Many parents are scared when they see a birthmark on a newborn. The reasons for this attitude towards this phenomenon are different. Some people are frightened by the appearance of these spots, and representatives of the older generation often say that these are signs of terrible diseases or misfortunes. In fact, birthmarks in most cases are an ordinary cosmetic defect, although some even consider it an advantage. Often, no medical intervention is required, however, if such a spot is detected in a child, you should consult a doctor to exclude the possibility of the development of malignant tumors.
In this article you will learn what types of birthmarks there are in newborns, the reasons for their appearance, how to treat them, as well as methods of removal, treatment and prevention of various complications.
What is a birthmark?
birthmark in a newborn: causes
It is customary to differentiate birthmarks in newborns into vascular and pigmented. In the first case, the skin color changes if the vessels change their diameter and come to the surface. The second group of spots appears under the influence of melanin:
- if there is a lot of it, the stain will be darker than the skin,
- if it’s not enough, it’s the other way around.
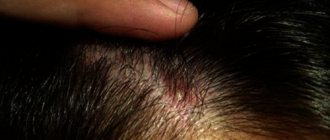
Capillary hemangiomas often occur in children and are called “salmon spots” because of their color. The spots appear on the head, as well as the bridge of the nose, forehead, eyelids or upper lip. When crying, birthmarks in newborns turn red; if the child is cold or sleeping, they turn pale. Capillaries return to normal after reaching 3-5 years.
Spots on the face disappear over time, but on the back of the head they can remain under the hair throughout life. The second type of vascular spots are common hemangiomas. They are benign neoplasms of various shades, shapes and sizes. The color of the hemangioma depends on the diameter of the vessels and depth.
The further the hemangioma is from the upper layers of the skin, the more pronounced its color. Hemangiomas tend to increase in size, gradually turning from a small elevation into a pronounced tumor.
An ordinary hemangioma goes through three stages in its development. At the first stage (appears from birth to 18 months), hemangiomas actively grow; in the second stage (from 1 to 5 years) the spots become paler and disappear.
Sometimes there is a third stage, in which the stain disappears only when the child is 15 years old. Signs of recovery include lightening of the skin in the hemangioma itself, as in the photo. Sometimes a common hemangioma causes complications.
The most common of these is stain damage caused by friction with diapers, fabric and clothing seams. The child can scratch the stain himself if, for example, an insect has bitten the area. The inflamed area should not become infected; this will seriously complicate treatment.
There are also more dangerous causes and consequences of infection, which involve disruption of the functioning of the organ with which the hemangioma is adjacent.
If the hemangioma is located on the eyelids, complications can reduce visual acuity, on the nose it can make breathing difficult, and near the mouth it can make eating difficult. If the spot is located near the anus, problems with bowel movements may occur.
It happens that birthmarks in newborns that do not lighten become a negative factor for the development of psychological disorders. Other children may tease the child and avoid him. Hemangioma has a dangerous but rare complication - spontaneous bleeding from the spot. If a complication occurs, you must immediately consult a doctor.
Nevus is the rarest, but also the most unpleasant type of vascular spots. We are talking about a “wine” or “flaming” nevus. Unlike other spots, nevus cannot disappear on its own over time. At birth, a child often develops nevi of an intense pink color, and the size and shape of the spot can vary in each individual case.
Over the years, the intensity of the color becomes greater; after the child reaches 10-12 years of age, the spot takes on the character of a tumor. Depending on its location, it can cause breathing problems or glaucoma.
To avoid such serious consequences, treatment should be carried out from birth to 2 years. During this period, the nevus is in the spot stage. Timely treatment will be completely effective and will relieve all associated troubles.
Moles or nevi appear due to the fact that melanin levels fluctuate in the child’s body. According to statistics, nevi are registered in 13% of infants. Congenital melanocytic nevus or “Mongolian spot” is considered the most harmless disease that does not degenerate into a malignant form.
The name was not chosen by chance; the fact is that the causes of melanocytic nevus are related to race (for example, all children belonging to the Mongoloid race have it). This is about the question of what a melanocytic nevus is.
This mole is a gray-blue spot that looks like a bruise. The Mongoloid spot can have different shapes and sizes, but it is always localized in the sacrococcygeal region. The spot is noticeable immediately after the birth of the child; after a few years, the nevus will turn pale and disappear.
The next type of moles is a large group of dysplastic nevi. The formations can be of all shades of brown, they remain on the body throughout life. However, among these moles there are also dangerous species.
The doctor must monitor the situation when the child has a large number of spots or they constantly appear. Particular attention should be paid to those spots that change color or shape. It is dangerous if the stain takes the shape of a tree leaf.
An immediate visit to the doctor should occur if the child experiences discomfort, or when the spots become swollen, painful, or itchy. Such dramatic changes are the reason for surgical elimination of the spot.
Congenital pigmented nevus, which has large pigment cells, is quite common. A nevus can be located in any area of the body and have any shape. The spot may also be covered with hair. The color of the nevus varies: from light brown to deep black.
Doctors divided the spots depending on their size:
- So, small spots less than 0.5 cm,
- medium spots - about 7 cm. are considered harmless and do not require surgical intervention.
- The spot is considered large on the body if its size is above 7 cm;
- Giant if more than 14 cm.
A spot on the head is considered large if it exceeds 12 cm, giant - over 14 cm. In these cases, close monitoring of the situation and work with a doctor is indicated. With additional negative factors, small spots may also require therapy.
There are several such factors. The mole is injured or burned. The mole grows, changes color and (or) shape, hurts, and bleeds. Other formations appeared around the mole. If any of these signs appear, you should visit a dermatologist.
Source: rodinkam.net
Precautions and possible complications
If the spot on a newborn is small, smooth, does not grow, and does not cause discomfort, then no special measures need to be taken. Parents must ensure that pigmentation does not change its appearance, size, shape, borders, shade, hairs do not fall out, and new growths do not form around.
- Do not expose your baby's skin to prolonged exposure to sunlight.
- Make sure that the child does not tear off or damage the mole with clothing, toys, or when combing.
- Pigment spots should not be exposed to harmful substances contained in household chemicals.
When exposed to unfavorable factors, the nevus degenerates into a malignant tumor - melanoma. It's not easy to cure. To prevent this from happening, dark moles need to be monitored and consult a doctor if they change.
In children, nevi are removed that transform, interfere with the functioning of organs (localized on the eye, lip, armpits), and are often injured. In the absence of such indications, the formations are periodically shown to the doctor.
Classification
Birthmarks vary in shape, color and texture and are generally divided into the following categories.
Strawberry hemangioma. These are soft, raised, strawberry-red birthmarks, small like freckles or large. They consist of underdeveloped vascular material, separated from the circulatory system during the development of the embryo. They may be noticeable at birth or appear suddenly in the first weeks of life. This is common in one in ten newborns.
Vascular hemangiomas may increase slightly in size, but eventually begin to fade to a pearly gray color and almost always disappear completely between five and ten years of age.
Although parents may feel a strong urge to treat an overly visible birthmark, especially when it is on the face, it is best to leave such marks alone unless they continue to grow in size or interfere with some function, such as vision.
Treatment may lead to worse consequences than a conservative approach based on the principle of “let’s leave everything as it is.” If your children's doctor recommends treatment, you will have a choice. The simplest method of treatment is compression and massage designed to speed up involution.
More aggressive treatments for vascular hemangiomas include steroids, surgery, lasers or X-rays, cryotherapy (freezing with dry ice), and injection of strengthening agents (the same ones used to treat varicose veins).
Many doctors believe that no more than 0.1% of such birthmarks require radical therapy. If a vascular hemangioma, overcome by time or treatment, has left behind a scar or residual tissue, plastic surgery can help correct the problem.
Sometimes a birthmark can bleed either spontaneously or as a result of a cut or blow. The flow of blood should be stopped by applying a cotton swab or tissue.
Cavernous hemangioma. This birthmark is less common than strawberry hemangioma - only in one in a hundred newborns. It is often combined with strawberry-type hemangioma, but unlike it, it consists of larger and more mature vascular elements and affects deeper layers of the skin.
It is a bluish-red loose mass with less distinct boundaries than a strawberry spot, and at first may appear almost flat. In the first 6 months the spot grows rapidly, in the next 6 months the growth slows down, and from 12 months it begins to shrink.
Half of the cavernous spots completely disappear by the age of five, and by the time the child is 12 years old, they disappear completely, and only sometimes a scar can be seen in this place. Treatment methods for cavernous spots are the same as for strawberry hemangiomas.
Simple nevus, or “stork bites”. These orange-pink spots can appear on the forehead, eyelids, around the nose and mouth, but are most often found where storks carry babies, hence the humorous name “stork bites.”
They lighten in the first two years of a child's life and are noticeable only when the child cries or becomes very tense. Because these birthmarks disappear completely, they are less likely to cause cosmetic problems than others.
Port wine stain, or fiery nevus. These purple-red birthmarks, which can appear anywhere on the body, are made up of dilated capillaries. In newborns, they appear as slightly raised pink or reddish-purple patches of skin.
Although they may change color slightly, these spots do not fade over time and are considered permanent. To disguise them, use a waterproof cosmetic cream; laser treatment can give good results.
In rare cases, damaged areas of the skin are associated with excessive growth of soft or bone tissue, and also, if the spot is on the face, with abnormalities in the development of the brain. Ask your child's doctor if you have any particular concerns.
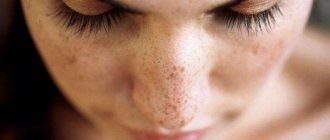
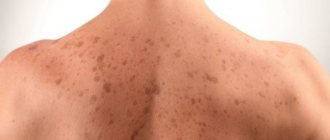
Cafe-au-lait stains. These are flat areas of skin, ranging in color from light tan (coffee with a lot of milk) to dark brown (coffee with traces of milk), can be located on any part of the body, are quite common, appear at birth or in the first years of life and do not disappear over time. If your child has many of these spots (six or more), take him to the doctor.
Mongolian spots. Blue to pale gray, bruise-like spots occur on the back and buttocks, sometimes on the legs and shoulders, in nine out of ten children whose parents are black, Asian or Native American.
These subtle spots are also quite common in children of the Mediterranean region, but are very rare in fair-haired and blue-eyed infants. Although these spots most often appear at birth or during the first year of life, they sometimes occur in adults.
Large stains are usually recommended to be removed if this can be done easily, but otherwise they should be under the constant supervision of a doctor who knows how to treat them.
Source: babyportal.ru
When not to worry
If a child is born with a bluish-colored birthmark in the area of the sacrum or buttocks, it is a Mongolian spot. It can be up to 10 cm in diameter and have a gray tint. If a child's birthmark is located on the back, there may be problems with the structure of the spine. In most children, it disappears by the age of 5, but even if it does not disappear, there is no data on the degeneration of such spots into malignant ones.
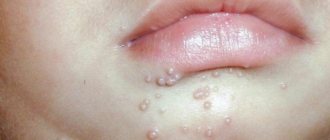
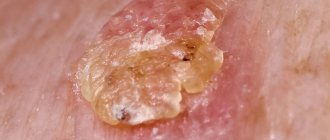
Papillomatous nevus is caused by the human papillomavirus (which is present in 99.9% of us) and has the unpleasant appearance of a dark fungus on a stalk. It looks unsightly on exposed skin, but is not life-threatening.
Fibroepithelial moles are the most common. They are usually round, with an elastic consistency. They grow for a while and then their growth stops.
Halonevus appear against a background of reduced immune status and are characterized by a lighter halo. Round or oval, they rise above the skin and can serve as a symptom of internal autoimmune pathologies.
An intradermal mole is a feature of the pubertal period of human development. It can change its shape and disappear completely.
Birthmark in a newborn - causes
It is a very common belief that the newborn baby will bear some external mark or otherwise be affected by something his mother sees during pregnancy, and especially by something that frightens her. They say that birthmarks come from this, and that by their shape you can determine what it was. Unusually set or strangely colored eyes, nervous tics, speech impediments, and sometimes more serious troubles are often attributed to prenatal influences.
There are a large number of superstitions and prejudices associated with birthmarks, for example, if a cross-shaped spot is on the back, then you should expect betrayal from your nearest and dearest people. If the same spot is on the leg, then its owner will have to flee from danger, etc.
As for pregnant women, it was believed that the expectant mother should not swear, because The child may develop a birthmark. Of course, scientists have not found a direct connection between the appearance of spots in a newborn and quarrels of a pregnant woman, but it is known that when a quarrel occurs, the expectant mother’s blood pressure increases, which leads to disruption of placental blood flow, and this, indeed, can subsequently affect the baby’s health.
Previously, it was also believed that birthmarks would form if a pregnant woman saw a fire or was burned, but I dare to assure you that not all pregnant women who saw a fire or were burned subsequently had birthmarks in their babies.
Here, most likely, the role of a stressor plays a role (it can be not only a fire, but also a flood, the death of a loved one, severe fright, etc.), the duration of which occurred during the formation of the embryonic skin.
However, despite all the scientific descriptions and classifications of birthmarks, humanity has long had questions about why the number and location of moles is different for each person, and therefore they suddenly appear and also suddenly disappear, because there is very little that is random and thoughtless in the human body.
Now almost everyone knows that a person can be cured of a disease with acupuncture or hardware influence on the so-called biologically active points, the location of which rarely coincides with the location of the diseased organ. Moreover, this method of treatment is officially recognized by medicine.
All systems and organs are connected into a single system and these biologically active points (BAP) are a kind of antennas with the help of which the body exchanges energy with the outside world. Presumably it is believed that moles are located precisely in these BAP, reflexogenic zones and are a kind of filter that regulates a person’s energy exchange with the outside world. They thus restore the energy balance disturbed as a result of pathological physiological and mental processes. Perhaps this is why there has long been a belief that “many moles on the back means a person will be born happy.”
Unfortunately, this hypothesis about the energy function of moles is still speculative, and if it is ever proven scientifically, then at birth it will be possible to predict the hereditary characteristics of the baby and what diseases await the newborn in the future. And now, before removing a cosmetic defect that seems ugly to you, think a hundred times whether it is necessary.
Of course, there are hopeless situations when the birthmark is located in places where clothing rubs, and then constant irritation can lead to malignant degeneration of the formation if it is not removed. But there are also stories in which close people describe that after the removal of a birthmark, a person’s behavior becomes unrecognizable, and it does not change for the better.
There are many operations to remove birthmarks, but no one has really studied the consequences of removing birthmarks for a specific person (meaning changes in a person’s life and character). What are the dangers of having a birthmark?
Small pigment spots that are present in most of us, apart from minor cosmetic defects (some actors turn this skin defect into an advantage), are perhaps not dangerous in any way.
But those with large pigment spots measuring more than 5-10 mm should think about whether to sunbathe or not to sunbathe, and especially whether or not to go to the solarium, which has become so popular these days. This applies more to those with multiple spots.
Melanocyte cells exist in the skin in order to protect our body from excess ultraviolet radiation and they are the ones who give the skin a tan color after exposure to the sun and thereby prevent the penetration of excess ultraviolet radiation.
Pigment spots, as we mentioned above, are accumulations of melanocytes, and hemangioma, despite its benign quality, is still a formation, therefore it is extremely undesirable to expose pigment spots and hemangiomas to ultraviolet irradiation (sun, solarium).
Pigment spots with intense irradiation, in addition to the production of melanin and darkening, can also begin to actively divide, thus degenerating into the well-known malignant tumor “melanoma”.
If any formation is detected after childbirth, it is necessary to draw the attention of the pediatrician supervising your baby, and if there is a noticeable growth or change in the structure of the birthmark, the appearance of inflammation, additional rashes around it, or an increase in the intensity of the color, you should definitely contact a pediatric oncologist.
Of course, it is rare in young children. The doctor will be able to tell you which of the formations listed above it is similar to and whether it is a manifestation of any other disease or syndrome.
In any case, it is advisable to trace the detected formation on tracing paper immediately after birth and monitor further growth.
Mom should also pay attention to ensuring that there is no constant mechanical irritation of the birthmark with tight-fitting clothing, which can lead to its growth or damage with subsequent infection, which is, of course, extremely undesirable.
Source: babyportal.ru
Say “thank you” to mom
All nevi are formed in the embryonic period of development, when the circulatory system and skin cells are formed. And the reason for this is a disruption in the migration process of melanocyte precursors (melanoblasts), which are in the skin of each of us and give it its original color. The more melanoblasts, the darker we are, and their number is determined genetically.
Some birthmarks may appear during childbirth, but most often go away within a few years.
There are many reasons for disturbances in cell migration during the intrauterine development of the fetus and the appearance of birthmarks in children, the main of which are:
- Various infectious diseases suffered by a woman during pregnancy.
- The influence of toxic allergenic agents, including the use of contraceptives.
- Ionizing radiation, including ultraviolet radiation.
- Pathologies of pregnancy and hormonal surges during its course.
- Injury to the fetal skin.
- Hereditary characteristics.
But that’s not all. There is a separate category of birthmarks in children, which appear only in newborns and disappear like simple bruises.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the best men's face creams
Is treatment necessary?
What to do with moles? The doctor’s decision will depend on many factors: location on the baby’s body, shape, size of the nevus. Particular importance is attached to the location of the defect. It is known that the factor that provokes the development of skin cancer from a mole in children is its trauma, therefore such defects located on the feet, palms, and in the collar area are more dangerous.
In this regard, skin-traumatic methods for removing nevi, for example, cryodestruction, electro- and chemocoagulation, and even a simple diagnostic skin biopsy, may be contraindicated.
In the case of a “dangerous” nevus in children, prevention of malignancy of the tumor through complete surgical removal with skin grafting comes to the fore. However, this method is quite dangerous, as it may require general anesthesia for the child, which is more dangerous for him than the risk of developing melanoma. When exactly the operation will be performed in such cases will depend on the development of the defect.
Parents of children with such a skin defect should definitely photograph the birthmark throughout the child’s life in order to track its growth over time. Parents of these children should protect the defect from the sun and injury, since these factors increase the risk of complications.
Parents should consult a doctor if any of the following changes occur:
- change in shape and surface (the edges become convex, red, the nevus itself may become convex, folds may appear),
- the appearance of itching (itching may begin to bother the child, which can be manifested by crying, nervous scratching of the mole),
- inflammation (the surrounding skin becomes red and swollen),
- color change (the color can change to anything different from the original, up to red),
- change in the shape of the edges (become more jagged, uneven).
These changes matter most. When you see at least one of them, consult a doctor. After all, skin cancer is a serious illness that develops unnoticed and metastasizes profusely, and in the case of late stages it is extremely difficult to treat.
Source: papillomnet.ru
Surgical solution
When deciding whether to remove a birthmark, there are two options to consider.
Some moles can be easily removed with a laser. This procedure has many advantages, and these are, first of all, the speed of the operation and the minimum recovery period. You can go home immediately after the procedure as you will not experience any pain or complications. When removing a mole with a laser, it is very important that it be examined by a specialist doctor, a dermatovenerologist, as soon as possible. Not all moles can be removed with laser. Some moles must be excised and sent to a laboratory for histological examination. In such cases, time plays a very important role!
Only with timely detection of skin cancer - melanoma - is there a chance for a favorable future. At your appointment at the appointed time, the doctor will first examine the moles with a digital or manual dermatoscope. If it is decided that it would be better to have the mole removed surgically, your doctor will schedule your next appointment.
The whole procedure consists of disinfecting the mole and the skin around it, applying local anesthesia, surgically cutting it out and suturing the wound.
The number of stitches corresponds to the size of the mole. The tissue sample is sent to a specialized laboratory for testing. As soon as the results are ready, you will be informed about it.
After approximately 7 days, you will need to come for an appointment to check and remove the sutures. During these days and the following weeks, strenuous activity should be avoided to ensure the wound heals well. Also remember that the skin at the fusion site is thin and tension can lead to scarring.
We use evaporative lasers to remove different types of skin growths anywhere on the body, whether we are talking about filiform warts, some types of birthmarks, senile warts and pigmentation, scars, viral warts, connective tissue tumors, excess fatty tissue on the eyelids (the so-called xanthelasma) or nasal hypertrophy (rhinophyma) in patients with rosacea.
The resulting wound is not sutured; it heals with a crust like a classic burn for about a week. After the crust falls off, it is necessary to protect the area from the sun, using creams with a high UV factor to prevent unwanted pigmentation.
Given the excellent aesthetic results, the laser is an excellent assistant in removing unnatural formations not only on the face, but also on the back or chest, where there is a high risk of scarring during classical surgery.
A special indication is the correction of wrinkles; after evaporative laser surgery, collagen remodeling and skin smoothing occurs, it is used in individual areas and on the entire face.
Source: lasermed.cz
Traditional methods of getting rid of stains
Do not think that you can get rid of birthmarks only with the help of special expensive procedures that are carried out in beauty salons.
In fact, you can get rid of this aesthetic problem with the help of effective traditional medicine recipes that will not cause much harm to your health. The most common method for getting rid of birthmarks is a compress of milkweed juice. Before practicing this method on yourself, check whether you are allergic to this plant. If not, then squeeze milkweed juice onto the birthmark and then bandage the area. Walk around with this bandage for about two hours. It is recommended to do this procedure no more than two to three times a day. Alternatively, the bandages can be soaked in milkweed juice and then covered with clean bandages on top.
A similar compress can also be made using celandine juice as a basis. Just keep in mind that the juice must be fresh. It is also necessary to take breaks from using this method due to the high toxicity of this medicinal plant. It is best to conduct three courses lasting five to six days, but in no case more.
It is recommended to use a maximum of three compresses per day. Another common traditional medicine method that will help get rid of birthmarks is based on the use of onions. To do this, you need to finely chop the onion, then apply it to the birthmark and tie it.
You can also use its juice instead of the onion itself. At the Green Pharmacy you can buy a ready-made drug “Mountain Celandine” for removing papillomas and warts.
It turns out that the procedure for getting rid of birthmarks can be not only useful, but also enjoyable. But this is only possible if you use fruits and berries. The most common recipe that will help remove birthmarks in this case is the use of strawberry puree.
To do this, you need to prepare a puree from these berries, put it on the birthmark and bandage it. A similar procedure for getting rid of birthmarks can also be carried out using slightly unripe figs. To get rid of unnecessary growths on the body, you will need to be patient for 45 days.
Try cleansing your body with a rice diet. Papillomas and brown spots on the skin will disappear without a trace. In addition, the entire body will be cleansed, both inside and outside: joints will begin to bend better, the sclera of the eyes will cleanse, constipation will disappear, sleep will improve, etc.
Prepare 5 clean glass jars (0.25 or 0.5 l). Rinse 2 tbsp. l. round Krasnodar rice. Fill it with water in a jar (up to the shoulders). The water must be clean (preferably spring water) or at least settled. By the end of the day, you should rinse the rice 2-3 more times, each time filling the jar with water up to the shoulders.
The next day, we carry out all the manipulations with the 2nd jar, placing it in a row behind the 1st. And so on for five days with all 5 banks. Do not cover with lids! Do not forget to rinse the rice in all jars and fill it with clean water. On the 6th day, drink as much water as you want in the morning on an empty stomach.
Then cook the rice from 1 jar until tender, without salt, oil, sugar, and eat it. You can’t eat or drink anything else until lunch (3.5-4 hours). Eat as usual at lunch, and at dinner too. Don't forget to pour the rice into the empty jar, after rinsing it, and place the jar at the end of the row.
Soaked rice should be eaten for 45 days in the morning instead of breakfast. But if breakfast is important to you, then set your alarm for 6 am, cook and eat rice. And from 9:30-10:00 in the morning, lead a normal lifestyle. But do not forget to drink 1.5 liters of clean water (without gas) every day during the day. This will help the body cleanse itself of waste and toxins, which are difficult to “pump” out of our body.
You will immediately understand that the body has begun to cleanse itself: on the 30-35th day, depending on the contamination, the urine will become cloudy, you will feel slight discomfort, and your joints may ache slightly.
But this is a very small price to pay for the return of your health, even partial. Or maybe you will get a taste for it and try other methods to restore your health! Simultaneously with the rice cleansing, do not forget to nourish the body with the following composition for 45 days: dried apricots, raisins and prunes in equal quantities (less prunes are possible).
For example, steam 300-400 g of each dried fruit to remove dirt, add 1 cup of peeled walnuts, 3-4 lemons with peel, but without seeds. Grind all this through a meat grinder and pour in honey to form a viscous mass. You need to eat it 1-2 dess. l. 2-3 hours after lunch and also after dinner.
This must be done, just as it is mandatory to drink 1.5 liters of water per day in addition to tea, compote, etc. But don't drink excess water right before bed: this can lead to swelling in the morning.
The cleansing will be more intense if you help the body by eating lighter foods: mainly plant-based or plant-dairy. It is allowed to eat meat 2-3 times a week, but not heavy meat broths, but steamed cutlets, meat soufflés, a piece of boiled or poached meat.
Also eat fish no more than 2-3 times a week, in a small piece or in the form of a steam cutlet. Check yourself: if after eating you do not feel a surge of fresh energy, but feel sleepy, you are not eating correctly. Change your diet!
Source: apteka72.com
Dangerous borderline and dysplastic nevi
Borderline pigment spots in children can occur on the palms and soles and do not have a clear border. In addition, they contain many melanocytes, which causes their bright brown or even purple color. Such a birthmark can appear on a child’s face, body, or limbs. And it grows with the body.
Dysplastic nevi can appear in both newborns and adults. But more often such pathologies are hereditary. These moles are located singly or in groups, in the groin and armpits, on the back and on the thighs. They are not flat and smooth and do not rise above the skin. Coloring is very variable. Such spots lead to melanoma in 90% of cases and are therefore removed after a biopsy.
Precancerous blue nevus
It can be of all blue colors. There is no clear boundary and can appear in any part of the body. A distinctive feature is that upon palpation, a compaction is felt, and hair does not grow in this area.
Such nevi require careful examination and, if necessary, a biopsy.
Young children also have a number of birthmarks that mothers should not worry about, namely:
- Simple red nevus - the most common red spots on the back of the head and limbs of newborns, which are simply collections of blood vessels. Pediatricians are advised not to worry about them.
- Hemangiomas (berry, cavernous, stellate) are hemorrhages under the skin in newborns. They often go away with age, but sometimes persist throughout life.
- “Coffee” stains are often self-passing flat formations with clear boundaries, the color of light coffee. You should only worry if there are a lot of them and they are more than 5 cm in diameter. This may indicate problems with the child’s liver.
- Flaming nevus - such a formation is removed with a laser at an early age. Most often located on the face and upper extremities. It is bright purple in color and does not go away on its own.