What it is?
Microsporia, or ringworm, is an infectious disease caused by the fungus Microsporum canis. This pathology is more common in children and quickly spreads in children's groups.
The disease occurs in 60 people per 100 thousand people, which is not so rare.
Pathogen
The direct causative agent of the disease is the fungus Microsporum cani, which is capable of multiplying in the skin, namely in the hair and the stratum corneum of the epidermis.
There are two variants of the disease:
- Anthroponotic.
- Zoonotic.
They are caused by different strains of the fungus and have different transmission mechanisms.
After infection with a skin fungus, several weeks and sometimes months pass. At this time, the pathogen incubates, after which symptoms of the disease appear.
Does it happen in animals?
Microsporia in its anthropozoonotic form can affect domestic animals. The disease occurs in dogs and cats; the fungus multiplies on the fur and may not be visible to the naked eye.
Only upon close examination of the animal can you notice red spots under the hair.
Source of infection
A child can become infected in several ways:
- In the zoonotic form - through contact with the fur of sick domestic animals. In this case, direct contact is not necessary. Cats and dogs regularly lose hair that a child may come into contact with.
- In the anthroponotic form, the fungus is transmitted from a sick person. It can settle on clothes, combs and other household items.
Taking these features into account, methods for preventing the disease can be developed.
Causes of microsporia
microsporia of smooth skin photo in humans
close-up photo
Sources of infection with microsporia can be both animals and sick people. The causative agents of this disease parasitize the human body and remain on household items used by an infected person.
Inoculation of the fungus (infection) is possible through damaged areas of the skin (in the presence of microtraumas, abrasions, calluses and cracks in the skin). At the same time, with frequent hand washing, the possibility of infection with this microorganism is significantly reduced.
Among the causes of microsporia, factors predisposing to infection can be identified:
- frequent contact with soil and animals (especially wild ones);
- high degree of sweating;
- reduced functionality of the glands that secrete sweat;
- insufficient bactericidal protection of the body surface due to problems in the sebaceous glands.
- childhood and adolescence;
- the presence of microcracks in the skin;
- lack of vitamins (vitaminosis);
- weakened immunity.
Symptoms of the disease
The clinical manifestations of the disease depend on which area of the skin was affected by the fungus. Most often it is the smooth skin of the body and the scalp.
Damage to the nails is called onychomycosis and is uncommon in microsporia.
On smooth skin
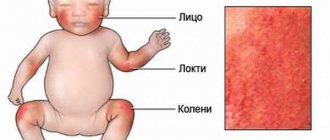
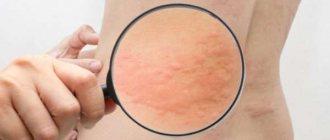
Clinical manifestations of the disease on smooth skin are as follows:
- A red spot appears at the site where the fungus invades and multiplies.
- The outbreak has clear boundaries.
- Gradually increases in size.
- Scales or bubbles may form on the surface of the infiltrate.
- Over time, the center of the lesion turns pale and the spot turns into a ring.
- Characterized by itching of the skin at the site of the lesion. However, it is not always expressed.
The localization of such spots can be very different, but most often the fungus affects the head, neck and upper limbs.
Scalp
Fungal infections of the scalp are very common among school-aged children. Clinical picture:
- The skin in the affected area changes in the same way as on the body (redness and mild itching).
- Hair begins to fall out, but not at the root, but at a distance of about 5 mm from it.
- This is how foci of alopecia form on the head.
- The base of the hair may become crusty.
The fungus is not visible on the surface of the hair, unlike seborrhea.
Nails
Nail damage is characterized by redness of the subungual bed and thinning of the nail plate.
Itching in the area of the distal phalanges of the fingers is often disturbing.
The process is weakly expressed and may not attract attention for a long time.
Quarantine for microsporia (lichen) in kindergarten: timing of the event, how many days, admission to the group
.
Young children are more susceptible to fungal diseases due to underdeveloped immunity. Ringworm is most often diagnosed in preschool children. The disease is classified as highly contagious.
The danger is that fungal spores are very resistant to environmental influences and can remain active for 1.5-2 years, therefore, if one child from a group is infected, it is imperative to notify the management and urgently introduce a microsporia quarantine in the kindergarten .
Ringworm may require quarantine
Manifestations on the head
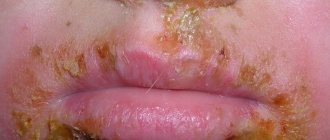
The first symptoms of the disease appear as a rash on the head, eyebrows or along the eyelash line. The rash appears as isolated pink or reddish spots, separated from healthy areas. The diameter of the neoplasms is approximately 3.5 cm. A ridge formed by bubbles can be observed around the spot.
After just a few days, the hyperemia in the inflamed areas disappears and peeling begins. The fungus feeds on keratin, a protein that promotes hair growth. Fungal spores fill the follicle, forming a dense dome, which interferes with the normal nutrition of the hair, so at the site of the rash, it becomes fragile and begins to break off.
A mild form of microsporia in children may look like a severe manifestation of dandruff that appears suddenly.
At the site of the inflamed areas of the skin, mild or severe itching may be felt, which causes discomfort. The child becomes whiny, capricious, and sometimes has sleep disturbances. When affected by the microsporum fungus, symptoms of intoxication, fever, increased temperature, and inflammation of peripheral lymph nodes may be observed. This complication is called scab; it is quite dangerous and difficult to treat.
In children with allergies, the manifestations of microsporia will be more pronounced. Infection with the microsporum fungus is fraught with the appearance of an erythematous-edematous form. This type is characterized by severe burning, itching, the appearance of a purulent infiltrate, and swelling. The surface of the new growths is covered with small bubbles, which often pour out, leading to the formation of a hard crust.
Ringworm causes severe itching and discomfort
Skin manifestations
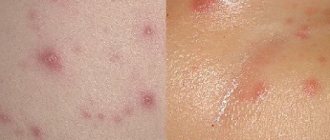
Ringworm of smooth skin is characterized by the appearance of large neoplasms. The lesions, round or oval, are surrounded by a dense ridge and rise slightly above the healthy areas. In the central part of the lesion, the skin is light and covered with small scales.
New growths can merge, forming large lesions with jagged edges. The rash can be localized on any part of the body, but most often affects the skin of the face, neck, and upper shoulder girdle. The affected areas of smooth skin are very itchy.
Diagnosis
As soon as parents suspect lichen, it is necessary to go to an appointment with a local pediatrician. He is involved in treatment together with an infectious disease specialist and a dermatologist. Neoplasms are examined under a Wood's lamp. In a darkened room under the light of the device, they acquire an emerald color.
In addition, a scraping is prescribed. Skin, hairs, and follicles from the affected areas are used as biomaterial for research. Such studies must be carried out at least 5 times. So that the doctor can see the full picture, it is necessary to take blood and urine tests.
In case of deviations from the norm, they are retaken once every 10 days.
Biochemical blood tests are performed to exclude oncology and autoimmune diseases (lupus erythematosus).
The study is carried out before starting treatment and again after a month. If the diagnosis of ringworm is confirmed, the pediatrician is obliged to inform the management of the preschool institution and the SES about a possible outbreak of the disease and demand that the group be quarantined.
Wood's lamp will help make the correct diagnosis
According to SanPiN, within 3 days a notification must be submitted to the Federal Budgetary Healthcare Institution and its branches, territorial skin dispensary organizations about the identification of a patient with ringworm diagnosed for the first time. When each new case appears, it is considered as being initially diagnosed.
In a preschool setting, patient information must be included in the Infectious Disease Reporting Register. This is a mandatory document maintained in all educational institutions.
It is necessary to control the number of patients and record the exchange of information between healthcare organizations.
Activities in kindergarten
Microsporia in children: quarantine in kindergarten, events, timing will be discussed below.
- The patient is isolated until hospitalization or until the child is taken home. Disinfection is carried out urgently. It is necessary to remove all the patient’s clothes, bedding, toys, and remove carpets.
- The child is not allowed to attend kindergarten, swimming pools, or various clubs until recovery is confirmed. The absence of fungus must be proven 3 times by blood tests and by examination under a Wood's lamp.
- To ensure maximum isolation, the patient is allocated a separate room; personal items belonging to him must be removed from general use.
- During the first 3 days after reporting a patient with ringworm, preschool medical workers should examine the entire group of children who have been in contact with the patient. Regular inspection should be carried out until final disinfection measures are taken. Observation is carried out 1-2 times every 7-10 days for 3 weeks using fluorescent lamps. A prerequisite is to maintain an observation sheet in which the data of each medical examination is entered.
Routine disinfection must be organized by the health authority that diagnosed the disease. Preventive measures until hospitalization or until the child is taken home are organized by the kindergarten.
A sick child should be isolated
Disinfection is carried out on time if the measures were started no later than 3 hours from the moment the first signs of the disease were detected. Disinfection in the garden involves the following activities:
- washing all bedding, clothes, soft toys;
- steam treatment of mattresses and pillows;
- roasting toys made from other materials;
- boiling all dishes;
- shoe processing;
- steam cleaning of carpets;
- floors and all surfaces, including beds, windows, window sills, are washed with disinfectants or chlorine.
The final stage of disinfection is carried out when the child is admitted to the hospital for treatment or goes back to the garden, regardless of the timing of treatment and recovery. Sometimes it is carried out 2 times.
Final disinfection should be carried out not only in the kindergarten, but also at the patient’s home. If several patients are identified, a study of the territory of the children's institution should be organized.
The examination is carried out by medical workers of a dermatovenerological profile and a sanitary and epidemiological surveillance epidemiologist. The epidemiologist determines the timing of final disinfection and the scope of work.
The health worker who diagnosed the disease must carry out explanatory work to identify the source of infection.
According to sanitary standards, there should be no stray dogs or cats on the territory of the institution, and in the kindergarten itself, no group should contain aquariums with fish and reptiles, parrots, or other animals. A separate living area should be equipped for them, to which only teachers take children. If lichen was detected in kindergarten, quarantine lasts a month or longer.
The timing is set in accordance with the length of the incubation period. When infected from a person, incubation lasts 8-30 days, from an animal - 4-7. Quarantine lasts longer than 30 days if there is an outbreak of the virus in several groups. At this time, the garden should be closed for several days for disinfection; it should not be carried out in the presence of healthy children.
Disinfection in the kindergarten is mandatory
Recommendations for parents
All parents who have been in contact with a patient with lichen, or those who are just about to go out into the garden after a long illness, must be informed about the possibility of infection. Parents of contact children should take preventive measures:
- wash all the clothes the child was wearing at high temperatures;
- disinfect the apartment with antiseptics;
- go to an appointment with your local pediatrician, find out about further actions, ask to prescribe immunotherapy.
Those who have just suffered from an infectious disease are advised to refrain from visiting kindergarten until the situation stabilizes, because a child with weak immunity risks getting sicker than others.
Usually, groups in kindergartens are not closed, and responsibility for the choice to drive or not to drive the child is placed on the parents. If you do not want your child to become infected, ask the doctor for a certificate until the epidemic ends.
The doctor is obliged to issue such a document and has no right to refuse you.
Conclusion
Microsporia of smooth skin and scalp in children is seasonal and highly contagious through direct contact with the patient or his belongings, pieces of furniture, etc.
To avoid the spread of the disease, it is necessary to ensure that all preventive measures are carried out in kindergartens on time and the standards prescribed by SanPiN are observed.
Although the disease does not pose a great danger if treated in a timely manner, it is important to remember that for children with allergies and children suffering from chronic systemic disorders, the disease can be a difficult ordeal. Parents whose child is not sick are still advised to refrain from visiting a child care facility until the situation is stable.
Source: https://kozhmed.ru/lishaj/mikrosporiya-u-detej-karantin-v-detskom-sadu-meropriyatiya-sroki.html
Features in adults
The clinical picture in adults is very similar. Just a few features can be highlighted:
- Itching is more pronounced.
- The source of inflammation grows more slowly and is poorly expressed.
- More often it occurs on the head when sharing a comb with a sick child.
- A rare atypical form with deep inflammation of the skin and subsequent suppuration is possible.
Diagnostics
Diagnostic search includes the use of the following methods:
- Dermatoscopy.
- Examination of the skin under a Wood's lamp.
- General clinical examinations of blood and urine.
However, the most informative methods are microscopic examination of skin scraping and culture.
Microscopy of scraping
Several scales of the stratum corneum are taken from the affected area of skin using the scraping method. After this, the material is examined under a microscope using a special stain.
If the result is positive, characteristic mycelial threads are detected.
Sowing
The most informative method is cultural. It involves inoculating scrapings onto nutrient media, which makes it possible to detect the fungus with high accuracy. The disadvantage of the study is the duration of its implementation.
A positive culture result comes only after 7–10 days.
How to treat in humans?
Treatment for children and adults under microscopy is practically the same. It involves the use of antifungal agents internally and externally.
Pills
The microsporia pathogen is most sensitive to the antifungal drug terbinafine. This remedy is available in tablets and is used from two years of age.
Contraindications for use may include liver and kidney diseases, pregnancy and breastfeeding.
The product has no direct analogues, but in some cases the fungus may be sensitive to other drugs:
- Fluconazole.
- Itraconazole
- Nystatin.
All these medications are prescribed exclusively by the attending physician. The dosage is selected individually.
Deep forms of microsporia are treated with dimethyl sulfoxide.
Ointments
External agents also help well with local forms of microsporia. Terbinafine-based emulsions and ointments are available in pharmacies:
- Lamisil.
- Exiter.
- Fungoterbin.
You can use the products if smooth skin and nails are affected. It is still better to treat the scalp with tablets.
Folk remedies
Traditional healers offer a large number of remedies for fungus. However, their effectiveness is often overestimated.
It is impossible to completely get rid of microsporia without antifungal drugs.
Use folk remedies only to speed up treatment and have a symptomatic effect:
- Raisin decoction orally 3 times a day.
- Birch tar in local form.
- Honey with garlic in the form of compresses.
Other recipes are also used to treat fungus, but the effectiveness of these remedies is very controversial.
Prevention
There are a number of preventive measures that will help you avoid becoming infected with the fungus:
- Take dogs and cats to the veterinarian for regular checkups.
- Do not allow your child to come into contact with stray animals.
- All family members should have individual combs and other hair care products.
- Identified children and adults must be isolated and treated.
- In kindergartens and schools there are medical examinations that can identify children suspected of microsporia.
The disease is highly treatable if detected early.
Is it possible to go to school?
A child with ringworm definitely cannot go to school or kindergarten. This increases the risk of infecting other children in the group.
The disease is treated at home, avoiding infecting family members.
Is the pathology dangerous?
Microsporia itself does not pose a danger to the life and future health of the child. However, in order for the hair to recover as quickly as possible, it is necessary to begin adequate treatment.
When qualified medical care is not provided in a timely manner, there is a risk of complications. It is important to prevent inflammation and suppuration of the skin. If treated incorrectly or too late, some areas where hair should grow may not recover completely.