The human body is constantly attacked by numerous bacteria that can cause harm to health. A disease caused by such microorganisms is furunculosis. It is not always possible to get rid of it without using antibacterial agents, but you should not try to cure the disease yourself. Antibiotics for furunculosis should only be prescribed by a qualified specialist.
Causes and treatment
The main reason that serves as a prerequisite for the appearance of boils (on the body, under the armpit, in the groin, in the groin area and in the area of the buttocks, nose) is the penetration of staphylococcal bacteria. Penetration of pathogenic microflora occurs:
- for damage to the skin (scratches, abrasions, cuts);
- for diseases of the endocrine system;
- decreased functionality of the autoimmune system.
Antibiotic therapy is considered the best and most effective treatment for infection. Pharmaceutical factories produce many medicinal substances that can cope with the ailment that has arisen. You can use medications in the form of tablets, injections, ointments.
Indications for prescribing medications
Antibacterial therapy is prescribed in cases of:
- The location of abscesses in the face and nose - in the absence of the necessary treatment, in half of the cases death is possible due to the occurrence of complications (meningitis, encephalitis).
- In case of furunculosis - when there are a large number of abscesses on the body. Relapses and chronic courses of the disease indicate a low level of functionality of the autoimmune system.
- The location of abscesses in the groin area is dangerous due to the close location of the lymphatic and circulatory systems, and therefore it is possible for the infection to spread throughout the body and cause a septic condition.
- If the patient has immunodeficiency conditions and is undergoing chemotherapy.
- For complications of furunculosis - phlegmon, subcutaneous abscesses.
Medicines should be taken strictly according to the treatment regimen recommended by a specialist.
Treatment with antibiotics
Treatment of the disease achieves the best effect with complex therapy and uses the following methods:
- immunotherapy – it includes means to maintain the body’s general immunity and increase its functionality;
- ozone therapy – allows you to increase the barrier function of the body with the help of introduced oxygen;
- medicinal – includes various drugs that help suppress pathogenic microflora. These include anti-inflammatory, decongestant, antibacterial and painkillers.
The treatment regimen with antibiotics is prescribed by the attending physician; independent use of drugs is unacceptable.
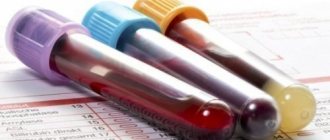
Before prescribing antibacterial drugs, a test for the resistance of pathogenic microflora is carried out. After determining the level of sensitivity to certain medications, an antibiotic against boils is prescribed.
What antibiotics should I take to treat furunculosis? Broad-spectrum medications are used to treat the disease; effective ones include:
- penicillin group;
- macrolides;
- cephalosporins;
- aminoglycosides;
- tetracyclines.
The main indications for the use of antibacterial agents are:
- stable damage to the skin by multiple foci of localization of the disease (furunculosis);
- purulent rashes in the face area;
- complicated conditions - abscesses, lymphadenopathy, etc.
When selecting the necessary remedy, the specialist takes into account the age and body weight of the patient, the general condition of his body, allergic reactions to antibiotics, and chronic diseases present in the anamnesis.
Subgroup of macrolides
The action of this subgroup is to disrupt the protein synthesis of a foreign cell, with bacteriostatic (at low concentrations) or bactericidal (at high) effects. The most common include:
Pharmacological substances are available in tablet, capsule, granular, and powder forms. The positive qualities of these medications are:
- high efficiency against different types of pathogens (bacteria);
- low level of toxicity;
- good tolerance by patients;
- Possibility of use in childhood;
- permission for use during pregnancy;
- safety.
A subgroup of macrolides is recommended for use in the primary stages of the disease. The drugs speed up the healing process and prevent the development of possible complications - purulent abscess, sepsis. Severe degrees of the disease require the administration of drugs by injection - for rapid penetration into the circulatory system.
Subgroup of penicillins
To get rid of boils, protected penicillins are used - they destroy the structure of the cell wall of pathogenic microorganisms. Antibiotics can be used:
- "Amoxiclav";
- "Ampicillin" - 20 tablets per pack, 250 mg;
- "Amoxicillin";
- "Ecoclave";
- "Medoclav";
- "Oxamp";
- "Augmentin";
- "Augmentin";
- "Benzylpenicillin";
- "Penicillin";
- "Ampioks";
- "Flemoxin Solutab";
- "Femoclav".
Penicillins have been used in the fight against boils since the discovery of the drug until the present day. A treatment regimen for chiriya is recommended after consultation with the attending physician.
Subgroup of cephalosporins
Furunculosis can be cured with cephalosporins. The drugs prevent the spread and penetration of bacteria into the inner layers of the dermis. These include:
- "Cefuroxime";
- "Cefipime";
- "Cefazolin";
- "Cephalexin";
- Ciprofloxacin is most often prescribed at 1000 mg, or more precisely, 500 mg twice a day.
For the treatment of furunculosis they are the most effective remedy. The drugs are modern antibiotics and the possible resistance of microflora to them is minimal. Vitamins for furunculosis are necessarily prescribed when using antibiotic therapy.
Subgroup of topical medications
In addition to internal administration, a group of drugs of a number of antibiotics for boils are used topically, in the form of ointments. In modern medicine we use:
"Levomekol" is indicated for the purulent-necrotic phase of the disease, but is prohibited when determining an individual allergic reaction. Ointments are applied to cotton-gauze bandages and fixed to the affected areas of the skin. Tetracycline in the form of an ointment is prescribed in most cases.
In some cases, the drug is injected directly into the wound surface, in cases of abscess development. The dressing material is changed daily.
Other antibiotics
Used to treat furunculosis:
- "Levomycetin";
- "Lincomycin";
- "Fucidin";
- "Tetracycline";
- "Fuzidin";
- "Chloramphenicol."
For boils, you can take medicine in the form of tablets, and sometimes you need to give injections. The choice of type of medication depends on the degree of advanced disease and the age of the patient. In childhood, tablet forms are prescribed less frequently - children deny tablets. Tetracycline is most often used in the form of tablets or ointments.
Principles of taking medications
Prescription of medications is carried out exclusively by the attending dermatologist. The main contraindications to the use of antibacterial therapy are:
- periods of gestation and feeding;
- psoriasis;
- eczema;
- individual allergic reaction to antibiotics;
- impaired liver function.
Medicines based on ointments are considered safer - they have a minimal number of side effects, there is no systemic effect and their use does not require specific preparation.
Tablet forms of medications can cause negative consequences that affect the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Local forms of medications are not used for the formation of boils on the face - accidental softening of the necrotic core and further spread of purulent bacteria are possible.
After taking the pills, it is necessary to restore the internal microflora of the body using eubiotics. When using several drugs, an analysis must be carried out to determine the compatibility and perception of these substances by the body.
Basic rules for taking medications:
- Taking medications without any gaps in time - the active substance of any antibiotic must accumulate in the blood and have a certain concentration.
- It is not recommended to drink any alcohol-containing drinks - alcohol destroys pharmacological drugs.
- It is forbidden to change the recommended dosage or the medicine itself.
- If an allergic reaction occurs, you should stop taking the medication and consult your doctor.
- The use of probiotics during periods of taking pharmacological agents is prohibited - they are used after antibiotic therapy.
Results and answers to questions
Multiple boils can be cured with antibiotics, but the process takes a long period of time. Children can be given medications only according to the regimen prescribed by the pediatrician. Self-prescription of medications is unacceptable.
If the specialist prescribed a regimen that caused an allergic reaction in the child, then it is necessary to change the course of administration. You can seek advice again and clarify that the medicine is causing side effects.
- Do you have to take all the pills prescribed by your doctor? Take your medications before your scheduled appointment time—the boil will not go away if you interrupt the treatment.
- What is the best antibiotic? The one that the doctor recommended to use. Do not forget to take vitamins along with the antibiotics you take.
- I take medication, but the boils get bigger. If the abscess increases significantly, a visit to a dermatologist is mandatory.
If antibacterial therapy does not help in the fight against the disease, the patient is hospitalized in a hospital setting for further treatment.
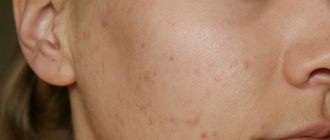
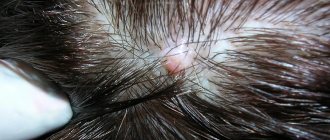
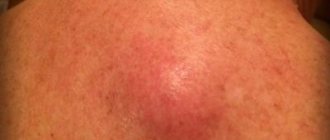
Inflammation of the sebaceous glands and hair follicles, caused by various microorganisms, is called furunculosis. More often, the pathology manifests itself as boils, which are localized on the face, neck, back, and groin area. The inflammatory process is caused by staphylococcus bacteria, the most dangerous of which is Staphylococcus aureus. Various therapeutic measures are used for treatment, but the most popular medications have been and remain antibiotics for furunculosis, which are prescribed in the form of ointments, injections or tablets.
Definition for furunculosis
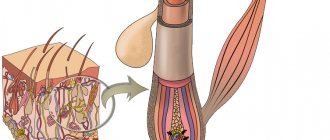
Furunculosis is an active inflammation of purulent-necrotic origin caused by certain microorganisms and originating in the hair follicle, sebaceous gland, as well as tissues surrounding the described pathology.
A boil, or boil in other words, is a rather large, painful pimple with purulent content. For a single abscess that is not complicated by anything, antibacterial therapy is usually not prescribed. In such cases, the inflammatory process can be dealt with using external medications in the form of ointments and antiseptics.
Treatment with antibiotics may be prescribed if numerous boils appear on the skin associated with multiple foci of inflammation. A similar pathology is diagnosed as furunculosis, which, with a weakened immune system, can develop into a chronic form of the described disease, which is difficult to treat.
In such a situation, it is necessary not only to treat the boils themselves, but to take all measures to prevent secondary infection, as well as further spread of the disease. Therefore, in such cases, the use of antibiotics cannot be avoided.
Important! Microorganisms in the form of staphylococci quickly spread in the external environment of the surrounding world, and therefore the described disease is conditionally infectious.
From the above, it becomes clear that the infection can be picked up at home, but the nature of its development will depend on the state of the human body itself. Having a strong immune system, the patient can only be a passive carrier of the infection and know nothing about infection with the described microorganisms.
What is furunculosis
The disease is characterized by the formation of purulent-necrotic inflammation of the hair follicle, which also develops in the tissues surrounding it. The causative agent of the infection is Staphylococcus aureus or Staphylococcus epidermidis, which is common in the environment. These bacteria live on the surface of the human mucosa and skin without causing pathologies. However, with predisposing endogenous (internal) or exogenous (external) factors, staphylococci are activated and multiply, causing furunculosis.
Causes
The most important reason for the development of the disease is the presence of immunodeficiency. Under the influence of decreased immunity, staphylococcal microflora provokes a purulent-inflammatory process. Bacteria invade the follicles after trauma to the skin, when they are contaminated or when there is local hypothermia. Other factors that can trigger furunculosis:
- hypovitaminosis;
- diabetes;
- presence of chronic infection;
- intoxication of the body;
- errors in diet.
Causes of boils
As we said earlier, furunculosis is not an independent disease; it develops against the background of other diseases that inhibit the body’s defenses.
The main cause of the disease is staphylococcus bacteria. A healthy person has a certain amount of these bacteria on the skin, but in people with boils, it is increased. Bacteria penetrate the tissues, causing inflammatory and purulent processes. This occurs when the skin is heavily soiled, infected, or when the immune system is weakened.
Thus, boils are quite common in patients with AIDS, tuberculosis, hepatitis, bronchitis, and metabolic disorders. Such people have reduced immunity and when bacteria enter the skin, the tissue becomes inflamed.
Staphylococci can enter the hair follicle as a result of scratching, mosquito bites, scratches, dermatitis or scabies. And formations in the nose or ears of boils occur due to increased secretion of mucopurulent masses (otitis media, sinusitis and others).
In childhood and adolescence, the formation of boils is most often preceded by hypothermia and against the background of sore throat or pneumonia.
Factors that can trigger the formation of boils include:
- Overwork
- Weakened immunity
- Infectious diseases
- Lack of vitamins, especially vitamin C and A
- Impaired metabolism
- Chronic diseases
- Contaminated skin
Increased sweating coupled with poor personal hygiene
Thus, the main reason for the formation of boils on the surface of the skin is inflammation, which occurs due to a bacterial infection. Factors that provoke the occurrence of abscesses are hypothermia, infections, chronic diseases, overwork, vitamin deficiency and others.
Symptoms
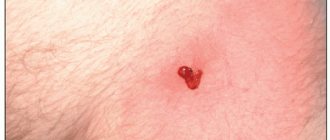
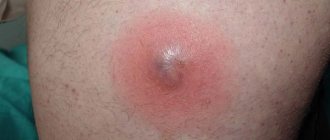
At the first stage of the disease, a small purulent-inflammatory infiltrate forms around the hair follicle. After a few days, the entire follicle, the adjacent sebaceous gland and the connective tissue surrounding it are involved in the inflammation process. The elements of the rash resemble a congestive hyperemic nodule, which has a cone-shaped shape protruding above the surface of the skin.
As inflammation develops, pain and swelling increases. Next, the boil ruptures, and its purulent contents come out. The process ends with healing, after which a scar remains. The purulent-necrotic process may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- weakness, increased fatigue;
- headaches;
- insomnia;
- loss of appetite.
Types of furunculosis
Furunculosis can be of two types: acute and chronic.
The acute manifestation of this disease is manifested by the formation of multiple boils. In this case, in the places where the tubercles appear, after some time pus is visible. These are painful areas that open spontaneously over time. Pus is released from the necrotic masses and the core of the boil itself is visible.
With acute manifestations of the disease, a person feels malaise, headache and increased body temperature.
The chronic form of the disease is characterized by recurrent boils. Ulcers can form when the immune system is low. At the same time, the places of the abscesses are also painful, and the patient’s general condition worsens.
Types of boils:
- Furuncle
- Carbuncle
- Cystic acne
- Pilonidal sinus
- Hidradenitis suppurativa
A boil is a single abscess.
When inflammation of several follicles merges, a carbuncle appears. This is extensive tissue damage. In this case, pus is released in different places of inflammation.
Cystic acne is characterized by inflammatory processes deep in the tissues.
The pilonidal sinus is a boil in the intergluteal region. It is very painful and causes discomfort.
Hidradenitis suppurativa is multiple purulent skin inflammations, usually localized under the armpits or in the groin area. Such inflammation cannot be cured with medications; surgical intervention is necessary.
Thus, furunculosis as a disease can occur in acute or chronic form. Boils are divided into several types, depending on the symptoms and course of the disease.
Treatment methods
Therapeutic regimens are selected by the doctor, depending on the stage of the inflammatory process. During the period of infiltration, ultraviolet irradiation is prescribed. During the maturation of the boil, a blockade is placed with a solution of novocaine and antibacterial drugs to relieve pain and relieve infection. An antibiotic is selected based on its resistance to infection. For purulent abscesses, a bandage with a solution of silver nitrate (1%) is applied to the inflamed area.
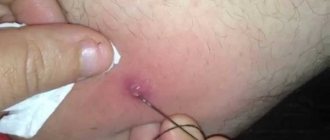
After opening the boil, it is washed with hydrogen peroxide (3%), then a bandage is applied with a sodium chloride solution to cleanse the necrotic masses. The rod is removed only after it is separated from the surrounding tissue. Do not open purulent foci by squeezing, as there is a high probability of breaking the protective ring and spreading the infection throughout the body. This will entail a number of life-threatening complications. In case of an abscess, it is better to contact a surgeon who will carefully open the abscess and clean out the purulent contents.
The main methods used in the treatment of furunculosis with antibiotics
The standard treatment regimen for furunculosis includes opening an already mature abscess using a surgical method. In this case, the lesion is injected with a cocktail of novocaine with an antibiotic. Such actions relieve the patient of pain and prevent the subsequent spread of infection.
But it happens that a person turns to a specialist for help with an already advanced abscess and an inflammatory process in the tissues surrounding the lesion. At the described stage, the surgeon has to open the abscess and clean out its purulent contents. After such an operation, the remaining wound is treated with antibacterial ointments and covered with a sterile bandage.
Antibiotics are prescribed in tablets in more complex cases, for example, with multiple repeated rashes or with existing ulcers localized in the head and neck area. Medicinal prescriptions of drugs are carried out based on the type of pathogen, due to the fact that many strains are designated as resistant to certain groups of antibiotics.
Therefore, before prescribing one or another remedy, the composition of the boil itself is examined by a laboratory method.
Antibacterial therapy using ointments
As mentioned above, after cleaning the purulent contents from the boils, bandages are applied over the wounds, which are soaked in special ointments in the form of:
- Levomekol;
- Gel Fucidina;
- Bactrobana;
- Baneotsina
The list of such antibacterial drugs is quite wide. So, for external use in the treatment of boils, chloramphenicol, gentamicin, erythromycin, tetracycline ointment, as well as products in the form of Dioxidin and Fucidin can be used.
But in any case, one or another local remedy must be prescribed to the patient by the attending doctor.
Treatment of furunculosis with antibiotics
Therapy with antibacterial drugs for single or multiple boils on the skin is carried out with five types of antibiotics. They are produced in the form of injection solutions, tablets, suspensions, and ointments. The most common antibiotics for boils are the penicillin series, since they have been successfully fighting Staphylococcus aureus and other strains of bacteria for many decades. Cephalosporins, macrolides, tetracyclines and anthraglycosides are prescribed if pathogens are resistant to penicillin.
After the breakthrough/opening of the abscesses, a bandage with antibacterial ointments is applied to the wound. The following drugs are used for this purpose:
- Levomekol ointment. The most popular topical antibiotic. The active component chloramphenicol destroys a wide range of bacteria, and methyluracil helps tissues regenerate faster. Gauze pads are soaked in the drug and filled into the wound. Change the dressings daily until the problem is completely eliminated. With prolonged use, skin rashes are possible.
- Bactroban ointment. It has proven itself excellent in the fight against Staphylococcus aureus. Ointment for boils with the antibiotic Bactroban exhibits powerful antibacterial properties. It is allowed to apply the drug directly to the site of skin infection 1 to 3 times a day. Course duration is 7-10 days. In some cases, the development of allergic reactions, nausea, and headaches is noted.
Pills
Antibiotics in tablet form are prescribed for recurrent furunculosis or if their location is the upper torso and head area. The difficulty of such treatment is that staphylococcus is resistant to many antibacterial drugs, so tablets are selected after a microbiological sensitivity test. The most popular medicines.
- Lincomycin. An antibiotic with a powerful bacteriostatic effect, active against a wide range of bacteria. For furunculosis, adults take the drug Lincomycin 500 mg 3 times a day before meals. The antibiotic sometimes provokes adverse reactions in the form of surges in blood pressure and allergic reactions. The course of treatment should not exceed 2 weeks.
- Cephalexin. Antibacterial drug of the cephalosporin group. Has a bactericidal effect on most strains of staphylococcus. The daily dosage is 1-4 grams. Take pills at regular intervals. Possible side effects: hand tremors, disturbances in the functioning of the stomach and intestines, dizziness. Duration of therapy is 7-14 days.
Review of effective antibiotics for treating boils on the body
Other
For a boil that affects a large area, in the presence of several foci of a purulent-necrotic process, the doctor prescribes broad-spectrum antibiotics in tablets or injections.
In modern pharmacology, several hundred types of antibacterial drugs are produced. To understand this variety of antibiotics, you need to understand that many different drugs have the same active ingredient, that is, they are analogues.
For skin infections caused by pathogenic staphylococcus, antibacterial agents based on penicillin are prescribed. These drugs are divided into oxacillins, ampicillins, amoxicillins and others.
On pharmacy displays, ampicillin is presented with the following drugs:
- Zetsil;
- Penodil;
- Pentrixil et al.
These drugs have an extended spectrum of action and are active against Staphylococcus aureus, Shigella, Salmonella, etc. Penodil is prescribed to drink for boils, 250 mg 4 times a day at intervals of 6 hours; the half-life of this antibiotic is less than 12 hours.
From a number of semisynthetic penicillins, related to oxacillins, antibiotics are prescribed for boils:
- Ampiox;
- Oxamp;
- Oksamsar et al.
The powerful effect of Ampiox is due to the fact that it contains two antibiotics: ampicillin and oxacillin, so it has a detrimental effect on most known pathogenic bacteria. For adults with furunculosis, this antibiotic is prescribed in tablets of 2-4 mg per day. The course of treatment depends on the severity of the disease and can be extended up to 10 days.
Macrolides
A broad group of antibacterial agents that interfere with protein production in bacterial ribosomes are called macrolides. When figuring out what pills to take for furunculosis, many doctors prefer drugs from a number of macrolides, as they have an antibacterial effect, partially restore the body’s immune properties, and have an anti-inflammatory effect.
Incorrectly selected medications lead to increased suppuration and decreased immunity. Cheap antibiotic therapy may not cope with its task of eliminating the causes of inflammation, but will cause a greater burden on the liver and kidneys. Therefore, a specialist should be involved in the treatment of boils and the selection of antibiotics.
Natural macrolides include Erythromycin, Spiramycin, and semisynthetic macrolides include Klacid, Fromilid, Sumamed.
Klacid is prescribed in the form of tablets and powder for diluting a suspension. For adults, the dosage is 0.5 g twice daily every 12 hours. In children, the daily dose is 15 mg per kilogram of weight, divided into two doses - morning and evening.
In addition to antibiotics, preparations based on brewer's yeast are used to treat acne and boils. Yeast tablets improve metabolic processes in the skin and help in the production of certain vitamins, so they are prescribed to be taken in long courses for furunculosis.
What antibiotics to take for furunculosis
People whose bacteria have caused boils are wondering which antibacterial drugs are best to choose for treatment. It should be remembered that antibiotics have many contraindications and adverse reactions that can even cause death. For this reason, it is strictly forbidden to prescribe them yourself. Antibiotics for furunculosis are prescribed by the doctor, based on the stage of the disease, the patient’s history of chronic diseases and other reasons.
In the groin
For inguinal treatment of furunculosis, external preparations are more often prescribed. Antibiotics for boils in the groin are used in the form of creams, gels, and ointments. They are applied to the affected area of the skin up to 3 times a day, and sealed with a bandage on top. The advantage of such drugs is that they promote the rapid release of the purulent contents of the boil. List of antibiotics that are used for inguinal treatment of furunculosis:
On the face
Since this pathology that occurs on the face poses a danger of an infectious agent entering the cerebral cortex, antibiotics are prescribed mainly for oral administration. Before the boil matures, the inflammation site is treated with an antiseptic (salicylic alcohol, furacilin solution and others). Antimicrobial drugs for boils on the face are prescribed even before the stage of opening the abscess. Basic antibacterial drugs:
Antibiotics in purulent surgery have long become a necessary and main means of treatment. The ways of introducing them into the body are varied. There are products for topical use in the form of ointments, gels, solutions, there are capsules and tablets, you can administer them intramuscularly, intravenously and even in suppositories. Antibiotics for boils and boils (which are the same thing) can be in any of these groups - it all depends on the stage and severity of the process, the age of the patient, and concomitant pathology.
Every patient with furunculosis wants to use an antibiotic that “definitely helps.” Obviously, a doctor will help you choose which antibiotics to take for boils. Patients, with their careless attitude towards these powerful pharmacological agents, unauthorized use due to their availability in pharmacies, and non-compliance with treatment courses over a long period of time, have led to resistance of microbes to treatment on the one hand and sensitization of the human body on the other.
Despite this, the doctor has a way to select an effective antibiotic for boils on the body and face. To do this, it is necessary to culture the purulent discharge and determine the sensitivity of the pathogen to a whole range of antibiotics.
Symptoms of furunculosis
- The very first symptoms of the formation of a boil are redness of the skin of the area where it should form. There is a hair in the center of the area. At the first stage, this place itches, swells and hurts. Over time, the swelling area expands, and the inflammation goes deeper into the skin. The pain gradually increases.
- The second stage is characterized by compaction of the node, a red elevation. Pain increases and a person may feel pulsation at the site of the boil. The pain especially intensifies with movement.
The follicle dies, and the tissue around it begins to die, forming a necrotic process. This causes severe pain in the affected area. Pus and blood accumulate inside the abscess.
After 3 days of this condition, the formation of a dense rod inside the ulcer is observed, the person feels general malaise, the body temperature rises, and the lymph nodes may become inflamed.
When the pus reaches the edges of the skin, it becomes yellow.
- The third stage of development of the focus of the disease is characterized by the bursting of the crust of the pustule, while the pus comes out and a yellow-green core emerges.
- After this, the pain disappears and the wound gradually heals. It takes about 7 days for the wound to heal.
- The symptoms of a boil last about 8 days, after which the wound heals.
- Thus, we can distinguish the following symptoms of the disease, which appear at various stages:
- Skin itching. In this case, there may be a tingling sensation in the inflamed area.
- A red bump appears on the skin, and there is an increase in pain in the affected area.
- After a few days, the abscess opens and a core of dead tissue is visible.
- The pain subsides as pus is released and the rod comes out.
- After all, there is a wound that heals within 1 week.
Causes of furunculosis
There are many reasons for developing a common form of boils in one or another area of the human body. The variety of external and internal risk factors creates favorable conditions for the main causative agent of furunculosis, Staphylococcus aureus, to transform into a pathogenic form. 97-98% of all cases of furunculosis owe their occurrence to it. That is why bacterial culture is not done for everyone, but is performed when there is no result from the therapy.
2-3% of the causes are due to other pathogens. Among them:
- beta-hemolytic streptococcus;
- pseudomonas;
- Staphylococcus epidermidis;
- mycobacterium;
- fungi.
Antibiotics according to the mechanism of action on the pathogen are divided into:
The fundamental difference between them is that bactericidal antibiotics cause the death of microbial cells, while bacteriostatic ones suppress their reproduction in the patient’s body.
Bactericidal include:
- beta-lactams (penicillin, amoxicillin);
- fluoroquinolones (ciprofloxacin);
- aminoglycosides (kanamycin).
- tetracycline group;
- chloramphenicol.
When choosing an antibiotic for furunculosis that effectively affects the pathogen, preference is given to broad-spectrum antibiotics. This means that the drug is active against several types of microorganisms (ciprofloxacin).
The main subgroups of antibiotics for boils and boils are discussed below.
Subgroup of macrolides
Medicines in this group are divided into natural (erythromycin) and semi-synthetic (azithromycin).
General characteristics of the subgroup:
- bacteriostatics;
- active against staphylococci and streptococci, as well as chlamydia;
- concentrated in tissues higher than in plasma;
- low toxic;
- there is no cross-allergy with penicillins.
The first representative of macrolides is Erythromycin. Minimal adverse reactions make it one of the safest antibiotics. Dyspeptic disorders and pylorospasm in newborns, allergic reactions may occur.
- pills;
- ointment;
- bottles with powder for dilution and intravenous infusion.
Indications for use include infections of the skin and soft tissues, which confirms the validity of the use of Erythromycin for furunculosis.
Azithromycin is better known under the trade name Sumamed. Azitrox is also Azithromycin.
It has a number of advantages over Erythromycin:
- maximum accumulation in tissues of all macrolides;
- the half-life is longer, which means you can reduce the number of doses to 1 time per day and the course to 5-7 days;
- higher tolerance.
The combination of Azithromycin with lactulose is called Azithromycin eco or Ecomed.
There are capsules. tablets, syrup and powder for preparing a suspension. It is not injected into a vein or into a muscle.
Macropen is a semi-synthetic macrolide with improved pharmacokinetics. It is particularly important because it is active against staphylococci resistant to other macrolides.
Available as tablets and powder for suspension.
Medicines in tablets
Medications in this form are needed in severe cases of the disease. Tablets for furunculosis, the duration of therapy is prescribed by the doctor. The course should not exceed 14 days. Antibiotics have a bad effect on the mucous membranes of the stomach, intestines and oral cavity, causing dysbacteriosis and stomatitis. It is important to simultaneously take probiotics, which restore the body's microflora.
Antibiotics for boils in tablets are prescribed if the patient’s temperature rises sharply to 38.5–39 °C.
Other cases when medications are needed:
- A large number of abscesses.
- Boils on the buttocks, armpits, which can cause phlegmon (extensive purulent inflammation).
- Abscesses that are located near blood vessels and can cause complications (on the head, neck or face).
- Chronic furunculosis with frequent relapses.
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
- Immunodeficiency states.
Amoxicillin
An inexpensive antibiotic destroys the walls of bacteria and quickly copes with furunculosis. Amoxicillin is prescribed for the treatment of children and adults. Contraindications are taken into account: sensitivity to penicillins, renal failure, lactation, pregnancy.
For kids, the tablets are crushed and dissolved in water or juice.
Side effects after taking - skin rashes, nausea, diarrhea. Price – 30 rub. for 20 pieces.
Ampioks
The medicine is released in capsule form. Ampiox counteracts most harmful bacteria and stops the development of ulcers. Ampicillin and oxacillin in the composition provide quick results in the fight against furunculosis.
Nuances: during treatment it is not recommended to stay in the sun for a long time and drive a car.
Contraindications: poor tolerance to penicillins, lymphocytic leukemia, mononucleosis, age under three years. Side effects - diarrhea, vomiting, skin rash. Price – 26 rub. for 20 pieces.
Tsiprolet
One of the most commonly prescribed antibiotics for furunculosis stops the growth and reproduction of bacteria. The boil passes quickly - the pathogens do not have resistance to Tsiprolet. The medicine lasts 12 hours and does not affect the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract.
It is contraindicated for use in children under 18 years of age, pregnant women and nursing mothers, and patients with liver and kidney diseases.
Side effects: allergies, vomiting, diarrhea, dizziness and decreased blood pressure. Price – 100 rub. for 10 tablets. There is a cheap analogue - Ciprofloxacin. Cost – 16 rubles. for 10 tablets.
Erythromycin
The medicine effectively treats ulcers on the skin. Erythromycin for furunculosis is prescribed to adults and children of any age. The antibiotic eliminates complications and quickly deals with the infection. Contraindications for use: sensitivity to components, renal and liver failure.
The drug is prohibited during lactation and pregnancy.
Side effects - heart rhythm disturbances, diarrhea, convulsions. Price with a dosage of 250 mg – 26 rubles. for 10 pieces.
Sumamed
Tablets are prescribed to adults and children over the age of three for abscesses on the face, soft tissues, and with a high risk of septic shock and death of the patient. Sumamed is drunk five times a day. The antibiotic is contraindicated for use by pregnant women, nursing mothers, and patients with kidney and liver failure. Possible side effects - skin rash, headache, diarrhea. Price Sumamed, 125 mg – 280 rub. for 6 tablets. A cheap analogue of the drug is Azithromycin. Its price for a dosage of 500 mg is 65 rubles. for 3 tablets.
Articles on the topic
- Suppositories for teething in children - a list of painkillers with descriptions
- Painkiller injections for back pain - a list of drugs with descriptions and composition
- Fast acting migraine tablets - the best medications with description and dosage
Subgroup of penicillins
Penicillin is the progenitor of the entire group of antibiotics. Since its discovery by A. Fleming in the forties of the last century, hundreds of new, more active and safe drugs have entered the market.
According to the modern classification, penicillins belong to beta-lactamase antibiotics. Impairment of bacterial cell wall synthesis is a common mechanism of action for this subgroup.
The subgroup includes natural (penicillin) and semi-synthetic, which in turn are divided into:
- antistaphylococcal (Oxacillin);
- extended spectrum (Ampicillin, Amoxicillin);
- inhibitor-protected (Amoxiclav);
- combined (Ampiox)
Long-acting penicillins - Bicillins.
There are antipseudomonas penicillins, but they are not applicable for furunculosis.
General properties of the subgroup:
- bactericidal activity;
- cross-allergy within a subgroup;
- wide range of dosages;
- low toxicity.
Staphylococci have developed resistance to this subgroup due to the production of beta-lactamase enzymes that can destroy antibiotics.
Penicillin is a natural parent, but the drugs are called Benzylpenicillin (potassium and sodium salt). These antibiotics are not used in the treatment of furunculosis.
Augmentin, Ecoclave and Medoclav are varieties by trade name. Each of them is based on the semi-synthetic Amoxicillin and clavulanic acid. Adding it to Amoxicillin made it possible to bind and inhibit beta-lactamases produced by staphylococcus, and therefore prevent microbes from developing resistance to the drug. Antibiotics - amoxiclaves are very effective for boils.
Subgroup of cephalosporins
Cephalosporins, by their origin and action, also belong to beta-lactamase inhibitors, like penicillins.
In this subgroup there are 4 generations of antibiotics. As the generation grows, the spectrum of antimicrobial activity of cephalosporins expands.
General characteristics of the subgroup:
- bactericidal nature of the effect on the microbial cell;
- wide range of activities;
- cross-allergy with beta-lactam antibiotics;
- low toxicity.
Cefazolin and Cephalexin are representatives of the first generation of cephalosporins. Compared to subsequent generations, they are inferior in the spectrum of activity to drugs of the fourth generation, but they also retain differences between them.
The parenteral antibiotic Cefazolin is more active compared to Cephalexin, available in tablets. The first generation of antibiotics of this subgroup is not a sufficiently effective treatment for complicated furunculosis, but in mild forms it is possible to treat the boil with antibiotic tablets or capsules for internal use.
Cefuroxime Cefuroxime axetil is a second generation oral cephalosporin. They have a more pronounced effect on gonococci, but in the treatment of infections of the skin and subcutaneous tissue their use is justified.
Ceftriaxone and Cefotaxime are the third generation. They are not intended for oral administration but are administered parenterally. They can be prescribed for severe forms of chronic furunculosis and septic complications.
Cefepime is a fourth generation cephalosporin. It is administered parenterally for severe mixed infections with complex forms of resistance.
To summarize the rationale for the use of a subgroup of cephalosporins for furunculosis, it can be noted that for adults it is advisable to recommend Cephalexin tablets in a dose of 2 to 4 grams per day.
Subgroup of fluoroquinolones
Ciprofloxacin, a representative of the second generation quinolones, is indicated for the treatment of skin and soft tissue infections of varying severity. It is considered to be the “gold standard” among this subgroup.
It has a bactericidal effect on a variety of microorganisms, including gram-positive coccal flora, which includes staphylococcus.
Among the large number of side effects, it is necessary to note the negative impact on the development of cartilage tissue of a growing organism, therefore, use for pregnant and lactating women is contraindicated. It is prescribed to children only in special cases.
Increased physical activity while taking Ciprofloxacin can cause rupture of tendons and ligaments.
Another important point to remember when treating furunculosis with this antibiotic. Taking Ciprofloxacin together with a group of NSAIDs increases neurotoxicity, and the development of seizures is possible.
Release form: tablets, ampoules for parenteral administration and eye drops.
Local antibiotics for furunculosis
In the treatment of any boils, one cannot do without prescribing antibacterial ointments. The goal is to combat the infectious agent in the wound, relieve inflammatory reactions, cleanse the wound and accelerate healing.
Levomekol is one of the frequently used ointments. It is based on 2 components:
- chloramphenicol (the familiar Levomycetin);
- etiluracil.
The antibiotic acts bactericidal, killing the infection in the wound. The addition of methyluracil enhances local immunity and enhances regeneration.
The structure of the ointment is such that it allows it to penetrate deep into tissues without destroying biological membranes.
The advantage of the ointment is that it is capable of destroying several types of microorganisms, and also that it has no contraindications, with the exception of individual intolerance.
For boils, apply it to the affected area or apply a napkin soaked in Levomekol. Cover the top with adhesive tape. The dressing is changed 1-2 times a day.
Synthomycin liniment is an ointment based on the antibiotic chloramphenicol. The difference between ointment and liniment (there is also synthomycin ointment) is in a different base. The ointment is created on a fat basis, while liniment is created on a water basis.
The method of using the ointment for furunculosis is the same as for Levomekol.
Levomethyl is the same Levomekol from a different manufacturer.
Netran - oddly enough, it is the same Levomekol, with the same chloramphenicol and methyluracil.
Levomekol, with all its advantages, is a pulling ointment with an antibiotic for boils.
What regimen is needed for therapy?
Antibiotics for furunculosis are drugs that help eliminate the staphylococcus bacterium, which causes inflammation.
Antibiotics are used to eliminate chirps. The products are available in the form of tablets, injections, and ointments. The prescription of drugs is carried out by a doctor. Taking medications as directed. Treatment of furunculosis with antibiotics provides a quick recovery when the boil is on the cervical area or on the head. This placement of the abscess is dangerous because it leads to infection entering the brain. An abscess provokes complications, including death. Spreading quickly, Staphylococcus aureus provokes the appearance of new foci of inflammation. Most often, boils are found on the face, back, neck area, ears, and intimate places.
Furunculosis requires treatment:
- when enlargement occurs, enlargement of lymph nodes;
- painful lesions spread over areas of the body;
- when furunculosis develops into a chronic stage;
- when placing abscesses on the cervical, head, and facial areas.
Additional drugs used in treatment include drugs to enhance immunity and vitamins. It is important to adhere to the diet prescribed by your doctor.
It is forbidden to treat inflammation at home on your own. Infection can lead to carbuncles.
Antibiotics for the development of boils are aimed at combating the pathogen:
- relieve redness;
- eliminate Staphylococcus aureus;
- restore soft tissues and skin.
Skin scraping helps to accurately identify the pathogen. Bacteriological culture analysis determines the reaction of pathogenic microorganisms to the antibiotic. Based on the test results, the doctor selects an effective form of the drug. The pharmacy sells antibacterial agents: tablets, injections, ointments. They help cope with the infection and remove pus.
Therapy depends on the stage of development of the pathology. For mild cases, ointments, rinses, and lotions are used. At elevated temperatures and boils spreading throughout the body, the patient is given injections and antibiotics are prescribed.
The best antibiotics for eliminating furunculosis in tablets
Valid for 12 hours. A large number of pathogenic microorganisms remain sensitive to the medication. Effective in combating infection of the body when other medications do not work.
Diarrhea, gastritis, rashes, headaches, irritability.
The drug eliminates: staphylococci, streptococci; Klebsiella, Escherichia coli; clostridia, peptococci. Used in case of chiria, meningitis, sepsis.
Drug treatment is prescribed by a doctor after tests. The physician takes into account the age, type of pathogen, patient’s condition and contraindications for use.
The use of antibiotics for babies and pregnant women is controlled by a doctor.
The doctor prescribes a regimen to eliminate the disease:
- Ultraviolet irradiation is used in the presence of purulent infiltrate.
- Painkillers: "Novocaine" antibiotic. Medicines are selected based on the sensitivity of the infectious agent to the antibiotic.
- When pus is present, a lotion with silver nitrate (1%) is used.
- The abscess is opened surgically using a scalpel. The rod inside the lesion is removed.
- The cavity is rinsed with 3% hydrogen peroxide and a sodium chloride bandage is applied to clear the wound of pus.
It is forbidden to squeeze the rod out with your hands. With such manipulation, it is possible for foci of infection to multiply throughout the body. The surgeon removes the abscess. The doctor prescribes bandages with gels and antibiotic therapy.
After the autopsy, the doctor prescribes treatment with antibacterial ointments, according to the instructions:
- Levomekol ointment is used topically. Chloramphenicol kills pathogens. Methyluracil restores tissue. You will need to soak the bandage and close the outbreak. Change the fabric every day or go to the nurse to change the dressing. Sometimes allergies occur.
- Bactroban ointment eliminates staphylococcus. You will need to apply the contents 1 to 3 times in 24 hours. The duration of treatment is 7-10 days. Rarely does a rash appear.
Strong antibiotics Cephalexin or Lincomycin are often prescribed to treat adults:
- Take Lincomycin tablets 3 times 24 times, 500 mg each, before meals. The course of treatment is up to 14 days.
- The drug “Cefalexin” should be taken from 1 to 4 grams per day, depending on the course of the disease, and consumed after an equal amount of time. Course – 7-14 days.
It is forbidden to use antibiotics for more than 10 days.
For the best effect, intramuscular antibiotic therapy is used at a prescribed injection dose.
To restore the body, the doctor prescribes drugs to boost immunity and vitamin complexes. It is important for children and adults to adhere to the diet during the course of treatment:
- Use natural products.
- Eat fresh vitamins.
- Use kefir, yoghurts without dyes and low calorie content.
- Supplement your diet with oatmeal, buckwheat, and rice.
- Avoid baked goods and sweet foods.
For the treatment of furunculosis in a child, the following suspensions are suitable: “Zinnat”, “Klacid”, “Azithromycin”.
Take 100 mg for children from 6 months to 12 months. Older children are prescribed a dosage of 10 mg per 1 kg of child weight.
The duration of the appointment is determined by the doctor. Standard scheme: 3-5 days.
Antibiotic therapy is contraindicated if:
- renal, liver failure;
- allergic reactions to the drug;
- fungal diseases of the skin.
Use with caution during pregnancy, breastfeeding, and childhood. Antibiotics for illness will bring the desired result when the patient follows the doctor’s recommendations, does not exceed the dosage, and adheres to proper nutrition.
Antibiotics in purulent surgery have long become a necessary and main means of treatment. The ways of introducing them into the body are varied. There are products for topical use in the form of ointments, gels, solutions, there are capsules and tablets, you can administer them intramuscularly, intravenously and even in suppositories. Antibiotics for boils and boils (which are the same thing) can be in any of these groups - it all depends on the stage and severity of the process, the age of the patient, and concomitant pathology.
We suggest you read: What antibiotics should adults take for whooping cough?
Every patient with furunculosis wants to use an antibiotic that “definitely helps.” Obviously, a doctor will help you choose which antibiotics to take for boils. Patients, with their careless attitude towards these powerful pharmacological agents, unauthorized use due to their availability in pharmacies, and non-compliance with treatment courses over a long period of time, have led to resistance of microbes to treatment on the one hand and sensitization of the human body on the other.
Despite this, the doctor has a way to select an effective antibiotic for boils on the body and face. To do this, it is necessary to culture the purulent discharge and determine the sensitivity of the pathogen to a whole range of antibiotics.
There are many reasons for developing a common form of boils in one or another area of the human body. The variety of external and internal risk factors creates favorable conditions for the main causative agent of furunculosis, Staphylococcus aureus, to transform into a pathogenic form. 97-98% of all cases of furunculosis owe their occurrence to it. That is why bacterial culture is not done for everyone, but is performed when there is no result from the therapy.
2-3% of the causes are due to other pathogens. Among them:
- beta-hemolytic streptococcus;
- pseudomonas;
- Staphylococcus epidermidis;
- mycobacterium;
- fungi.
The fundamental difference between them is that bactericidal antibiotics cause the death of microbial cells, while bacteriostatic ones suppress their reproduction in the patient’s body.
Bactericidal include:
- beta-lactams (penicillin, amoxicillin);
- fluoroquinolones (ciprofloxacin);
- aminoglycosides (kanamycin).
- tetracycline group;
- chloramphenicol.
When choosing an antibiotic for furunculosis that effectively affects the pathogen, preference is given to broad-spectrum antibiotics. This means that the drug is active against several types of microorganisms (ciprofloxacin).
The main subgroups of antibiotics for boils and boils are discussed below.
In the treatment of any boils, one cannot do without prescribing antibacterial ointments. The goal is to combat the infectious agent in the wound, relieve inflammatory reactions, cleanse the wound and accelerate healing.
Levomekol is one of the frequently used ointments. It is based on 2 components:
- chloramphenicol (the familiar Levomycetin);
- etiluracil.
The antibiotic acts bactericidal, killing the infection in the wound. The addition of methyluracil enhances local immunity and enhances regeneration.
The structure of the ointment is such that it allows it to penetrate deep into tissues without destroying biological membranes.
The advantage of the ointment is that it is capable of destroying several types of microorganisms, and also that it has no contraindications, with the exception of individual intolerance.
For boils, apply it to the affected area or apply a napkin soaked in Levomekol. Cover the top with adhesive tape. The dressing is changed 1-2 times a day.
Synthomycin liniment is an ointment based on the antibiotic chloramphenicol. The difference between ointment and liniment (there is also synthomycin ointment) is in a different base. The ointment is created on a fat basis, while liniment is created on a water basis.
The method of using the ointment for furunculosis is the same as for Levomekol.
Levomethyl is the same Levomekol from a different manufacturer.
Netran - oddly enough, it is the same Levomekol, with the same chloramphenicol and methyluracil.
Levomekol, with all its advantages, is a pulling ointment with an antibiotic for boils.
Dicloxacillin is a semi-synthetic from the penicillin subgroup and belongs to a narrow-spectrum antibiotic. It is aimed at Staphylococcus aureus and therefore the drug is suitable for the treatment of boils and other skin infections. There is cross-intolerance with penicillins and cyclosporines.
For children, the most acceptable form of release is in the form of a suspension. This makes it possible to calculate the dose for a child depending on body weight.
Antibiotics for furunculosis in children
Dicloxacillin is a semi-synthetic from the penicillin subgroup and belongs to a narrow-spectrum antibiotic. It is aimed at Staphylococcus aureus and therefore the drug is suitable for the treatment of boils and other skin infections. There is cross-intolerance with penicillins and cyclosporines.
For children, the most acceptable form of release is in the form of a suspension. This makes it possible to calculate the dose for a child depending on body weight.
Vancomycin is an antibiotic active against staphylococcus, but is intended to treat infections in the gastrointestinal tract. It is poorly absorbed into the blood and has no systemic effect, so its use for furunculosis is unjustified.
Erythromycin is effective in the treatment of furunculosis, dosed depending on weight, age and severity of the disease. Older children can be given tablets; if swallowing is difficult, a suspension can be used.
For children
Antibiotics in the form of a suspension are more suitable for children; they have a pleasant taste (or at least should have one) and it is easier for the child to use a suspension than a large capsule.
Suspensions suitable for babies:
- Azithromycin;
- Zinnat;
- Klacid.
As always, we remind you that you cannot prescribe an antibiotic yourself.
Antibiotics for boils on the face
A feature of boils on the face is the need to use antibiotics not only locally in the form of ointments, but also systemically. This is due to the close proximity of the brain and large vessels.
Ciprolet is the same as Ciprofloxacin, a subgroup of fluoroquinolone. One of its advantages is the slow development of microbial resistance to its administration. It is quickly and well absorbed and penetrates into tissues. Easily tolerated. Not for pregnant women, lactating women, children and adolescents.
In adults, the dose is 1 gram per day in 2 divided doses. We must remember that taking Tsiprolet disrupts concentration, so you must be careful when driving a car.
Sumamed is easy to use. The package contains 3 tablets, which must be taken over 3 days, one per day.
Doxycycline is a semisynthetic antibiotic from the tetracycline subgroup. Broad spectrum of action, blocks protein synthesis in microbial cells. Contraindicated in children under 8 years of age, pregnant women from the 2nd trimester, breastfeeding women and those with severe liver diseases. Oral and parenteral administration.
Antibiotic ointments
The ointment is prescribed when the boil has already opened. Such remedies are used if the lesion is located on the face, neck, or nose. A boil in such a place is prone to relapse.
First, the cavity is treated with an antiseptic solution (furacillin, chlorhexidine), and then the drug is added. If possible, apply a sterile dressing.
Levomekol
The ointment is white and contains chloramphenicol (the well-known chloramphenicol) and methyluracil.
The drug belongs to combined antimicrobial drugs.
Levomekol has an anti-inflammatory effect and has a detrimental effect on staphylococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli. It also stimulates the process of tissue regeneration (healing) well.
Indications for use: any purulent wounds and skin lesions. Side effects: allergic reaction.
The ointment is applied once a day into the cavity of the boil (you can use a syringe). Treatment lasts until the wound is cleansed. Complete analogues - Mekol, Levomethyl. Price from 130 rub.
Tetracycline ointment
For external use, a 3% ointment is produced, the active ingredient is tetracycline hydrochloride.
The antibiotic blocks protein synthesis in bacterial cells, disrupting metabolic processes. Microbes stop dividing and die after a while.
Tetracycline is used to treat inflammatory skin diseases (furunculosis, streptoderma, acne).
The product is applied to the affected area 2-3 times a day for a week.
Contraindications: acute liver failure, leukopenia, pregnancy, breastfeeding, children under 8 years of age. Cost - 50 rubles.
Baneocin
Consists of bacitracin and neomycin. Both antibiotics enhance each other's effects.
The drug is indicated not only in the treatment of boils and carbuncles, but also for skin infections that affect a significant amount of tissue (contagious impetigo, trophic ulcers, burns).
The ointment is also used after surgical operations to avoid suppuration of the suture.
Baneocin is applied in a small layer to the formation 2-3 times a day.
Contraindications: very extensive skin damage (risk of complications to the ears), acute renal failure, individual intolerance to the components of the drug. Due to its broad antimicrobial effect, the product has a high cost - 330 rubles.
Oflokain
A combination drug containing the antibiotic ofloxacin and the anesthetic lidocaine.
The product has anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, wound healing and analgesic effects.
Oflocaine is prescribed for the treatment of boils, carbuncles, abscesses, phlegmon of the face and neck, as well as bedsores.
It is enough to use the medicine once a day.
Oflokain should not be used if you are allergic to the active ingredients. Price – 130 rub.
Children with furunculosis are usually prescribed Levomekol, Baneocin or Oflocain. For older children, tetracycline can also be used. All dosages are prescribed exclusively by a doctor.