constantly remind your child that he needs to take a bath every day, not walk barefoot in public places, wash his hands, and much more.
- Synthetic and rubber shoes. Such materials cause the child’s feet to sweat, thereby preventing his skin from breathing. This promotes the spread of bacteria.
- In children, foot fungus develops in warm and humid environments. For example, this is a bathhouse, a sauna, a hot bath. After these procedures, the baby should thoroughly wipe his feet with a towel.
- Long uncut nails. This also promotes the spread of infection, especially on the foot.
- Wearing very narrow shoes. It also contributes to foot sweating and the occurrence of disease.
Other reasons can be identified:
- Lack of beneficial vitamins in the child’s body.
- Trauma and deformation of the leg.
- Diabetes. With such an illness, parents should pay special attention to their child, since sweating also intensively produces glucose. Bacteria love to multiply in this environment.
- Adult families, as well as those people with whom the child comes into contact very often, who suffer from this disease, have a huge chance of infecting the baby. And all because he has not yet developed an immune system that would completely protect against infection.
As mentioned above, if this disease is detected, you should consult a doctor. But often people don't do this.
Therefore, as a last resort, there are universal drugs and folk remedies that will help solve the problem than treating fungus on the legs of a child at 3 years old and other ages.
But in no case should you try to cure everything yourself if the following symptoms are noticeable in your child:
- long-term loss of appetite;
- itching;
- change in the color of the nail plate;
- constant complaints of pain;
- peeling skin between the toes;
- the appearance of blisters.
Only a doctor can determine the type of disease and prescribe the necessary medications. Often, only drugs in the form of ointment or cream are enough for a child, and for a 100% effect, tablets are prescribed.
One of the most common medications when asked: “How to treat foot fungus in a 2-year-old child?” is Diflucan. It is produced in three forms: mixture, injection solution and regular tablets.
It does not have any age restrictions.
Ointments, creams
The most common and popular ointments when asked: “How to treat foot fungus in a child 10 years old or even younger?” are:
- "Nizoral";
- "Exoderil";
- "Lamisil";
- "Flucostat";
- "Clotrimazole".
To use these medications, you must first wash your child’s feet well and dry them thoroughly. After which these products are applied to the affected areas of the body. Before use, you must carefully read the instructions, since some ointments cannot be applied to open wounds and healthy skin, and they have a number of contraindications.
All ointments are applied in small quantities. But it is important to note that these drugs are not recommended for children under two years of age.
ethnoscience
Folk remedies are especially effective for children. There are two types distinguished and used: foot baths and various compresses. They will help with the question: “How to treat fungus on the feet of a child of 5 years old and other ages?”
Baths
They are used to relieve itching, irritation, and reduce inflammation on the legs.
Popular procedures include the following:
- Euphorbia plant. Use one and a half glasses of raw materials per glass of hot water. After which this decoction should be placed in warm water. The procedure should not exceed 15 minutes.
- Sagebrush. For this medicinal decoction you will need 500 grams of the plant per 3 liters of water. Bring to a boil and simmer for 15 minutes. After preparation, the broth should sit for about 30 minutes, then you can add it to the water. The product helps fight inflammation and itching well.
- Salt. The ratio of water and salt is 5:1. This mixture should be brought to a boil and cooled naturally to room temperature. The procedure should last no more than 20 minutes.
- Celandine. For this remedy, one rule should be applied: boil two tablespoons of raw materials in a liter of water. Allow to cool to room temperature. The bath procedure lasts no more than 20 minutes.
- Coffee. Strange as it may sound, this product also helps with fungus. All you need to do is steam your feet three times in strong coffee.
- Soda. This is the cheapest and most accessible method of getting rid of fungus once and for all. You should stir one tablespoon of soda in a small amount of water until a certain creamy state is obtained, after which you can apply a generous layer to the affected areas of the body. After 10 minutes, rinse off the mixture, dry your feet and apply any foot powder. The duration of these actions is no more than two weeks; after a week of break, the procedure can be repeated.
Tip: You should steam your feet before going to bed. After this action, it is recommended to apply the healing cream to dry skin. The main thing is to remember that these procedures must be regular, only then will a positive result be visible.
Also, for effective treatment, you can take various compresses and rubbing. For example, when asking the question: “How to treat foot fungus in a 7-year-old child or another age?”, the following options are suitable:
- If certain areas of the body are affected by a fungal infection, rub with a mixture of garlic and butter in equal proportions.
- You can chop the onion into small pieces, wet it and rub the affected part of the body.
- A compress of rowan or burdock leaves is also used. At night, you should wrap your feet with the leaves of these plants and cover them with a cotton cloth or sock.
- If the nail plate is damaged, iodine solution or tea tree oil will help.
Features of treatment and possible contraindications
Of course, the greatest effect is brought by those products that are intended for internal use. But this type may not always be beneficial due to the age of the baby.
For example, if in an older child (teenager) the choice of funds may be limited by certain contraindications or due to individual qualities, then in infants everything is much more complicated:
- Treatment is contraindicated before the age of two years. We are talking specifically about systemic therapy, which includes various drugs for internal and external use.
- For a child under two years of age, only maintenance therapy is provided.
- Medicines can harm the baby much more than the fungal infection itself.
Fungus prevention
These measures to prevent fungus are the same for both children and adults. That's why:
- It is not recommended to wear other people's clothes, shoes, socks, etc.
- Each child should have his own set of various accessories, for example, manicure.
- Watch out for sweaty feet.
- Shoes should be true to size; it is recommended to buy them from “breathable” material.
- Shoes should be constantly treated with antifungal agents.
- You need to wash your feet constantly.
- If various signs of a violation of the integrity of the skin and deformation of the nail plate appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Despite the fact that the treatment process is much better in children than in adults, this does not mean that time should be neglected. Only prevention and timely examinations will help the child recover as quickly as possible.
Source: //FB.ru/article/463170/chem-lechit-gribok-na-nogah-u-rebenka-v-domashnih-usloviyah
Main types of onychomycosis
Experts distinguish three types of onychomycosis in a child:
- Normotrophic. The structure of the nail remains the same, but you can notice pronounced spots and stripes of a yellow-gray hue on it. There is no pain.
- Atrophic. In this case, the nail begins to atrophy, its plate slowly detaches, and the nail itself begins to change color to brownish-gray. Painful sensations begin to appear.
- Hypertrophic. There is deformation and initial destruction of the nail plate due to increasing hyperkeratosis. The nail begins to fade and also lose its natural shine. Pain appears to a greater extent when walking.
Types of fungal infections of the feet
There are 4 forms of fungal infection based on localization:
- Interdigital. Is the most common form. When a fungus appears between the fingers, cracks appear or eczema appears on the folds between the fingers. Peeling of the affected area is also observed.
- Hyperkeratic. The lesion is localized on the sole of the foot and is characterized by the formation of a stratum corneum of the skin and circular peeling. In this case, a change in the color and structure of the nail occurs, and itching of the foot occurs.
- Erased form. There is slight peeling of the skin of the foot, itching, cracks between the toes and crater-like changes in the skin.
- Vesicular. Very rare. Weeping rashes and blisters appear on the skin. After opening them, erosions appear, which become infected and lead to dangerous complications.
Return to contents
Classification by distribution type
The following locations of fungal infection in a child can be identified:
The following article shows a photo of a child’s nail fungus.
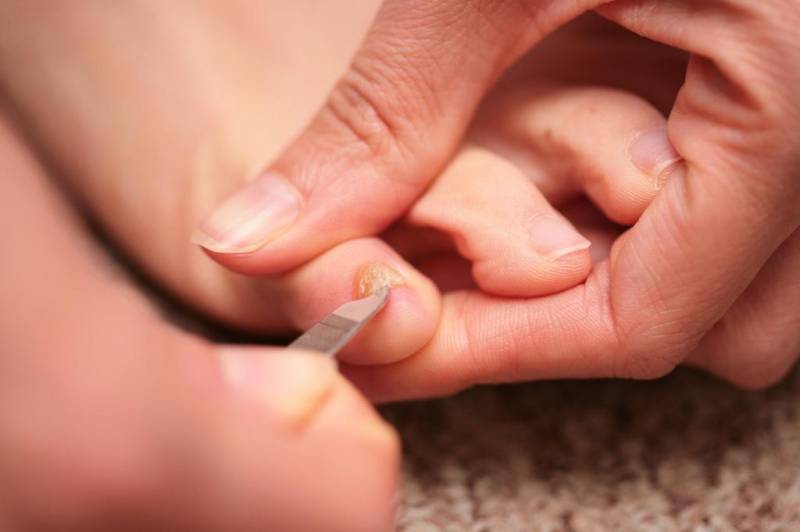
Causes of onychomycosis in children
Speaking about the causes of onychomycosis in children, first of all, it is necessary to note the body’s weak protective reactions. The immune system in children is formed before 3-5 years of age. Therefore, nail fungus in newborns is a common problem. In infants, fungi of the genus Candida are most often diagnosed. They enter the baby's body through mother's milk. Candidiasis in a young mother is transmitted to the child. It can also manifest itself as a type of fungus on the nails.
Also, if a woman suffered from thrush during childbirth, candidiasis will automatically be transmitted to the baby through the birth canal. That is why, before giving birth, girls undergo sanitation of the birth canal to avoid the baby becoming infected with fungus. As for older children, the following public places can lead to infection:
- Sport halls;
- Swimming pools;
- Baths;
- Kindergartens;
- Beach.
Very often, children bring many diseases from kindergartens. Of course, every child must suffer from some diseases in childhood. This way you can avoid severe manifestations and complications. Nail fungus, especially on the toes, is also a common childhood disease. As a rule, the groups are overcrowded. A large number of children and close contact with an infected child will certainly lead to the development of onychomycosis in a healthy child.

Children often confuse indoor slippers and shoes for walking in the gardens. It is through shoes that nails are damaged. Increased sweating creates a favorable environment for the development of fungi. After all, they exhibit their active life activity in conditions of high humidity and heat. Even trying on shoes in a store can serve as a catalyst. Therefore, the child must have his own shoes, his own tights and socks.
Injury to the nail plate should not be allowed. Fungus develops in microcracks in the plate. If you want your baby to be healthy, carefully monitor his hygiene. Legs and arms should be washed at least twice a day. Children's shoes must be disinfected. Also, it is necessary to regularly trim the nails on the child’s hands and feet.
Attention! Our portal strongly recommends not to self-medicate.
- Leave a message to the doctor using the comment form at the end of the article;
- Call: 8 (800) 505-39-76 (free and anonymous);
- Make an appointment with a dermatologist using this link.
How does the lesion develop?
Infection and bacteria spread rapidly in a humid, slightly alkaline environment. In newborns and children under one year old, their feet often sweat due to undeveloped thermoregulation, which is considered an ideal condition for the spread of fungal infection.

Infection also often occurs from already infected family members. The fungus usually appears on the legs, and then spreads to the arm area. In children under one year of age, the disease spreads and progresses at a rapid pace, affecting not only the nails, but also nearby tissues.
Carrying out diagnostic activities
At the appointment, the specialist conducts a thorough examination of the child’s body and collects information about his condition from the parents. Afterwards, the doctor prescribes a medical history and conducts a differential diagnosis, excluding the development of the disease, pathological syndromes and complications. Onychomycosis is often confused with the following lesions of the nail plate: lichen planus, keratoderma, psoriasis of the horny plate. To establish the exact cause of a fungal disease, you need to carry out the following diagnostics:
- Microscopy. When conducting a diagnostic study, the doctor takes a sample of tissue from the horny plate or performs a deep scraping. The material is treated with a special solution to remove keratin, after which the nail is carefully examined under a microscope. This method of determining a fungal infection is the most common and accurate; it helps confirm the presence of a fungus. Other additional tests will help determine the specific type of lesion and pathogenic factors.
- Fungal inoculation on Sabouraud's medium. When conducting such an examination, particles of infected samples are collected and placed on various nutrient media that are suitable for certain strains of pathogens. After one week of continued cultivation, high colony activity is released, causing the doctor to determine the exact type of fungus. At the end of the study, the most successful sample with a fungal infection is divided into several parts and special antifungal agents are added to them to determine a more effective drug that will help quickly destroy the pathogenic infection and prevent complications.
The doctor conducts a thorough examination of the child’s body and sends him for additional tests. A specialized specialist who identifies the clinical picture of fungal infection is a mycologist or dermatologist.
How to treat foot fungus in children
Before starting treatment for foot fungus in a child, you must see a doctor. This is necessary so that the specialist can determine the specific type of disease.
The earlier the diagnosis is made, the easier and faster the treatment will be.
In addition, many symptoms are characteristic not only of mycosis, but also of many other dermatological diseases, in which case the therapy will be very different.
Most often, local medications in the form of an ointment or cream are sufficient to treat children, and to enhance the effect, similar medications are prescribed for oral administration. One of the most popular medications is Diflucan.
The drug is available in three forms:
- capsules for oral administration;
- injection;
- suspension.
Diflucan has no age restrictions, the only difference is in the dosage of the drug. Only a specialist should prescribe the exact dose.
Medicines
Let's consider popular and effective means:
- Nizoral;
- Flucostat;
- Lamisil;
- Clotrimazole;
- Exoderil, etc.
When using ointments, creams and patches, you must first wash and dry the child’s feet. The products are applied to the affected areas of the skin and nails.
Some drugs cannot be applied to healthy skin or open wounds, so before use you should carefully read the instructions and list of contraindications.
Folk remedies
In addition to medications, folk remedies are also used to treat mycosis; herbal and salt baths are especially effective.
Here are some recipes:
- Bath with milkweed. For one and a half glasses of plant leaves, you need a glass of boiling water; in this form, the mixture should be simmered in a steam or water bath for half an hour. The finished broth is poured into a bath of water at a comfortable temperature. The duration of the procedure is about 15 minutes.
- Wormwood bath. To prepare a medicinal decoction you will need 500 g of dried plant per 3 liters of water. The mixture must be brought to a boil and simmered for 15 minutes. The finished broth should sit for half an hour, then it can be poured into a bowl of water.
- Salt bath. The ratio of water and salt is 5 to 1, the mixture must be boiled and allowed to cool naturally to a comfortable temperature. The procedure lasts 15-20 minutes.
Herbs for treating children should be used with great caution and only after consulting a doctor.
Important! Baths and lotions do not replace full-fledged therapy and can only be used as support for the main treatment.
Carrying out treatment
Treatment of toenail fungus in children will be chosen depending on the type of pathogen, stage of development of the disease, general neglect of the lesion, as well as the individual characteristics of the baby’s body.
Parents should not use any antifungal drugs to treat fungus without first consulting with their doctor. Such procedures can lead to a worsening of the symptoms of the lesion, the formation of special resistance of pathogenic microorganisms to the drugs used, which will complicate the treatment of the disease and provoke complications.
Here's what's important to know about treating nail fungus in children. A photo of the manifestation of the disease is presented above.

Types and provoking factors
Fungus on children's feet can vary. Criteria according to which its classification is carried out (Table 1).
Table 1 - Classification of fungal pathologies
| Criterion | Characteristic |
| Pathogen | Types of fungal diseases:
|
| Localization | According to this criterion, the following are distinguished:
|
Fungal diseases affect 20 to 30% of the world's population. Damage to the skin of the legs and nails in children occurs only in 2-8% of cases. But in childhood, symptoms of infection appear faster.
Possible causes of fungus on a child’s feet include:
- genetic predisposition;
- close contact with sick parents and children;
- wearing uncomfortable (not the right size), low-quality shoes. This provokes the appearance of cracks on the child’s legs and facilitates the penetration of infection;
- untimely or improper cutting of nails (both long and short nails can cause fungus);
- putting shoes on bare feet while trying them on in a store;
- staying barefoot in the pool and other public places with high humidity;
- excessive sweating of the feet;
- putting on someone else's shoes, socks;
- using other people's hygiene products (washcloths, towels);
- visiting the beach.
A child can become infected with foot fungus in different ways. But the infection does not appear immediately: the activation and reproduction of pathogenic organisms occurs only when conditions are favorable for this.
Factors that contribute to the spread of fungus to the skin of the feet and the development of the disease include:
- weakened immune system;
- neglect of personal hygiene rules;
- the presence of wounds, abrasions, cracks on the legs;
- unbalanced, monotonous diet with an excess of carbohydrates, preservatives, sweets and a lack of protein and other useful and nutritious substances;
- damage to the nail plate;
- deficiency of vitamins and microelements in the body;
- frequent stress, emotional overstrain;
- long-term use of medications (antibiotics, hormonal agents).
In childhood, the skin is softer. Therefore, there is always a risk of foot fungus in children. But the likelihood of a child developing the disease is much higher if he has:
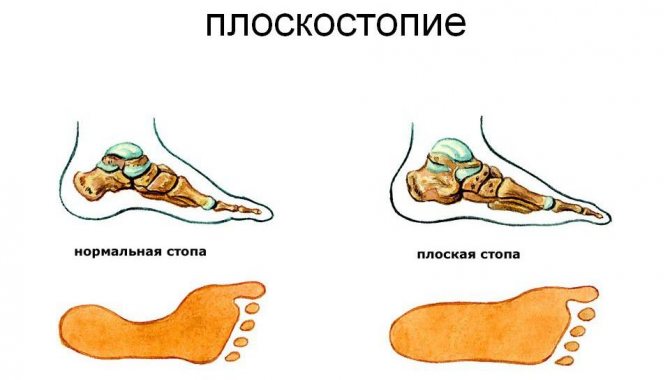
flat feet;- intestinal diseases (dysbacteriosis);
- excess body weight;
- diabetes;
- diseases associated with metabolic disorders;
- congenital pathologies of blood vessels of the lower extremities.
The risk group also includes children with immune deficiency: HIV-infected or AIDS patients. In them, fungal diseases are more severe and difficult to treat.
Use of ointments
If the stage of the disease is not particularly dangerous, then treatment of the infection is carried out conservatively. To do this, the doctor prescribes special antifungal ointments or topical gels.
This treatment of fingernail fungus in children can be effective only in cases of mild skin lesions, when the pathogens have not spread to the child’s internal organs. The local method of treatment is considered safe for the child and brings good results. Ointments will be prescribed depending on the type of fungus identified - Terbinafine, Clotrimazole, Ketoconazole or iodine alcohol tincture.
Fungus prevention
To prevent foot fungus, it is recommended to follow the rules of hygiene, wipe your feet dry after taking baths, and wear comfortable and high-quality shoes. Additionally, you need to monitor the child’s immune system and enrich the menu with vitamins and minerals. It is imperative to ensure that the child’s feet do not sweat, to exclude contact with sources of infection and to disinfect shoes. If symptoms of fungus appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Fungal diseases occur not only in adults, but also in children. Despite the similar causes of infection, the methods and speed of treatment will differ depending on age. In childhood, tissue renewal occurs faster and often only local remedies are sufficient to completely cure fungus on a child’s legs. What else is important to consider?
Conservative treatment of the lesion
This treatment for nail fungus in a 2-year-old child (or any other age) is prescribed for severe stages of the disease. It can be a complex therapy for systemic lesions: mycosis of the skin, nail plate, candidiasis of internal organs, or act as an independent treatment.
Before prescribing medications, the doctor evaluates the general clinical picture of the disease, possible consequences for the child’s body, as well as the need to take the drug. The most common medications for the treatment of nail fungus in children include Fluconazole and Itraconazole.
Treatment of nail fungus in children
The duration of treatment for infectious fungal nail infections in a child depends on the patient’s age, the presence of severe organic lesions, complications of the disease, the cause and stage of the pathology. As a rule, systemic and local medications (ointments, creams, varnishes), and folk methods are used. When the process is advanced, surgical removal of the affected nail is indicated.
In addition, during the treatment period, the child should follow a diet (limit the consumption of sweets, excessively salty, fatty and fried foods). Parents also need to carefully monitor the child’s personal hygiene (daily shower, timely change of bed linen, socks), cleanliness of shoes (use disinfectant sprays, wash or wash, dry on time).
The course of treatment for fungus lasts on average from 2–3 weeks to six months. To prevent infection of other family members and successful treatment of the child, it is recommended to carry out general disinfection of common items (dishes, linen, etc.), floors, walls, and home textiles. The rooms must be ventilated several times a day, and high humidity in the rooms must be avoided.
Drug treatment
To treat fungus in a child, you cannot use medications without consulting a doctor, because some medications are suitable for eliminating mold infections, others for yeast infections, so self-prescription of drugs may be ineffective, and the disease will progress. Tablets, injections or capsules are used for severe, advanced pathology; for all other cases, topical agents (ointments, gels, varnishes, lotions) are well suited.
| Name of the drug | Active substance | a brief description of | Benefits of use | Flaws | Cost in rubles |
| Mycostop | Lactic acid; urea. | Antifungal drug for external local use, available in the form of lotion, paste, cream. | Several release forms; wide range of applications; low cost; well tolerated by children. | To obtain a therapeutic effect, long-term use is necessary. | 230 |
| Mikozan | Rye enzyme filtrate. | An antifungal agent for external use, available in the form of a cream. | Wide range of applications. | Not recommended for use in children under 4 years of age. | 470 |
| Lamisil | Terbinafine. | Antifungal agent for external local use, has a pronounced fungicidal effect. | Wide range of applications. | High risk of developing allergic reactions; a large number of side effects; To obtain a therapeutic effect, long-term use is necessary. | 350 |
| Exoderil | Naftifine hydrochloride. | Antifungal drug for local external use from the group of allylamines. Available in cream form. | Wide range of applications. | Use with caution in patients under 12 years of age. | 750 |
| Terbinafine | Terbinafine hydrochloride. | Antifungal drug of the allylamine group. Actively inhibits the action of squalene epoxidase in the cell membrane of the pathogen. | Convenient release form; wide spectrum of action. | Prohibited for use in children under 3 years of age; not recommended for use in congenital disorders blood coagulation system. | 760 |
| Clotrimazole | Clotrimazole | An antifungal drug from the group of imidazole derivatives. It is used externally, locally. | Low cost; convenient release form. | High risk of allergies. | 120 |
| Griseofulvin | Griseofulvin. | Systemic antifungal drug. It has a pronounced fungistatic effect. | Wide range of applications; effective for severe mycoses. | A large number of contraindications. | 320 |
| Lotseril | Amorolfine hydrochloride. | Antifungal medication for external local use. It has a fungistatic, fungicidal effect. Available in varnish form. | Wide range of applications; convenient release form. | Not recommended for use in children under 10 years of age. | 540 |
Article on the topic: Treatment of allergic conjunctivitis in adults - review of medications
Traditional methods
The use of traditional medicine recipes in combination with antifungal drugs has an antiseptic effect, helps relieve the main symptoms of the disease, eliminate the inflammatory process, prevent the spread of infection, complications, relapse of infection and the addition of a secondary bacterial infection. Among the most popular recipes for eliminating nail fungus in children are:
- Baths with hydrogen peroxide solution. Add hydrogen peroxide to a small container with warm water (30 ml of peroxide per 1 liter of water). Place your feet or hands in the solution for half an hour. The procedure should be performed every other day for 10 days.
- Celandine oil. Pre-steam the night in a bath in a warm, weak solution of soda with the addition of chamomile decoction, wipe your feet dry. Using a cotton swab, apply a small amount of celandine oil to the affected nails. The procedure should be repeated every week for 2 months.
- Compresses with vinegar. Take 1 tbsp. l. vinegar and vodka, mix, add the white of 1 egg. Soak a bandage or gauze in this mixture, apply to the affected nail and secure with a band-aid. Leave it overnight. Use the product every other day for two weeks. Not recommended for children under 3 years of age, as alcohol and vinegar may cause irritation or chemical burns.
- Baths with propolis. Fill a small basin with hot water, add 1 tbsp. l. propolis. Stir, leave for 10-15 minutes and place your feet or hands for 20-30 minutes. Use baths 2-3 times a week.

Surgery
Surgical intervention in the treatment of fungus in a child is prescribed quite rarely and only when all other treatment methods do not bring the desired effect and do not help get rid of the disease. In this case, the disease is often complicated by fungal and bacterial infections, an accumulation of pus occurs in the bed of the horny tissue plate, and the risk of sepsis and the development of gangrenous processes increases.
When performing an operation on a child, a low-traumatic chemical dissolution of the horny plate and diseased areas is used with layer-by-layer treatment with special substances that accelerate the growth of a new nail plate. Sometimes, when treating nail fungus in children, classic surgical removal of part of the nail or the entire horny plate is performed, followed by further antiseptic treatment and a subsequent recovery period.
Treatment regimen
The doctor decides how to treat mycosis of the legs after examining the child, collecting anamnesis and complaints, and receiving examination results. As a rule, in childhood, treatment of fungus is carried out with local external agents.
Local preparations
The following drugs may be prescribed:

Lamisil. Applicable only to children over 12 years of age. To cure mycosis, the cream is applied to the affected areas 2 times a day. Duration of use is a week.- Exoderil. This drug is available in liquid and ointment form. It can be used only on the recommendation of the attending physician. If your child has an infection between the toes, apply the ointment to the affected skin and the area around it once a day.
If the infection spreads to the nails, apply the product twice a day. If there are no signs of an allergic reaction, use of the drug continues until a healthy nail grows.
- Batrafen. The release form of the drug is cream and varnish. Prescribed for the treatment of skin and toenail fungus in schoolchildren over 10 years of age. Its effectiveness is higher with the simultaneous use of systemic agents.
- Clotrimazole. Apply a thin layer to the affected area. There is no need to rub in the product. For mycosis caused by mold and yeast fungi, the ointment is used for 2-3 weeks. For dermatophytosis, treatment lasts from 2 to 6 weeks. The frequency of use of the drug is 2-3 times a day. It is not prescribed for children under 2 years of age. Exceptions are possible in cases of severe fungal infection.
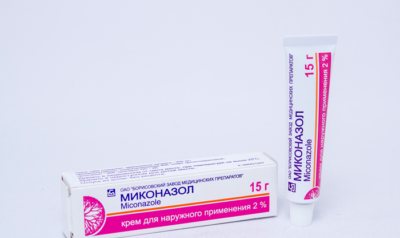
Miconazole. For mycosis of the legs, a small amount of gel is applied to the lesion and rubbed. The positive effect occurs after 2-6 weeks with daily use. But after recovery, it is recommended to use the gel for another 7 days. To treat onychomycosis, the product is applied to the diseased nail and the area around it, and a bandage is applied on top. The duration of treatment is until a new nail plate grows.- Amorolfine. Produced in the form of cream and varnish. The drug destroys pathogenic microorganisms, removes the unpleasant odor and itching that occurs in children with foot and nail fungus. The product is not absorbed into the bloodstream, therefore it does not have a negative effect on the body and does not cause side effects.
Systemic medications
In case of severe infection, the child is recommended to be treated with oral medications. Tablets are prescribed with caution: they all have contraindications and side effects. The use of most antifungal agents is permitted after 2 years. The list of most commonly prescribed systemic drugs includes:

Diflucan (Fluconazole). It is used for infections of the feet and nails with fungus of the genus Candida. It has powerful fungicidal properties, but is considered the safest for treating fungus in minors;- Terbinafine. The dosage of the drug depends on the age and body weight of the child. The standard course of treatment is 1-2 months with a break of 10 days. But how long to take the pills in a particular case is decided by the doctor individually, based on the stage of the disease.
In case of severe itching, antihistamines can be prescribed: Suprastin, Citrine, Zyrtec or Loratadine.
To strengthen the immune system and improve overall health in case of fungal diseases of the skin and nails, children are prescribed multivitamin complexes, immunomodulators, and are prescribed physiotherapeutic procedures. Magnetic therapy, electrophoresis and darsonvalization help speed up the healing process.
Additional recommendations and patient experiences
In the absence of ulcers or erosions on the feet, drug therapy can be supplemented with baths with table or sea salt.
But the use of traditional medicine to treat leg infections in children is usually not recommended. Their skin is very thin and delicate: the use of unconventional methods of fighting infection can lead to irritation, burns, and an allergic reaction.
Systemic therapy is not prescribed for children under 2 years of age. At this age, treatment with pills and ointments can be harmful. Therefore, local therapy in the form of low-concentration antifungal powders and varnishes, as well as nutritional correction, is recommended. If the child is breastfed, the mother must review her diet.
Patient reviews:
Anastasia: “At the age of 8, my son became infected with nail fungus. Most likely, this happened in the pool: he goes swimming with me. At first there were almost no symptoms (and I didn’t pay attention either).
But then the child began to complain of itching and changes in the appearance of the nail plate. She was half amazed. We went to the doctor. He prescribed Miconazole. The ointment was applied until a healthy nail grew back. 3 months have already passed, but we periodically use the drug for prevention.”
Katerina: “They discovered a fungus in me and my child. The analysis revealed: T. rubrum. The baby is 2 years old and is still partially breastfed. It all started with me, during pregnancy: first the infection affected my feet. Then it spread to my legs.
A year after birth, the child became infected, but the fungus immediately affected his little toe nail, and only after a while - other nail plates and the foot. Let's go to the doctor. He said that complex therapy cannot be prescribed at this age. I prescribed only Clotrimazole ointment. We used it for 3 months. The condition of my feet has improved markedly.”
Julia: “My daughter has a fungus on her toenail. We spent a long time visiting doctors. What they didn’t prescribe for us! There were no results until we had an appointment with a dermatologist, who is already about 70 years old. He recommended using Lamisil or Exoderil ointment. We took the first drug. When it ran out, we bought a second product. It takes a long time to treat fungus of the lower extremities in children. We fixed the problem after 5 months.”
Preventive actions
To prevent the development of a fungal infection in a child, it is important to follow some prevention rules that will help prevent primary and secondary infection:
- Following the rules of personal hygiene (regular bathing, washing hands and feet with high-quality soap). When caring for a child, it is important to use only personal hygiene products (separate towel, washcloth, clothes, socks). This applies not only to the home, but also to public places: when visiting baths, saunas, the beach and the pool.
- Strengthening immune defense. Experts recommend hardening the child, giving him vitamin complexes, preparing a proper diet, using physical therapy, and adding more fresh fruits and vegetables to the diet.
- Regularly monitor the condition of your nails, take proper care of them, and clean the nail bed.
- Change socks and other underwear regularly.
- Treat any chronic disease, regularly take the child for examination to the attending physician.
- Monitor the condition of your shoes and disinfect them regularly.
How to treat foot fungus in a child
Mycosis is a contagious disease; the fungus spreads through direct or indirect contact with a carrier. For young children, the source of infection can be parents, the risk of infection from whom increases if there is a hereditary predisposition. Pathways for pathogen penetration into a child’s skin include:
- visiting swimming pools, baths, saunas, beaches, where there is a favorable environment for fungal growth;
- using someone else's shoes, items of clothing, toys, household items;
- contact with a sick child in kindergarten.
The presence of fungal spores on the skin does not mean the development of the disease. Factors are needed that stimulate the activity of the pathogen, weakening local or general immunity. Reasons for its weakening:
- violations of personal hygiene rules;
- uncomfortable and tight shoes made of artificial materials that do not allow air to pass through well;
- injury to the skin, including small wounds and scratches;
- flat feet and vascular problems of the lower extremities;
- endocrine system disruptions and diabetes;
- overweight;
- lack of vitamins.
A favorable environment for fungal growth is high humidity combined with high temperature. Therefore, all circumstances that cause such a dangerous condition of the skin become risk factors.
Forms of fungus on the feet and hands of children
Fungal diseases on the hands and feet differ in the specific clinical manifestations. They are equally characteristic of any age, including children.
- The interdigital form of the disease, which is called membranous or intertriginous. It is considered the most common for children. Its signs are numerous microtraumas in the interdigital space in the form of ulcers and cracks. In the affected area, the skin peels off, becomes wet, and the healthy color changes to pale with a greenish tint. The problem is aggravated by warming, high humidity, and wearing tight shoes.
- Moccasin form or “athlete’s foot”, the medical name is squamous-hyperkeratotic. In addition to peeling of the skin, keratinization of the epithelium of the foot is added. The heel becomes covered with calluses and cracks. The infection can deform the structure of the child’s nails, change color, and begin to crumble.
- Vesicular or dyshidrotic type of infection, a characteristic manifestation is the appearance of watery blisters on the skin. Infiltration of vesicles leads to numerous erosions that cover the entire surface of the foot, down to the level of the ankle. At this stage, the disease is accompanied by pain and itching.
- An erased type of fungus is an early manifestation of oncoming onychomycosis. A typical symptom is subtle microcracks in the interdigital space and peeling of the surface layer of the skin.
How does the disease manifest in children?
Due to age characteristics, it is more difficult to diagnose fungus on the legs and arms of a child than in an adult. Faster regeneration of the skin and nail plates makes symptoms less severe at the beginning of the infection. At the same time, the disease quickly moves from an early stage to a severe one. Symptoms by which an infection can be recognized:
- redness of the affected area;
- peeling of the epidermis;
- the appearance of vesicles, their infiltration and weeping;
- erosions and defects of the skin on the fingers and toes, between them;
- stripes and spots on the surface of the nails;
- loss of natural nail color, appearance of yellowness;
- thickening and deformation of the nail;
- a feeling of itching and burning that periodically intensifies.
In order not to miss the occurrence of the disease, parents should regularly examine the child’s limbs. If one or more signs are detected that raise suspicion of a fungal infection, an urgent visit to a doctor is necessary.
Treatment of fungus on the feet and hands in children
Treatment of the disease begins with diagnosis. The doctor must determine the type of pathogen, the degree of damage, and sensitivity to mycotics. When choosing remedies, the patient’s condition and contraindications are taken into account. Therapy is carried out with medications, and traditional medicine can be used as an auxiliary one.
Drug treatment of foot and hand fungus in a child
If a fungus on the fingers is detected in the initial stage, treatment is carried out with external topical preparations. Severe forms will have to be treated comprehensively; in addition to ointments and solutions, in this case systemic agents in tablet form are prescribed. For external treatment, ointments are prescribed:
- Clotrimazole.
- Miconazole.
- Exoderil.
- Lamisil.
External agents are used for up to one and a half months, 2 to 3 times a day. Between procedures, wiping with antiseptics is recommended. This can be Boric acid, Furacelin, Manganese solution. More thorough treatment of the interdigital space is desirable. The systemic drug is selected taking into account age restrictions. From the age of two it is allowed to take:
- Terbinafine.
- Diflucan.
- Griseofulvina.
Antihistamines (Suprastin, Zyrtec, Loratadine, Cetrin) help relieve external discomfort. For severe, advanced forms, antibiotics may be prescribed.
Their intake should be accompanied by probiotics, which have a positive effect on the restoration of intestinal flora. Immunity restoration is achieved by taking vitamin complexes and rationally organized nutrition.
The specific treatment regimen, frequency of administration, dosage and course duration are selected for each patient individually.
Treatment of fungus in children with folk remedies
Folk remedies are used for general strengthening purposes, helping to cope with inflammatory processes, relieve itching, and various types of irritation. The main method of treating children is a bath of herbal decoctions, soda salt solutions, and other components.
- Euphorbia decoction. A glass of dry collection is poured with boiling water in an amount of 200 ml. Brewing duration is from 145 to 30 minutes. After filtering, the prepared broth is diluted with warm water in a basin of sufficient size. The procedure takes about 15 minutes.
- A decoction of wormwood is used in the same way. Half a kilo of freshly picked grass or dry collection is poured with boiled water from 2 to 3 liters. Brew for 25 minutes, after which the composition is filtered and used for the bath.
- A salt bath is prepared from sea salt. As an alternative, you can use a regular dining room one. Up to 200 g of salt is completely dissolved in hot water. The solution is cooled to a comfortable temperature and the limbs are steamed for a quarter of an hour.
- Celandine infusion, 2 tbsp. l. Pharmacy or self-prepared dry collection is poured with a liter of boiling water. Keep on medium heat for 5 minutes, then filter and pour into a basin. The procedure lasts 15 minutes.
In addition to steaming with medicinal baths, lotions and compresses can give a positive result:
- ointment made from a paste of garlic and butter mixed in equal proportions;
- an onion crushed to a mushy state, both options are applied to the affected areas for the entire period of sleep;
- fresh burdock and rowan leaves are placed on the fingers, the feet or hands as a whole are hermetically sealed with oilcloth, a sock or mitten is put on, and a compress is made before bed.
It should be remembered that the antifungal properties of such drugs are not enough for a complete cure. Treating a child exclusively with folk remedies is not only useless, but also dangerous due to serious complications.
Measures to prevent fungus in children
Preventing fungus on the hands and feet in children is easier than treating it. For these purposes, simple but quite effective measures are needed:
- regularly disinfect toys, children's things, and child's shoes;
- select clothes and shoes according to size, from natural materials;
- limit the child’s contact with street animals and, if necessary, with domestic animals;
- use special shoes for swimming pools and baths, and avoid walking barefoot on the street;
- monitor the cleanliness of hygiene supplies, use an individual manicure set.
Adults must monitor compliance with these measures and the state of health; the child is not capable of such a degree of self-control and cannot always correctly assess the danger of certain actions.
Source: //lecheniegribka.com/zabolevaniya/gribok-u-rebenka-na-nogah-i-rukah.html