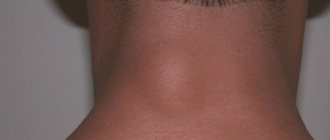
Why are condylomas dangerous?
Cervical condylomatosis increases the likelihood of developing cancer by 50-60 times
Condylomas should by no means be considered harmless. The fact is that the formation of condylomas is based on the same processes that underlie the development of tumors, therefore long-term condylomatosis is a precancerous condition. It has been proven, for example, that cervical condylomatosis increases the likelihood of developing cancer by 50-60 times. The human papillomavirus is also responsible for a number of cases of dysplasia (detachment) of the cervical epithelium and is transmitted to the baby during childbirth.
Overgrown condylomas can:
- get injured and bleed;
- interfere with normal sex life;
- bother as a cosmetic defect;
- cause psychological discomfort;
- interfere with normal childbirth.
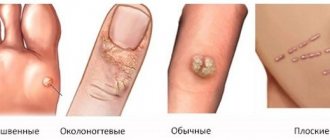
In addition to condylomas, the following types of human papillomas are distinguished:
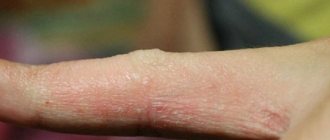
Simple (vulgar) papilloma in the form of a hard small lump - about 1 mm in diameter. Its keratinized surface protrudes above the surface of the skin. Papilloma without a stalk. Localized on any part of the body. But more often it occurs on the fingers, as well as in the knee area in children.
Plantar papilloma on the sole of the feet in the form of a rough protrusion, small in size, with a specific protruding rim. Mostly single form. But “daughter” growths can also form near the main papilloma. Causes discomfort and pain while walking. They often disappear on their own. This happens in children. In order not to confuse calluses with papillomas, you should take into account: the former have a smoother surface on which the skin pattern is visible.
Flat papilloma in the form of a round, smooth, flat lump. Can be polygonal. The color is similar to the color of the skin. This pathology is prone to occur on any part of the body. Most often it affects the face and hands. Painful. Causes inflammation of the affected area, redness and itching.
Filiform papilloma , often found at the age of 40-50 years. It is localized mainly in the area of the eyes, neck, groin and armpits. At the beginning of the process, the papilloma looks like a small yellowish protrusion. Then it turns into thread-like, elastic and elongated formations up to 5-6 millimeters in length. They may become inflamed. They do not disappear on their own.
Based on the level of oncogenicity, the following groups of HPV are distinguished:
- with a low level of cancer risk - numbers 81, 72, 70, 61, 54, 44, 43, 42, 40, 11, 6;
- with an average level of cancer risk - numbers 66, 58, 53, 52, 51, 35, 33, 31, 26;
- with a high level of cancer risk - numbers 82, 73, 68, 59, 56, 45, 39, 18, 16.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of viral rashes that are found in the vagina in women takes place in several stages. Each analysis is of great importance, as it helps the specialist determine the diagnosis.
To establish a diagnosis, you need to undergo the following diagnostics:
- History of the disease. The doctor should ask the patient for answers to questions about how long ago, according to her assumptions, the rashes appeared, whether she had unprotected sexual intercourse, when was the last examination in the gynecologist’s office, whether there are any complaints;
- PCR analysis. With its help, the specialist determines the presence and number of viral pathogens in the patient’s body. The diagnosis also provides information about the type of papillomavirus and the presence of antibodies to it. All this information helps to determine the extent of the spread of the disease throughout the body;
- Colposcopy. Designed to detect damage to the vaginal walls. A colposcope is used during the procedure. It is also necessary to stain the desired area, specifically the cervix, with an iodine-based solution;
- Anascopy. This method involves a thorough examination of the anal area for the presence of condylomas. During diagnostics, damaged areas are detected, pathogenic cells are studied and their main characteristics are determined;
- Histological analysis. The study is aimed at studying the structure of areas damaged by infection. If the human papillomavirus is really present in the patient’s body, then the analysis will definitely reveal it;
- Oncocytology. The analysis requires a scraping from the cervical area. A sample from the cervical canal is also needed. It is examined under a microscope to detect pathogenic cells.
If the diagnosis confirms the presence of papillomas at the entrance and directly in the vagina, the patient will immediately begin their treatment.
Neoplasms can be detected by a gynecological examination
Epidemiology
Differences between papillomas and condylomas
Pointed condylomatosis is an infectious viral disease found in venereological clinics, 3 times less often than gonorrhea in both sexes, but 9 times more often in men and 25 times more often in women than infectious syphilis. Consequently, genital warts are one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases characterized by ulceration or tumorous manifestations. Statistically in our country, condylomatosis acuminata is not taken into account, and therefore its distribution among the population can only be judged by relative data. The disease is diagnosed most often at the age of 20-25 years (from 52 to 54.8 percent). at the age of 26-30 years (from 9.7 to 12.3 percent). less often at the age of 13-19 years (about 10 percent) and 15-17 years (from 5.3 to 7.9 percent). However, the disease is possible in early childhood and old age. It is more common among prostitutes and women who have had a large number of sexual partners.
The causative agent of genital condylomatosis is a filterable virus from a group of viruses that are morphologically identical to one of them that causes the development of warts on the skin, but differs from it in antigenic composition.
The disease is contagious, and eutoinoculation is often observed. The development of genital warts is promoted by various local irritants, heat, moisture, and skin maceration. A combined disease is often observed, or rather the development of condylomas in patients with sexually transmitted diseases (gonorrhea, trichomoniasis and others) and accompanied by copious discharge from the urethra, cervix, vagina, rectum. I believe that genital warts develop more often in women, especially during pregnancy, and in case of poor hygiene of the genital organs (accumulation of smegma in men, contact of genital discharge on the surrounding skin in women), and with existing immune disorders.
Causes of growths
What are the causes of the disease? The papilloma virus is one of the most common types of viruses on the planet. It is carried by half of the world's population. The virus may not manifest itself for a long time and the patient, being confident in his own health, does not pay any attention to minor symptoms. The reasons why the virus enters the body have long been identified and studied. The disease can only appear in people with weak immune systems. Defense mechanisms must fight the virus and prevent its rapid development.
Chronic diseases, inflammatory processes and even a lack of vitamins can trigger the development of the virus. A month, two, six months or a year after infection, the first growths appear. Against the background of weak immunity, warts grow quickly.
The symptoms of condylomatosis quickly move from simple to acute form. It is necessary to find out the causes of illness before prescribing effective treatment. If chronic diseases are the root cause of the disease, they must be treated in parallel.
The reasons for infection are also simple - a person does not care about his own safety. It will not be possible to avoid infection, but every patient can reduce the likelihood of contracting the virus. The first step is to exclude the domestic route of infection. Under no circumstances should you use other people's personal hygiene products. Paying attention to your partner’s well-being will allow you to notice the first symptoms of papillomatosis before infection. Any reasons can be predicted, but they cannot be completely eliminated.
The causes of complications of condylomatosis lie in negligent use of one’s own health. You can achieve long-term remission if, for the purpose of prevention, you strengthen your own immune system and harden the body. Women's health should come first, because a woman is a mother and continuer of the family. The first signs of the disease will help you consult a doctor in a timely manner and fight back the virus that threatens the patient.

To avoid infection with papillomavirus, you should use only your own hygiene products
Classification of papillomavirus infection (PVI)
Clinical and morphological classification of HPV-associated lesions of the lower genital organs:
- Clinical forms (visible to the naked eye). -Exophytic condylomas (typical pointed, papillary, papular). -Symptomatic CIN.
- Subclinical forms (invisible to the naked eye and asymptomatic, detected only by colposcopy and/or cytological or histological examination). -Flat condylomas (typical structure with many koilocytes). -Small forms (various lesions of stratified squamous and metaplastic epithelium with single koilocytes). -Inverting condylomas (localized in the crypts). -Condylomatous cervicitis/vaginitis.
- Latent forms (detection of HPV DNA in the absence of clinical, morphological or histological changes).
- CIN or PIP: -CIN I (low-grade PIP) - mild dysplasia +/- koilocytosis, dyskeratosis; -CIN II (high-grade PIP) - severe dysplasia +/– koilocytosis, dyskeratosis; -CIN III or CIS - severe dysplasia or carcinoma in situ +/– koilocytosis, dyskeratosis; -microinvasive squamous cell carcinoma.
Clinic
Genital warts in women are most often localized on the inner surface of the labia majora
Condylomas acuminata are most often localized in men in the coronal sulcus of the penis, at the external opening of the urethra, on the inner layer of the premium sac and in the anus; in women - on the inner surface of the labia majora. on the labia minora, in the clitoris area, the entrance to the vagina, on the perineum and around the anus. In obese patients, condylomas can also develop in the inguinal-femoral folds, armpits, in the navel area, submammary glands. The disease is more often diagnosed in men than in women, and even much less often in children and the elderly. In children, growths in the vulva area and in the inguinofemoral folds are more common.
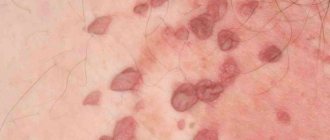
The incubation period varies - from 1 to 6 months. usually 2-3 months. Initially, small single papillary villous growths appear in the form of pink nodules in unlimited areas, then they are grouped, resembling a cockscomb or cauliflower on a narrowed base that resembles a stalk. Single condylomas are observed only in a small part of patients; in general, multiple growths are observed; less often, growths, merging into conglomerates, reach large and gigantic sizes. This type of lesion is observed more often in patients with pronounced subcutaneous fat and in pregnant women.
The elements acquire a bright red color with a cyanotic tint on the surface, are macerated, eroded, painful when touched, and bleed easily. Serous-purulent exudate accumulating between the lobules of condylomas, decomposing and combining with sweat, emits an unpleasant odor.
A serious complication, mainly of large and giant condylomatosis, is malignancy. Cases have been described, more often in elderly people, of transformation into warty cancer, so histological examination is necessary in such cases.
Major diseases
- HPV (human papilloma virus). A growth formed inside the female genitalia is medically called condyloma. The incubation period can last from 2 weeks to 3 months. During the formation of condyloma, a woman experiences itching, pain and burning. The mucous membrane may become swollen and red. The growths often emit an unpleasant odor. Untreated condylomas can cause cervical erosion, dysplasia and oncology.
- Lipoma. Wen is localized on the walls of the vagina and labia. Education occurs asymptomatically. The growth has an oval or round shape. There is no pain when palpated. If the lipoma is located outside the vagina, then when examining it, the woman will be able to notice yellow contents inside the seal. The patient is not recommended to squeeze the contents out of the seal, use burning devices, rip off the growth on her own, and take medications until a doctor makes an accurate diagnosis.
- Cyst. The formation of a vaginal cyst is asymptomatic and is detected during a routine examination by a gynecologist. When the growth reaches a large size, it can fester and make sexual life difficult (due to pain). The cyst is examined using colposcopy. The cyst has a round shape, and its structure is soft-elastic.
- Polyp. Characterized by a single growth in the area of the uterus and vagina. Multiple formations - uterine polyposis. If left untreated, polyps cause infertility. There are adenomatous polyps (grows in the mucous membrane and covers the inner surface of the uterus) and glandular polyps (formed from endometrial tissue and glands). Symptoms of formation: spotting and spotting during the intermenstrual period, discomfort and pain during sexual intercourse, nagging pain in the lower abdomen and menstrual irregularities.
- Genital wart. The growth causes discomfort, pain, and clings to underwear. The disease is transmitted through sexual and household contact. Condyloma has a pointed, papillary and flat shape. The base of the wart can be wide or thin. Papillomas are located on the labia minora and majora, mucosal walls, near the anus, in the groin and pubic area. Main symptoms: swelling, itching, redness, copious discharge with a pungent odor, possible bleeding, pain.
- Herpes. Genital herpes is a disease caused by herpes simplex viruses. The growths are filled with fluid and are localized on the thighs, pubis, anus, vagina and cervix. During the formation of a vesicle, the patient feels itching. After 7 days, the growth bursts, forming an ulcer.
- Haemorrhoids. The growth in this case is localized between the entrance to the vagina and the anus, and its shape resembles a nodule. Symptoms of the disease: varicose veins in the perineal area, pain in the lower abdomen, vaginal discharge, discomfort during sexual intercourse.
Types of growths are classified according to:
- sizes (small, medium, large);
- form;
- color;
- structure (hard, loose).
Formations can be located:
- Inside the vagina. The patient can observe this type of formation only in a photo taken during ultrasound diagnostics. Only a doctor can detect such formations during examination or palpation.
- Outside at the entrance to the labia, on the pubis, near the anus, on the thighs.
Diagnosis of papillomavirus infection
Clinical visual method
Localization of foci of human papillomavirus infection (PVI): cervix, vagina, vulva, perineum, perianal area, urethra and other epithelial integuments of the genital organs. According to visual colposcopic characteristics, acuminate, papillary and papular condylomas are distinguished; they are combined under the general term “exophytic condylomas.” Macroscopically, exophytic forms of human papillomavirus infection (PVI) have different sizes: from spots with small dots and low spiny protrusions to extensive tumors such as giant condylomas.
Symptomatic CIN is determined by the naked eye; they are represented by areas of pronounced keratinization (in the form of whitish plaques), exophytic formations or ulcerations. With condylomatous cervicitis and vaginitis, upon examination, a wavy (non-smooth) surface of the epithelium of the cervix and vagina is noted.
Subclinical forms are diagnosed by colposcopic and cytological studies.
Extended colposcopy for PVI
The most characteristic colposcopic signs of subclinical forms of papillomavirus infection are: acetowhite epithelium, mosaic, punctation, atypical transformation zone
There is no specific set of colposcopic signs of papillomavirus infection. The most characteristic colposcopic signs of subclinical forms of human papillomavirus infection are: acetowhite epithelium, mosaic, punctation, atypical transformation zone.
Pronounced (gross) colposcopic signs of papillomavirus infection:
- severe leukoplakia;
- rough mosaic and punctuation.
Minor colposcopic signs of papillomavirus infection:
- thin leukoplakia;
- delicate mosaic and punctuation.
In case of condylomatous cervicitis and vaginitis, after Lugol's staining with a solution of glycerin ©, the affected area of the ectocervix is stained in the form of whitish dots - “semolina”.
Cytological examination
The main cytological sign of human papillomavirus infection is the presence of cells with koilocytosis and dyskeratosis in the smear. Detection of cells with dyskaryosis in the smear suggests the presence of CIN. Koilocytes are formed in tissues as a result of the cytospecific effect of HPV and are intermediate-type stratified squamous epithelial cells with enlarged nuclei and an extensive perinuclear zone of clearing due to degenerative changes and necrosis of destroyed cytoplasmic organelles.
Laboratory research
- To identify and type HPV, it is advisable to use PCR with type-specific and species-specific primers to quantify the risk of malignancy - the Digene Capture test. The Digene Hybrid Capture II method (double gene trap method) allows you to determine the critical concentration of the virus (viral load), which is directly related to the risk of malignancy.
When the HPV DNA level is above 5000 genomes, the likelihood of developing CC is high.The method allows you to detect the entire group of oncogenic HPV types. Cell material taken with an endobranch brush, a preparation on a slide for cytological examination, as well as biopsy samples are suitable for the Digene test.
- Identification of concomitant genital infections and vaginal dysbiosis.
- Targeted biopsy of the cervix and curettage of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal with histological examination are indicated: - when atypia is detected during cytological examination; - with pronounced colposcopic signs of PVI (regardless of HPV typing data); - with mild colposcopic signs of PVI in combination with highly oncogenic types of HPV.
Histological manifestations of human papillomavirus infection of the cervix include exophytic and typical flat condylomas, mild changes in the squamous epithelium (single koilocytes in the presence of various changes in the epithelium, including condylomatous cervicitis/vaginitis), CIN of varying degrees and without them, CC.
The most common diagnosis is flat condyloma. A typical flat condyloma histologically is an area of ectocervix covered with stratified squamous or metaplastic epithelium with symptoms of dyskeratosis and acanthosis; in the intermediate layer of the epithelium there are always clusters of koilocytes.
With condylomatous cervicitis and vaginitis, a characteristic structure of stratified squamous epithelium with small pointed growths (“undulation” of the surface sections), koilocytosis and signs of inflammation are histologically revealed. The morphological picture of CIN depends on the degree of its severity (see section “Cervical dysplasia”). Exophytic condylomas of atypical appearance are also an indication for biopsy. Histologically, exophytic condylomas are a tumor-like formation with a surface covered with stratified squamous epithelium with symptoms of koilocytosis, papillomatosis, acanthosis and dyskeratosis.
- Immunogram.
- Examination of sexual partners.
The effectiveness of diagnosing human papillomavirus infection can be high only in the case of complex use of colposcopy, HPV typing and cytological examination.
Differential diagnosis of condylomatosis
Exophytic condylomas are differentiated from other skin diseases (condylomas lata with syphilis, squamous cell condylomas, psoriasis, molluscum contagiosum, etc.), small condylomas at the entrance to the vagina - with growths of the hymen. Subclinical forms are differentiated from benign processes of the vulva (inflammatory and dystrophic).
Indications for consultation with other specialists
- Dermatovenerologist - in the presence of exophytic condylomas of atypical appearance.
- Immunologist - for recurrent and extensive injuries.
- Gynecological oncologist - for patients with CIN III.
A process sticking out of the vagina
Frequently, frightened patients who have discovered a growth in their vagina come to the gynecologist. Of course, such a discovery will scare anyone, but you shouldn’t worry ahead of time.
Most likely you are faced with a benign neoplasm. The color of this process is usually pinkish or flesh-colored, if you can see it. Such formations indicate that HPV, the human papillomavirus, has been activated in the body.
Growths in the vagina, photos of which can be taken, are located near the entrance to it. There are also those that can only be detected by touch and can only be seen by a doctor during an examination, since they are located inside the vagina.
Often such neoplasms appear suddenly and a woman does not notice them until she accidentally feels them. Sometimes their appearance is accompanied by itching, burning and even spotting.
To protect yourself and your partner from HPV, you must use barrier methods of contraception, and never neglect intimate hygiene, especially after sexual intercourse.
The presence of a process in the vagina can interfere with sexual intercourse and also become an obstacle to the desired pregnancy.
If you find a growth inside the vagina, then you most likely have genital warts, which can grow over time. The reason for its appearance is precisely the same HPV. Education can appear at any time in life for a variety of triggering reasons.
Condylomas are classified as follows:
Condylomas can appear in different places - on the labia, pubis, near the anus, on the thighs. They are not dangerous in themselves, but can easily be injured upon contact and bleed.
A process from the vagina can also be malignant, so if you find one in yourself, you should definitely consult a specialist. To begin with, see a gynecologist. There are also cysts, lipomas, polyps, and warts in the vagina. So, if the growth is white, then this is a genital wart.
Sometimes women discover that they have hemorrhoids and do not immediately understand what kind of nodule it is. During the examination, the doctor, based on his many years of experience, will share his assumptions with you. And in this case, he will refer you to a proctologist to solve the problem.
The vaginal mucosa is a favorable environment for the appearance of condylomas. There may be one process in the vagina or there may be several of them at once. It is in the latter version that we are talking about the growth of formations. And then the affected area may resemble cauliflower inflorescences or the comb of a rooster.
Up to a certain point, HPV does not manifest itself in any way, but after some time growths appear. As we have already said, in color they are not much different from the color of the body.
Causes
The occurrence of a growth or condyloma in the vagina depends on the state of the person’s immune system. Once infected, the virus can live in the body for about three months and not make itself known. It rarely happens that within two weeks after contact with an HPV carrier, the first condylomas or papillomas appear.
Most often, a woman becomes infected with HPV if:
- her immune system is impaired;
- there are various infections in the genital tract;
- she often changes partners without thinking about safety.
Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules is also fraught with unpleasant consequences.
With a strong immune system, a woman can live her entire life and never find the appendage from the vagina. But at the same time, she is a carrier of the virus and can infect her partner. Most often, the risk of contracting HPV is higher during pregnancy, as well as during breastfeeding.
Of course, there are few women who, in such a difficult period, plunge headlong into intimate life and change partners, forgetting about everything.
Usually condylomas come out at this time, and the infection occurred a long time ago. After all, the load on the body is increased and dormant viruses and bacteria become more active.
So before you plan to conceive, you need to undergo all the necessary examinations.
Treatment
A process in the vagina, if it is a condyloma, usually must be removed. The final diagnosis is determined only by a gynecologist after a thorough examination.
To begin with, the doctor talks with the patient, and then conducts an examination on the chair. Then a colposcope is used to enlarge the detected formations on the walls of the vagina and cervix. Thanks to PCR diagnostics, it is possible to determine the HPV strain, because it comes in several types. For this analysis, it is necessary to take a scraping from the place where the growth is located.
Using the ELISA method, antibodies to HPV are determined. Be sure to take a smear of the flora to see if there is a bacterial infection. They also conduct an examination for the presence of oncological processes in the cervix and cervical canal - a smear for oncocytology.
Growths in the vagina, photos of which can be found on the Internet, are diverse. Therefore, treatment will differ in each specific case. Sometimes you can get by with antiviral medications.
The choice of therapy is also influenced by the woman’s age, her general health, and individual characteristics. Various medications are also used to support the functioning of the immune system. If the doctor deems it necessary, the growth can be treated with local means.
Removal
Quite often, gynecologists advise removing the appendage from the vagina as soon as possible using special devices used in gynecology. The operation does not last long, there are no scars left and the risk of relapse tends to zero.
Source: https://vsedlyavasdamy.ru/info/iz-vlagalishha-torchit-otrostok/
Treatment of condylomatosis
Patients with a latent form of human papillomavirus infection do not need treatment. Such patients are indicated for observation, the frequency of which depends on the presence or absence of persistence of highly oncogenic HPV types (see “Further management” below). Patients with CIN III and CIS should be treated and observed by a gynecological oncologist. Indications for treatment are clinical and subclinical forms of PVI, CIN and CC. The choice of treatment tactics is differentiated depending on the examination results, the nature and location of foci of papillomavirus infection. A complete cure for human papillomavirus infection is currently impossible to achieve.
Treatment Goals
Destruction of exophytic condylomas and atypically changed epithelium.
- Correction of immune homeostasis.
- Treatment of concomitant genital infections and vaginal dysbiosis.
- Treatment of sexual partners.
Indications for hospitalization
For biopsy, for surgical treatment. In most cases, treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis or in a one-day hospital.
Non-drug treatment of PVI
To destroy atypically changed epithelium, physical methods are used, for example, the laser method
To destroy atypically altered epithelium, physical methods are used (diathermo cryo, laser and radio wave methods), in some cases - chemical coagulation and treatment with cytotoxic drugs. Destruction of exophytic condylomas is carried out after local infiltration anesthesia with a 0.5% lidocaine solution (or in the form of a spray).
The effectiveness of destructive methods is 45–97%, the recurrence rate reaches 50%. Chemical coagulants (solcoderm ©, podophyllotoxin) are used to destroy exophytic condylomas. Solcoderm © (mixture of organic and inorganic acids). Treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis once a week (course of treatment - 5-6 procedures). The drug is applied precisely inside the condyloma at a time, up to 0.2 ml (1 ampoule). If there is no effect, change therapy. Can be used during pregnancy.
Podophyllotoxin (condylin ©) is used independently at home. Lubricate the affected areas of the skin and mucous membranes 2 times a day (every other day). The volume of the drug should not exceed 0.2 ml per procedure. The course of treatment is 5–6 weeks. Not used during pregnancy.
If hyperemia, itching, or pain occur, the intervals between procedures can be increased to 2–3 days. Cytostatic drugs: fluorouracil (5% cream) is used independently at home. Lubricate the affected areas of the skin and mucous membranes once a day at night for 7 days. If there is no effect from a course of treatment with chemical coagulants and cytotoxic drugs, the use of other destructive methods is indicated.
Drug treatment of PVI
Indications for immunomodulation and antiviral therapy are relapses of human papillomavirus infection, extensive and multiple lesions.
Immunomodulatory drugs
Immunomodulatory drugs (systemic and local action) for papillomavirus infection of the genitals are used both in monotherapy and in combination with destructive methods. Immunomodulatory therapy is carried out under the control of an immunogram. Interferons and their inducers, synthetic immunomodulators, and immunoglobulins are used. The use of immunomodulators with antiviral and antiproliferative effects is pathogenetically justified. Immunomodulators are used 10 days before destruction of the pathological focus. According to indications, the second course of immunomodulatory therapy is carried out after the destruction of exophytic condylomas and atypically changed epithelium.
Immunomodulatory and antiviral drugs are not recommended for use during pregnancy and lactation.
- When treating condyloma, I often prescribe Lykopid.
Synthetic immunomodulator . Likopid © - take 1 tablet (10 mg) 1-2 times a day for 10 days (course dose 200 mg); It is advisable to carry out two courses of treatment - before and after destructive techniques.
- Interferon preparations: Genferon © vaginal suppositories, 1 suppository (1 million IU) 2 times a day for 10 days; -Viferon © rectal suppositories, 1 suppository (1 million IU) 2 times a day for 10 days, -Kipferon © rectal suppositories, 1 suppository (1 million IU) 2 times a day for 10 days.
- Herbal immunomodulators : Echinacea preparations (capsules, tablets, drops) in doses recommended by the manufacturer for 2–3 weeks; -Panavir © (potato shoot extract) rectal suppositories, 1 suppository 2 times a day for 10 days.
Antiviral drugs
- Inosine pranobex (isoprinosine ©) 2 tablets (1000 mg) 3 times a day for 14–28 days in monotherapy in the treatment of genital warts and papillomatosis. In combination with destructive methods of treating genital warts or treatment with cytotoxic drugs, 2 tablets (1000 mg) are prescribed 3 times a day for 5 days (3 courses with breaks of 1 month). For CIN IIII associated with HPV types 16 and 18, isoprinosine© is used in combination with destructive methods of treatment, 2 tablets (1000 mg) 3 times a day for 10 days; 3 courses are carried out at intervals of 10–14 days.
- Indinol © (indole3carbinol) 2 capsules (400 mg) 2 times a day 10 minutes before meals for 3 months. Etiotropic anti-inflammatory therapy for other types of sexually transmitted infections (when combined with PVI of the genital organs) (see relevant sections). Adaptogens (preparations of ginseng, eleutheroccus, aralia, Schisandra chinensis, etc.), antioxidants (vitamin E, betacarotene, preparations containing complexes of plant flavonoids), multivitamin preparations.
Treatment of papillomas
The tumor should be removed even if it does not cause discomfort. The virus is transmitted through sexual intercourse, so the likelihood of infecting a sexual partner is too high.
It is not recommended to use pharmaceutical products for home use, as there is a risk of causing a burn to the mucous membrane.
Consultation with a dermatologist is required in the following cases:
- the presence of purulent or bloody discharge,
- inflammation of the skin in the area of the growth,
- discomfort when pressing on the papilloma,
- increase in tumor size.
Before learning how to treat the virus with drastic methods, it is necessary to transfer it to a latent form. For this purpose, medications are taken that stimulate the immune system. The greatest demand is: Likopid, Immunal, Anaferon, Estifan, Immunomax.
It is advisable to pay attention to chronic diseases. They negatively affect the immune system, which makes the body vulnerable to the virus. Of particular danger are endocrine disorders, pathological processes in the gastrointestinal tract and inflammatory pathologies.
Of particular danger are endocrine disorders, pathological processes in the gastrointestinal tract and inflammatory pathologies.
Removal methods

The likelihood of papilloma degenerating into a malignant growth increases with its constant trauma. Removal of papillomas in the vagina is a mandatory procedure, since the growth inside the genital organs is regularly subjected to mechanical stress.
The following methods of eliminating neoplasms are distinguished:
- cryodestruction,
- surgical removal,
- laser therapy,
- exposure to radio waves,
- electrocoagulation.
When performing cryodestruction, a stream of liquid nitrogen is directed to the problem area. Electrocoagulation uses high temperatures. Laser removal is considered one of the most effective and painless procedures. The likelihood of relapse in this case is minimal.
Radio wave exposure is a relatively new way to eliminate viral symptoms. Very often it is practiced when they are located on the genitals.
Surgery is suitable if the tumor is too large. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia using medical instruments.
After removal, the woman must be regularly monitored by a gynecologist. During the recovery period, it is advisable to limit sexual intimacy. Poor treatment of the growth is fraught with relapses.
The disease can spread not only to the walls of the vagina, but also to the inner thighs, near the anus, and even in the esophagus.
A sample of the removed growth is sent for histological examination. It helps determine its nature of origin.
During pregnancy

After conception, the likelihood of developing HPV increases several times. This is due to a decrease in the immune system and changes in hormone levels.
Papillomas in the vagina during pregnancy can be eliminated using gentle methods. Treatment begins at 28 weeks, when the fetal life support systems are already formed.
For local use, medications are prescribed in ointment format: Acyclovir, Celandine, Viferon, Oxolinic ointment and Solcoderm. Medicines that strengthen the immune system are taken internally: Reaferon, Kipferon, Viferon and Anaferon. If possible, therapy against the virus is carried out before pregnancy. If the growths cannot be eliminated before the moment of delivery, then delivery is performed by cesarean section.
The best way to prevent the virus is to strengthen the immune system through a healthy diet, exercise and replenishing vitamin reserves.
Conclusion
Growths in the vagina and around the outer surface of the genitals are common. Reviews indicate that such neoplasms bring severe physical and psychological discomfort.
According to survey results, laser therapy is considered the most preferable method of removing them. Its advantages include a short wound healing period and a low probability of relapse.
It is highly not recommended to remove condylomas yourself. This leads to infection and the formation of pustular wounds. Correct and timely treatment of HPV helps to avoid serious consequences.
Fungus in the groin area +18
Control observation
Patients with genital condylomas are subject to constant dispensary observation during treatment. Attention is paid to the general well-being of the patient, the response to treatment in the foci of the disease and the dynamics of regression of genital warts.
If necessary, the drug, treatment method is changed, or gentle anti-irritation therapy is added, i.e. In each specific case, the approach is individual, in compliance with the principle of “do no harm.”
Clinical observation is also necessary in order to prevent relapse of the disease in time and not to miss tumor metaplasia of giant condylomas.
Prevention
Personal prevention consists of hygienic maintenance of the skin and mucous membranes of the genitourinary organs, careful treatment of the disease, abstinence from sexual intercourse until complete recovery and termination of dispensary observation. Treatment of diseases that promote or create conditions for its development is of great preventive importance. Public prevention consists of timely identification, examination, if necessary, and treatment of partners who have had sexual intercourse with the patient after his contact with the source of infection, as well as identification of patients with genital condylomatosis during all types of preventive medical examinations.
Sources:
- https://medportal.ru/enc/venerology/condyloma/
- https://www.goodoktor.ru/21.html
- https://www.medsecret.net/ginekologiya/mochepolovye-infekcii/88-pvi
Causes of warts in the vagina
Warts near and inside the vagina are viral in nature. The causative agent, the human papillomavirus, is highly contagious and has many varieties. According to some reports, about 90% of the planet's population is infected with this disease. The insidiousness of HPV lies in the fact that this microorganism does not cause fever or signs of general intoxication, cough or inflammation, so it is very often not possible to suspect this disease.
Its main manifestation is the formation of benign epithelial tumors, but this process does not begin immediately. In some cases, the incubation period lasts 2-4 weeks, in others - 6-12 months or even several years. Cases of long-term carriage have been recorded. However, the person is still contagious.
The source of HPV that causes warts in the vagina is usually from people who are already infected, because The virus is most viable within the host, but there are also cases of indirect infection.
Let's consider the options for HPV infection:
- Contact method . The palm belongs to sexual intercourse, during which there is close contact with the skin and mucous membranes. The situation is aggravated by the increased humidity of certain areas and the characteristics of the microflora on the genitals, which accelerate the process of formation of warts near and inside the vagina. Slightly less often, the virus is transmitted through ordinary touching - during massage, cosmetic procedures, hugs, handshakes, etc. If there are warts at the entrance to the vagina, the risk of infection of the baby during childbirth is very high. This method of transmission of the disease is fraught with the development of a complex form of laryngeal papillomatosis in a child.
- Self-infection . The focus of the disease is at the site of infection. The pathology itself does not cause complex damage. But if there are warts, the person himself spreads the infection throughout the body. The presence of tumors on the hands is fraught with the appearance of warts near the vagina, on the face, and knees.
- Indirect contact . The microorganism remains on objects and things that the carrier used. The virus is able to survive for 2-3 hours outside the human body, and if the surrounding microclimate has high humidity, then longer. Thus, it is easy to become infected with HPV through toys, kitchen utensils, personal hygiene items and any surfaces in public places. Often warts around the vagina occur due to neglect of the rules of using a public toilet.
Let's consider the main factors that allow the virus to easily penetrate the human body, take root there and provoke the growth of warts in the vagina:
- High humidity . The intimate area in women is characterized by special microflora and high humidity. Such conditions allow the virus to maintain vital activity much longer, waiting for the right moment to penetrate the basal layer of the integument. In addition, after infection has already occurred, these factors also contribute to the accelerated progression of the disease and the rapid growth of warts in the vagina.
- Damage to the body . HPV enters the human body not through the respiratory or digestive system, but through the skin and mucous membranes. Thus, if there are even microscopic cracks in the epidermis, then through them the pathogen is able to penetrate into the basal layer. Violation of the integrity of the epidermis can occur due to mechanical, thermal or chemical effects or as a result of any pathology of the skin. The risk group is people with eczema, acne, psoriasis, etc.
- Weakening of the immune system . In rare cases, even with close contact, some people do not become infected with the virus. This is due to strong immunity. But if for some reason the immune system fails to cope with its task, then the pathogen readily invades the cells, multiplies and causes rapid growth of warts around the vagina. A decrease in immune status occurs due to many factors, for example, an unbalanced diet that causes vitamin deficiency and a lack of nutrients, bad habits that deplete the body, excessive emotional and physical stress, and insufficient sleep. Specific pathologies of the immune system, for example, HIV, as well as other dangerous diseases - hepatitis, diabetes, herpes, chlamydia, gonorrhea, have an extremely negative impact. Self-medication and long-term use of strong drugs also reduce immunity.