According to scientists, every second inhabitant of the Earth has the papilloma virus. Women are more often susceptible to it. The main sign of pathology are formations on the body, which in some cases pose a health hazard. If you have encountered such a phenomenon, you need to understand which doctor to see for papillomas. People who receive timely medical care usually do not face the unpleasant consequences of pathology.
Description of HPV
Human papillomavirus, abbreviated as HPV, belongs to a family of viruses that can cause warts and warts in skin cells. Today, 100 species of this microorganism have been discovered. Some of them can be dangerous. According to WHO, 70% of the world's population suffers from this insidious microorganism. It may not manifest itself in any way at first, but will make itself felt years later. At first, growths appear in various parts of the body.
Infection is possible even in childhood. The virus prefers areas with microdamages. Children have to deal with them regularly due to their increased activity. Kids love outdoor games. They often receive cuts, bruises and other types of injuries. On the surface of their skin, the infection manifests itself in the form of warts. Adults may encounter genital warts. They are transmitted sexually.
The virus penetrates the mucosa through microcracks from the partner. If the immune system is strong enough, then when microorganisms enter, they can be easily defeated. But when it fails, the disease manifests itself in the form of condylomas and warts. HPV invades the cell's DNA and affects its function, causing increased epithelial growth. Growths form on the epidermis. Any contact with a carrier of the virus can result in infection. Light contact with the mucous membrane or skin, for example, when shaking hands, can contribute to this. There are factors in which the development of the disease is observed especially quickly :
- decrease in the body's defenses;
- gastrointestinal pathologies;
- smoking and alcohol abuse.
How does papillomavirus infection manifest?
After conducting laboratory tests, the attending physician may decide on drug treatment, immune-restoring therapy, or prescribe elimination. Thus, if problems with the immune system are discovered, the patient will need to visit an immunologist.
Diagnosis of the disease is most often carried out by a dermatologist or venereologist. The first method used after a visual inspection is a PCR test. The polymerase chain reaction reveals the DNA of the virus itself. Thus, this method makes it possible not only to detect the virus, but also to identify the number of foreign agents in the body.
Also, PCR diagnostics can indicate a chronic form of the disease or an immediate one (due to reduced immunity). Taking into account the results obtained, the doctor treating papillomas will be able to prescribe adequate therapy. If PCR confirms the presence of the virus in the body, additional studies are carried out.
If a decision is made to remove the formation, it is necessary to take a biopsy of the papilloma for subsequent cytological analysis. Histology of the growth provides much more information about its structure, determines the correctness of its layers and the amount of obsolete tissue. This is very relevant in the issue of the malignant nature of papilloma. After all, the longer the virus stays in the human body, the higher the risk of developing cancer, and the less chance there is to cure the disease.
If a high-risk papillomavirus is detected, you should contact an oncologist who will prescribe additional examination and treatment.
If, after the examination, viruses of types 16, 18, 31, 33, 56, 66, 70 are detected, which appear in the form of condylomas or papillomas on the mucous membranes of the vagina, external genitalia, oral cavity and larynx, then the doctor will monitor the development of the disease.
Carriers of these viruses should undergo regular examinations to monitor the development of the disease. With a timely level of medical development, the risk of high-risk papillomas degenerating into cancer can be reduced to a minimal risk.
Virus danger
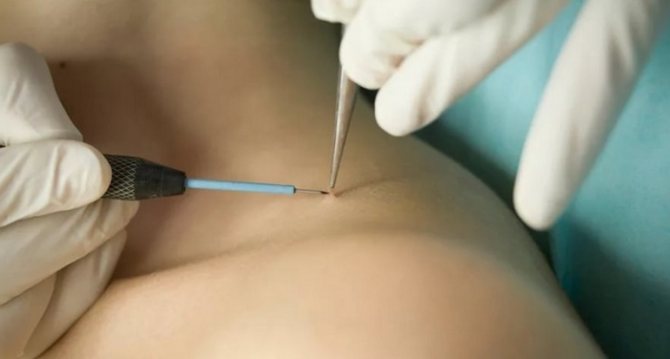
The HPV virus can be quite dangerous and unpredictable. In the first months and even years, it sometimes does not manifest itself at all. When a microorganism becomes active, serious changes occur at the cellular level. In women, this can provoke cancer of the internal genital organs.
Men are also at risk of cancer. When choosing which doctor to see for papillomas, you should consult a specialist - a dermatovenerologist . He conducts an objective examination, checks the condition of the inguinal lymph nodes, and interviews the patient to find out if he has a burning sensation and discomfort in the external genital area.
Urologist is another highly specialized doctor

A urologist is a specialist who treats ailments primarily of the male body. He knows everything about the strong field and the problems it may have.
We suggest you read How to get rid of warts on the tongue
Basically, the treatment scheme is the same as with a gynecologist. It is simply necessary to seek help and advice from this doctor. Of course, in men, serious problems due to HPV are much less common than in women, but this does not completely eliminate the danger.
If, with serious consequences, cervical cancer can form in women, then in men it is penile cancer. If you do not want to achieve serious problems with the genital areas, do not delay treatment and contact when the risk of malignant tumors is still absent or is still very small.
Diagnostic Basics
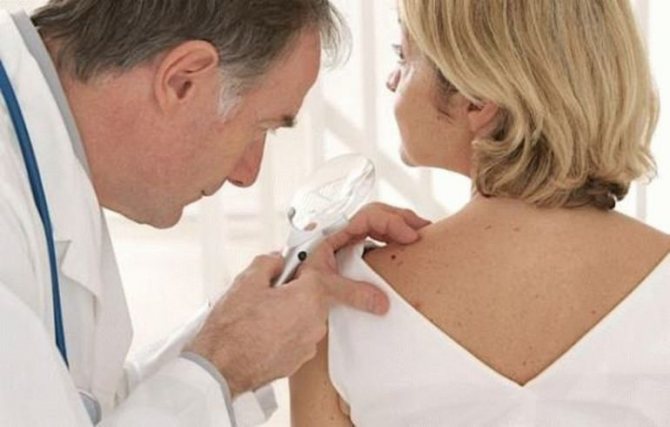
HPV on the skin provokes the appearance of neoplasms in the form of growths. Epithelial cells rapidly divide, which leads to an increase in growths. Depending on the state of immunity, one or another number of papillomas appear on the epidermis.
Initially, there is no discomfort from the presence of neoplasms. But despite this, you should not delay visiting a doctor. Sometimes warts and papillomas grow quickly and reach impressive sizes in 5-7 days. If you miss the initial stage of the disease, there is a risk that you will have to undergo treatment by an oncologist instead of a dermatologist.
Prognosis of the course of the disease
The most unfavorable prognosis is for type 18 of the virus. The disease can turn into cancer in 3-5 years, which quickly spreads metastases to other organs. The tumor behaves aggressively and grows deep into the genital organs. The prognosis for type 16 infection is slightly better, but the likelihood of tumor recurrence after treatment is high.
The prognosis for types 31, 33, 35, 39, 52, 58, 59 is unfavorable. 2-3 years after treatment, the disease manifests itself again and often becomes malignant. Cancers caused by these types of virus have high mortality rates.
Such unfavorable prognosis should alert a person if he discovers even a small growth on the skin. It is necessary to consult a dermatologist or gynecologist who can accurately diagnose. The type of human papillomavirus can be determined in laboratories. To do this, take a smear or scraping from the area of the skin where there are growths. Then the DNA of the virus is determined in the laboratory. Types of papillomavirus differ in the structure of sections of the DNA chain. The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) helps to recognize the differences
The need to visit a doctor
According to statistics, HPV is more common in women. In most cases, these are representatives of the fairer sex over 50 years old.
As the tumor increases in size, its owner experiences discomfort. The virus demonstrates activity in the following areas:
- groin area;
- skin under the arms;
- Hands;
- folds under the breasts;
- neck.
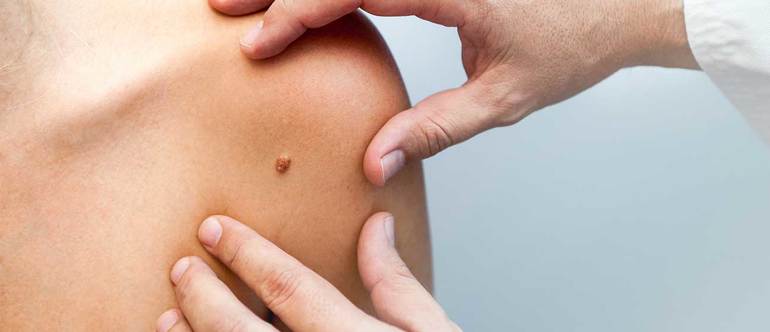
This localization leads to injury due to friction of the papillomas. For these reasons, patients experience pain. To avoid complications, you should contact a dermatologist as early as possible.
He will advise what actions should be taken. Thanks to modern diagnostic methods, it will be possible to make an accurate diagnosis.
You should not try to open papillomas yourself. This will lead to the emergence of a kind of “entry gate” for a number of other infections. If growths appear on the external genitalia, men should visit a urologist , and women should visit a gynecologist. The help of a proctologist is required in cases where condylomas appear near the anus.
Causes of papillomas
The culprit behind the occurrence of annoying growths is the human papillomavirus (HPV). This refers to a group of viruses that includes more than 170 strains. When introduced, it disrupts the processes of cell division. This is a very viable virus, the vast majority of people (about 80%) are its carriers.
How does the virus enter the body?
The appearance of papillomas is preceded by the penetration of their causative agent, HPV, into the body. This happens in several ways.
- The sexual route is the most common, previously considered almost the only one. Infection occurs through unprotected sexual contact (regardless of its type); a single case is sufficient for infection. Condoms do not always protect: the pathogen is located not only on the genitals, but also in the groin area. These places are almost always unprotected upon contact.
- From mother to child. Intrauterine transmission has been reported (although uncommon). HPV is very active and can cross the placenta. Infection is also possible during childbirth if a woman has growths on her genitals.
- The everyday route is relatively rare, but quite probable. Theoretically, the insidious virus is present in public transport, shops, schools and kindergartens. The most dangerous places in this sense are a bathhouse, a swimming pool, a gym (HPV “loves” high humidity and hot skin that is not protected by clothing). The risk of infection through household means increases if there are skin lesions - the entry point for the virus.
- Autoinfection. Growths can appear in new places when trying to pick out existing ones (this is especially true for children). An increase in the number of papillomas can be the result of standard hygiene procedures with a slight violation of the integrity of the skin.
The reason for the widespread spread of the papilloma virus lies in its viability and ease of transmission.
About the features of HPV and routes of infection - in this video:
Why does the virus activate?
After infection, a person may not know about it for a long time. The peculiarity of the culprit in the appearance of unaesthetic growths is that it does not spread throughout the internal organs, but remains in the layers of the epidermis. Such a neighborhood, while still friendly, can last for years.
In one moment, everything changes: the “enemy agent” dormant in the body suddenly begins to actively declare itself. What triggers this mechanism?
- Decreased immunity. As long as the body’s ability to resist “invasion from the outside” remains, the effect of the virus is suppressed. Bad habits, lack of rest, poor nutrition, past illnesses, prolonged use of antibiotics, stress make a hole in the natural defenses, and the virus is activated.
- Hormonal changes. Research confirms that HPV is hormone-dependent, and therefore can be activated against the background of changes in hormonal status. Papillomas often appear in women during pregnancy and menopause, as well as after gynecological diseases or abortion. Growths can also appear in adolescents at the time of puberty. Taking hormonal drugs also sometimes provokes the appearance of “surprises” on the body.
- Elderly age. A natural decrease in immunity often leads to the spread of growths throughout the body.
The “sudden” detection of tumors on the body actually has a long preceding period associated with the introduction and activation of HPV.
Localization by language
Papillomas in this area are caused by a special type of virus. These growths are formed from the mucous membrane of the epithelium. Neoplasms are localized in various areas of the oral cavity, on the tongue. They may or may not be painful. Sometimes they have hemorrhages. The process of papilloma formation is accompanied by inflammation of the mucous membranes. They look like a papillary growth of red or pink, sometimes white. Most often, neoplasms are localized in the following areas:
- sky;
- sublingual area;
- dorsum of tongue;
- the side or tip of the tongue.
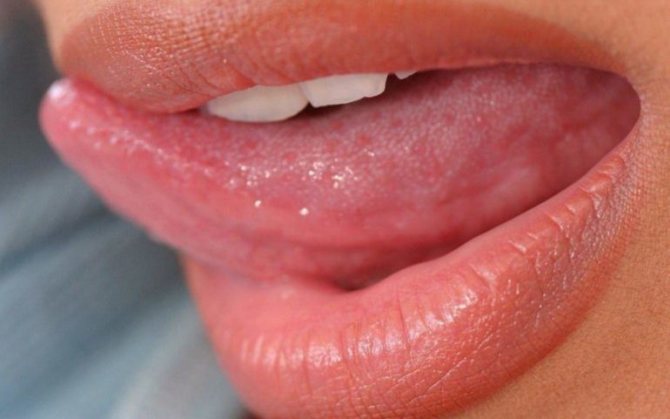
The first, second, third strains are the most dangerous types. Types 16−18 are considered oncogenic. When in contact with an infected person, there is a possibility of infection through mucous membranes, as well as through the use of his personal belongings. The cause of the disease is insufficient hygiene. This situation can also be provoked by open skin injuries, poor nutrition and stress.
Every person who is faced with HPV wants to know which doctor treats papillomas in women and men. A dermatovenerologist deals with this issue. With experience and qualifications, a specialist can establish the correct diagnosis and select an effective treatment regimen. It is not recommended to resort to carrying out neoplasms on your own.
If formations on the skin make you wonder which doctor to contact for papillomas, you should go to a dermatologist. Growths localized in intimate areas must be removed. This procedure is performed by a surgeon. To prevent human papillomavirus infection from recurring, such manipulation must be carried out with special care. For this reason, it is important to entrust the removal to an experienced doctor.
You can find out which doctor to go to if you have papillomas at the reception desk at your local clinic. Here they will indicate the name of the specialist and the number of the office in which he receives.
In the intimate area, genital warts form, which can degenerate into tumors. This requires some time, and the sooner treatment is started, the more favorable the prognosis for the patient will be.
Which doctor should I contact for papillomas on the body: who treats and removes growths
Papilloma is a benign tumor-like growth; such formations can grow on the surface of the skin and mucous membranes. The nature of origin is viral. The virus enters the body and causes disruption in the functioning of cells. Depending on the location of the warts, it is decided which doctor will help the patient with papillomas.
Why is medical advice necessary?
Warts are not an independent disease. This is a sign indicating that papillomavirus lives and multiplies in the human body. The infection has over 100 strains, including oncogenic ones. Depending on the variety, the following types of rashes are distinguished: genital warts, warts, bowenoid papulosis.
The described pathologies require mandatory medical consultation!
Most tumors do not cause problems and are a cosmetic defect. But with a decrease in immunity and the appearance of favorable factors, the viral agent begins to actively manifest itself, multiplying and capturing new areas.
If you are the owner of numerous papillomas or a single element, you need to consult a specialist. The reasons for applying are the following:
- the risk of degeneration of a benign growth into cancer;
- possibility of increasing the number of warts;
- skin injury and secondary infection.
Papillomatosis spreads quickly and unnoticed. First, a flat element appears, and then a pea is formed from it on a wide, or less often on a narrow, stem. The sizes vary, individual papillomas reach 2-3 cm. Removal is mandatory; constant friction and damage increases the risk of degeneration and inflammation.
What the doctor can prescribe
Self-medication is dangerous! Therapy against warty growths should include a set of measures that act in different directions. Medicine has not learned to completely cure the disease, but it has the knowledge of how to stop the virus and send the pathogen into a dormant state that is not dangerous to health. Doctors act in two ways - they act on the pathogen from the inside and outside.
Treatment
The main reason for the appearance of papillomas is low immunity and the body’s inability to fight back against viral attacks. The patient requires help in the form of antiviral agents and immunomodulators.
Antiviral - suppress the activity of the virus. At the same time, inflammation and growth of the tumor-like process are eliminated. A number of modern drugs have a stimulating effect on the immune system, helping the body recover and protect itself.
Immunomodulators are prescribed by a doctor! They are required in extreme cases, when an immunogram has shown that a person cannot suppress the enemy on his own and correction is required.
For external effects on the affected area, a specialist can prescribe ointments, creams that increase local immunity, relieve inflammation, pain, reduce and completely eliminate papillomas.
The drug is selected by the doctor, according to the research results.
Removal
If long-term drug therapy does not bring the desired results, removal of the warts is necessary. Modern surgery offers various safe but effective methods for excision of unwanted skin growths.
- Diathermoelectrocoagulation (DEC).
- Exposure to radio waves.
- Laser therapy.
- Cryodestruction.
- Excision with a scalpel.
Diagnosis is carried out before or after surgery, depending on the technique. Before the laser, dermatoscopy is required before removal; the beam completely evaporates the growth. With electrocoagulation and radio wave treatment, it is possible to conduct histology of the resulting tissues after the procedure.
The surgical method is preferable in complex cases when papillomas are large and have a high risk of oncogenicity. The surgeon removes the growth itself and the area around it with a scalpel to prevent recurrence.
Which doctor should I go to?
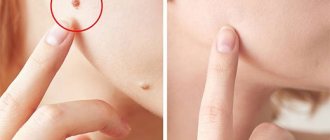
When a person discovers a changed nevus on the body, he must remember what caused the growth. Seeking medical help is mandatory; skin growths are viral in nature. The first person you should visit is a dermatovenerologist. He will develop further treatment tactics and, if necessary, refer you to specialists.
For growths on the body
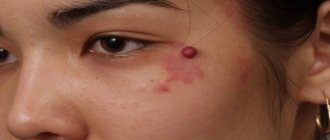
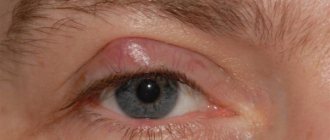
The dermatologist is responsible for the formations covering the body - neck, head, face (nose, eye, eyelids), armpits, legs, abdomen, palms. The doctor conducts a diagnosis, places each suspicious element under a dermatoscope, and studies its structure.
The occurrence of pain, discoloration, swelling can be a consequence of injury, then the papilloma is studied for benignity, and the patient is sent for destruction. If the elements are small, the doctor uses laser, radio waves, or current; if the diameter is large, surgery is indicated.
If the papillomavirus has affected the intimate area, the mouth, the dermatologist conducts a superficial examination and refers to the appropriate specialists.
For growths in the intimate area
If a woman is infected with HPV, she should go to an antenatal clinic. The gynecologist will conduct a preventive examination of the internal and external organs (pubis), and take mucous material for examination to determine the strain of the virus.
The appearance of multiple condylomas on the vaginal mucosa provokes dysplasia - a precancerous condition. Female HPV is dangerous; the virus has been found in cervical cancer. In order to prevent the development of dysplasia, the doctor recommends complete removal of all existing growths.
Do you need advice from an experienced doctor? Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
After surgery, antiviral therapy and intimate cream may be prescribed.
If a man notices warts that cover the mucous membranes along the rim of the head of the penis and anus (in homosexuals), he needs to consult a urologist or andrologist. Treatment depends on test results.
The doctor makes a decision to remove condylomas. The male version of HPV is the least dangerous, but can grow along the head of the penis and block the urethra.
When the butt (anus) becomes covered in rashes, this is a reason to consult a proctologist. In this case, the skin and intestines may be damaged. Anoscopy will help to obtain information about the degree of damage, the number of growths, and their size. It should only be seen by a qualified professional due to the high risk of intestinal damage.
For mucosal papillomatosis
HPV is an insidious disease that can affect the body and mucous membranes. Condylomas can appear in the mouth, nose, affecting the throat, tongue, cheeks, gums, and larynx. Sometimes a wart is found on the uvula. The growths tend to become inflamed, bleed, and multiply. It's worth seeing a dentist.
The doctor’s responsibilities include the treatment of viral diseases that affect the oral mucosa. In case of multiple growths, destruction is prescribed, which is carried out by a surgeon. After surgery, the dentist prescribes therapy to prevent relapses.
Now you know which doctor an adult patient with papillomas on the body or mucous membranes should contact. Medical staff will help determine the type of virus and take the necessary measures. The pharmacy offers a wide selection of drugs for the treatment of papillomas, but treating them yourself is strictly prohibited.
Who to contact for growths in children
Children and adults are susceptible to infection with the HPV virus. Infection occurs during childbirth, when pregnancy provokes the growth of condylomas on the external genitalia or by taking a nipple with HPV viruses into the mouth during feeding. There are many options for pathogen penetration into the body, but it is always expressed in one way - rashes on the body or mucous membranes.
If there are few elements, the sizes are small, you can be treated by a dermatologist. He will prescribe antiviral local or systemic treatment, and perform removal with laser, radio waves or electrocoagulation.
If the growths have reached large sizes and cover a large area, you need to get rid of them with the help of a surgeon or immunologist.
In adolescence, papillomas can appear in the intimate places of girls and boys who have begun to be sexually active. Treatment is provided by a venereologist, gynecologist, and urologist. The doctor will prescribe treatment, conduct research, and provide advice on safe sex.
Possible complications due to improper treatment
Many experts believe that it is not necessary to remove single papillomas; antiviral agents and immunomodulators can cure them. Treatment should be prescribed by an experienced immunologist; there is a risk of compromising immunity and provoking the development of severe systemic diseases.
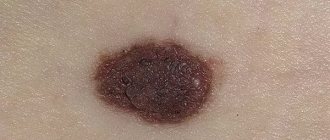
There is a certain risk during destruction. An incorrectly selected technique and inexperience of the doctor can lead to the development of cervical cancer and other oncological diseases. Any mole or papilloma with a high oncogenic risk reacts sharply to injury. During the operation, their integrity is violated, which can give impetus to degeneration and the development of an aggressive disease.
It is important that the doctor who removes papillomas first conducts the necessary examinations under a dermatoscope for cytology, which can first give an answer about the nature of the formation - benign or malignant.
Many owners of papillomas do not take papillary formations on the body seriously. This is wrong! Do not forget what a dangerous risk to life is hidden in small warts. In addition to oncology, they can cause inflammation, secondary infection and leave scars on the skin. Be careful not to injure the growths, remove them from the skin and mucous membranes in a timely manner.
The article has been reviewed by the site editors
Source: https://VashaDerma.ru/papillomy/kakoj-vrach-lechit
Benefits of the vaccine
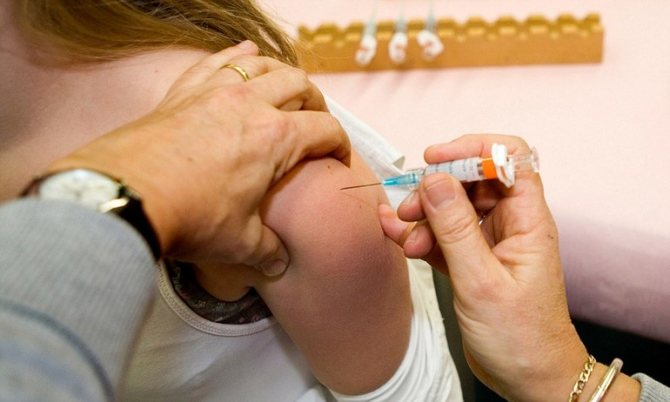
Laboratory tests have demonstrated the safety and effectiveness of HPV 16 and 18 vaccines. But in order for them to work, they must be administered before exposure to the pathogenic microorganism. This refers to the period before the first sexual contact. The vaccine does not cure infection or related illnesses. In a number of countries there are special medications for boys that can prevent the development of genital warts. This is an effective way to stop the virus from moving through the body during adolescence. It is recommended to vaccinate girls from 9 to 13 years of age.
Vaccination does not replace screening for cervical cancer. In countries where such vaccination has been introduced, appropriate surveillance programs are maintained for preventive purposes. Primary immunization in three doses of girls 12-13 years old makes it possible to reduce the risk of developing cancer. In Russia, the vaccines Cervarix and Gardasil are used. They represent a tool for the primary prevention of cervical tumors.
The mechanism of occurrence and development of HPV
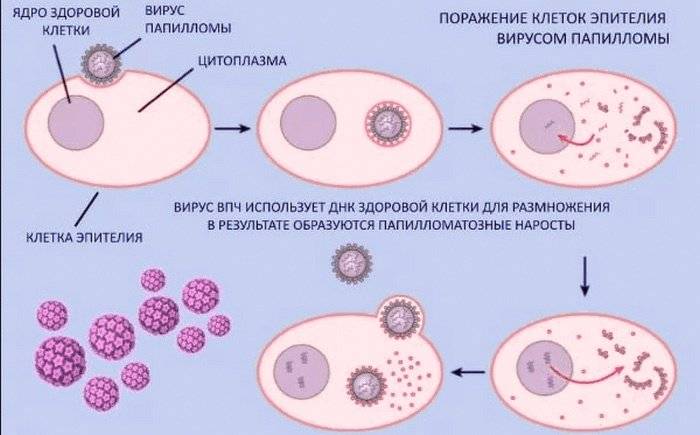
HPV is a nuclear DNA-containing virus, which during the process of infection can integrate (integration of the virus genome) into the cellular chromosomes of the infected organism
The papilloma virus enters the body through microcracks and damage, rushes into the cells of the very initial layer of the epithelium - the basal one - where it remains all the time. The incubation period from the moment of infection to clinical manifestations can range from 1 to 3 months. Spontaneous elimination (self-removal) of the virus from the body is possible (both with and without previous clinical manifestations), but, unfortunately, this happens extremely rarely.
HPV is a nuclear DNA-containing virus that, during the infection process, can integrate (integration of the virus genome) into the cellular chromosomes of the infected organism. An important role at the stage of HPV infection is played by viral proteins that are responsible for the transcription process, initiating viral replication and encapsidation of the viral genome. When infected cells of the basal layer of the epithelium divide, the virus genome is transferred to the daughter cell.
The effect of a virus on a cell can be varied: lead to the complete destruction of the affected cell, long-term coexistence of the virus and the cell without the death of the latter (latent and persistent infection), as well as to its transformation.
Viruses do not form typical toxins, however, both virions and viral components that accumulate in affected tissues have a toxic effect. In addition, cell breakdown products also have a toxic effect.
Due to the severity of the disease outcomes, much attention has been attracted to HPV damage in the cervix, which can lead to the formation of precancerous processes and cervical cancer. The role of HPV as a cause of the development of precancerous diseases and cervical cancer is confirmed by epidemiological data, the detection of viral DNA in affected cells, and the expression of viral genes in tumor cells.
Possible complications due to improper treatment
Many experts believe that it is not necessary to remove single papillomas; antiviral agents and immunomodulators can cure them. Treatment should be prescribed by an experienced immunologist; there is a risk of compromising immunity and provoking the development of severe systemic diseases.
There is a certain risk during destruction. An incorrectly selected technique and inexperience of the doctor can lead to the development of cervical cancer and other oncological diseases. Any mole or papilloma with a high oncogenic risk reacts sharply to injury. During the operation, their integrity is violated, which can give impetus to degeneration and the development of an aggressive disease.
It is important that the doctor who removes papillomas first conducts the necessary examinations under a dermatoscope for cytology, which can first give an answer about the nature of the formation - benign or malignant.
Many owners of papillomas do not take papillary formations on the body seriously. This is wrong! Do not forget what a dangerous risk to life is hidden in small warts. In addition to oncology, they can cause inflammation, secondary infection and leave scars on the skin. Be careful not to injure the growths, remove them from the skin and mucous membranes in a timely manner.
Source: VashaDerma.ru
Removal of papillomas and genital warts in the clinic
Treatment of human papillomavirus begins with the prescription of antiviral drugs or interferons. If papillomas appear on the body, face, or hands, you should contact a skin disease clinic or a dermatologist to remove this cosmetic defect. After examination and tests in the clinic, the papilloma is removed using the cryodisruptive method, which involves freezing the papilloma with liquid nitrogen. After treatment, the neoplasm dies, turns black and falls into small pieces. This operation to remove papilloma is carried out quickly and painlessly.
Surgical removal of papillomas
The operation is performed if the size of the papilloma is more than 1 cm or there is a suspicion that the formation contains cancer cells. Often the doctor also excises some healthy tissue. This is necessary to ensure that the growth does not reappear. After removal, a suture is applied. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia and takes 10-15 minutes. In this case, the patient does not experience pain. In some cases, when the papilloma has a thin stalk, it is cut off with surgical scissors. Then the vessel that fed it with blood is sealed (coagulated) using an electrocoagulator. The area is treated with an antiseptic. Disadvantages of the method: a fairly large area of skin is removed. Healing takes a long time, and scars may appear after surgery.
Cauterization of papillomas with liquid nitrogen
Cryodestruction – cauterization of papillomas with liquid nitrogen
Another name for this method is cryodestruction, that is, destruction by cold. After the tumor (papilloma) has been examined and the analysis has shown that it is benign and there are no altered cells in it, then the operation can begin. The doctor touches the papilloma with a cotton swab dipped in liquid nitrogen or a special attachment. Nitrogen temperature -196 degrees. Exposure time 5-20 seconds. The duration of cauterization depends on the size of the papilloma. Upon contact with liquid nitrogen, the water in the cells freezes, turns into ice, and its crystals destroy papillomas. The procedure is painless, but if the skin in this area is very sensitive, then it is anesthetized with an injection of novocaine into the sore spot. After treatment with nitrogen, the skin turns white, and gradually a small bubble forms in this place, filled with a clear or pink liquid. The surrounding skin turns red and swells. At this stage, a person may experience unpleasant sensations - burning and tingling. But they gradually pass. After the procedure, the doctor advises treating the skin with boric alcohol or a solution of potassium permanganate 2 times a day for a week.
Laser removal of papillomas
Before removal, an analysis is performed to exclude the presence of cancer cells. The area where the wart or papilloma is located is numbed with lidocaine spray. The patient is asked to put on safety glasses. A laser beam is directed at the tumor. One papilloma is affected for no longer than a minute. The laser evaporates the water in diseased cells, which shrink and turn into a crust. After half an hour, the surrounding skin turns red and swells; this is a normal reaction that will go away in a few days.
The crust disappears on its own after 5-7 days. In its place remains delicate pink skin. Gradually, its color evens out and no trace of papilloma remains at the site of the defect. Complete healing will take about 2 weeks. During this period, you need to protect your skin from direct sunlight. Otherwise, a dark brown spot will appear at the site of the papilloma.
Cauterization of papillomas with a laser allows you to avoid infection of the wound with microorganisms and seal the vessels. Therefore, bleeding does not occur during or after surgery.
It is not recommended to wet the crust that has formed at the site of the papilloma and steam it for 3 days. Also, decorative cosmetics should not be applied until complete healing. This will prevent scars from appearing. Treat this area with a solution of potassium permanganate or a healing ointment with an antibiotic (Levomikol), as recommended by a doctor. Using a laser, papillomas are removed on the arms, legs, face and genitals. Disadvantage of the method: when removing large papillomas with a laser, scars may remain.
Electrocoagulation of papillomas
A special device, an electrocoagulator, allows you to dry the narrow base of a papilloma or the entire wart
This is the removal of tumors using electric current. A special device, an electrocoagulator, allows you to dry the narrow base of the papilloma or the entire wart. After this, the growth is easily separated from the skin. Bleeding from the wound does not occur because the vessels are sealed with current. Recovery will take 7-10 days. At this time, it is recommended to treat the crusts with alcohol tincture of calendula 2 times a day. This will help avoid infection. After the crust falls off, a thin pink skin is revealed underneath, which must be protected from injury and direct sunlight. The main advantage of this method is that the papilloma can be sent to an oncologist for examination.
Disadvantages of the method. If it is not enough to treat the area where the papilloma was located, then after a while it may grow again. Removal on sensitive areas (genitals) may be painful.